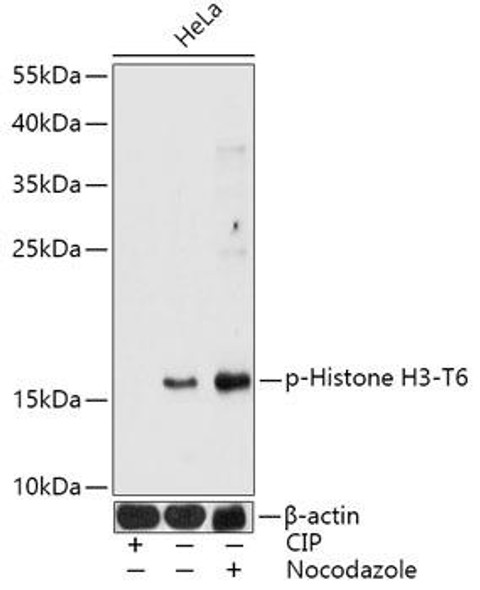
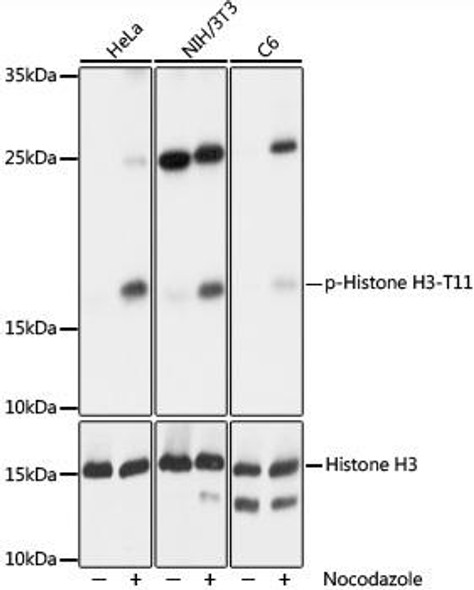
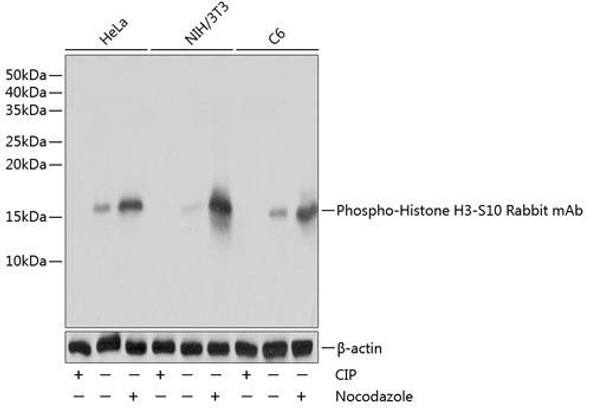
Cell Biology Antibodies 14
Anti-Phospho-Histone H3-T3 Antibody (CABP1152)
- SKU:
- CABP1152
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-Histone H3-T3 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP1152 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T3 of human Histone H3 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, NIH/3T3, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T3 of human Histone H3 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3020 |
| Uniprot: | P84243 |
| Cellular Location: | Chromosome, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 16kDa |
| Observed MW: | 16KDa |
| Synonyms: | H3.3A, H3F3 |
| Background: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. The linker histone, H1, interacts with linker DNA between nucleosomes and functions in the compaction of chromatin into higher order structures. This gene contains introns and its mRNA is polyadenylated, unlike most histone genes. The protein encoded is a replication-independent member of the histone H3 family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | H3F3A: Variant histone H3 which replaces conventional H3 in a wide range of nucleosomes in active genes. Constitutes the predominant form of histone H3 in non-dividing cells and is incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA synthesis. Deposited at sites of nucleosomal displacement throughout transcribed genes, suggesting that it represents an epigenetic imprint of transcriptionally active chromatin. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. The octamer wraps approximately 147 bp of DNA. Interacts with HIRA, a chaperone required for its incorporation into nucleosomes. Belongs to the histone H3 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q42.12 Cellular Component: extracellular region; nuclear chromosome; nuclear chromosome, telomeric region; nucleoplasm; nucleosome; nucleus; protein complex Molecular Function:histone binding; nucleosomal DNA binding; protein binding Biological Process: blood coagulation; cellular protein metabolic process; chromatin silencing at rDNA; DNA replication-independent nucleosome assembly; negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; nucleosome assembly; positive regulation of cell growth; positive regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; RNA-mediated gene silencing; telomere organization and biogenesis |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. The linker histone, H1, interacts with linker DNA between nucleosomes and functions in the compaction of chromatin into higher order structures. This gene contains introns and its mRNA is polyadenylated, unlike most histone genes. The protein encoded by this gene is a replication-independent histone that is a member of the histone H3 family. Pseudogenes of this gene have been identified on the X chromosome, and on chromosomes 5, 13 and 17. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P84243 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 55977062 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3021 |
| NCBI Accession: | P84243.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P84243,P06351, P33155, Q5VV55, Q5VV56, Q66I33, Q9V3W4 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P84243 |
| Molecular Weight: | 15,328 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone H3.3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | H3 histone, family 3B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | H3F3B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H3.3B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone H3.3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone H3.3 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | H3F3A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | H33_HUMAN |