Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 4
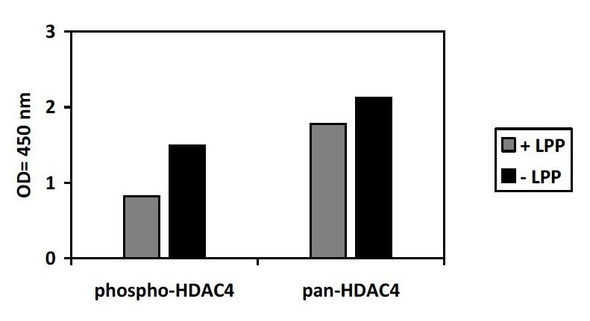
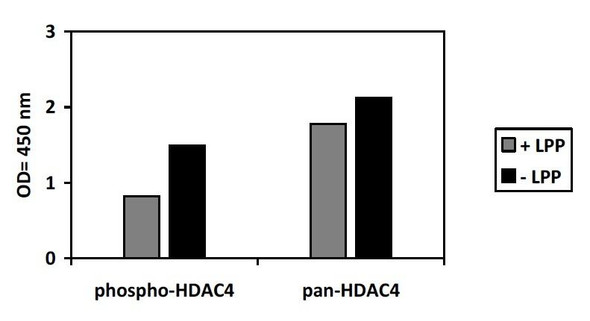
Anti-Phospho-HDAC4-S632 Antibody (CABP0359)
- SKU:
- CABP0359
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-HDAC4-S632 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0359 |
| Antibody Size: | 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
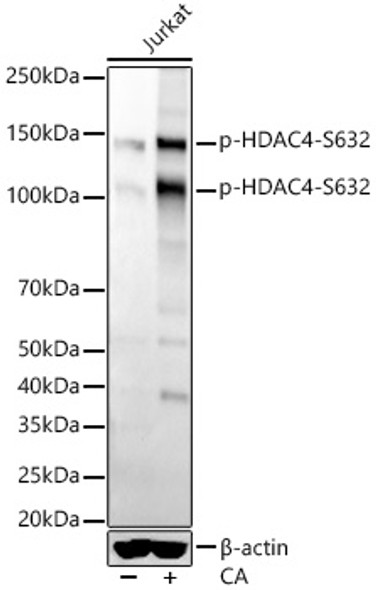
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S632 of human HDAC4 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
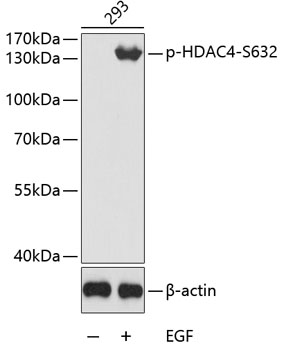
| Positive Samples: | 293 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S632 of human HDAC4 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 9759 |
| Uniprot: | P56524 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 106kDa/119kDa |
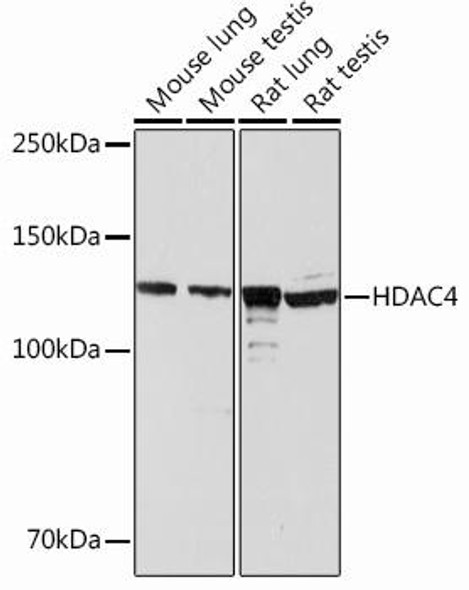
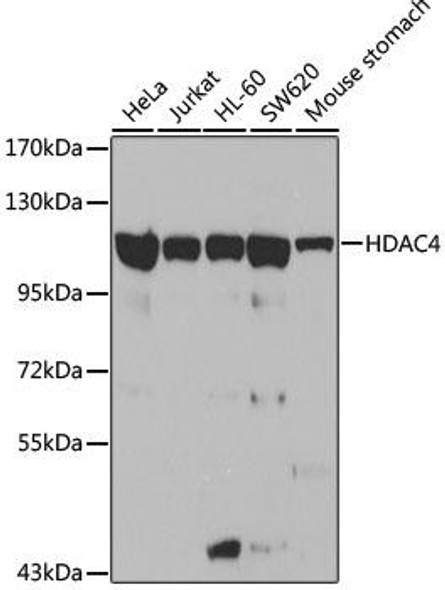
| Observed MW: | 140kDa |
| Synonyms: | HDAC4, AHO3, BDMR, HA6116, HD4, HDAC-4, HDAC-A, HDACA |
| Background: | Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class II of the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. This protein does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HDAC4: a transcriptional regulator of the histone deacetylase family, subfamily 2. Deacetylates lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3 AND H4. Plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Hydrolase; EC 3.5.1.98; Deacetylase; Nuclear receptor co-regulator Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2q37.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; transcriptional repressor complex; histone deacetylase complex; cytoplasm; actomyosin; neuromuscular junction; nucleus; Z disc; cytosol; A band Molecular Function:potassium ion binding; transcription activator binding; zinc ion binding; histone deacetylase binding; protein deacetylase activity; protein kinase binding; transcription factor binding; protein binding; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H3-K9 specific); NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H3-K14 specific); sequence-specific DNA binding; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H4-K16 specific); histone deacetylase activity; transcription corepressor activity Biological Process: cardiac muscle hypertrophy; response to drug; nervous system development; regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development; transcription, DNA-dependent; B cell activation; negative regulation of transcription factor activity; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; histone deacetylation; response to denervation involved in regulation of muscle adaptation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; osteoblast development; positive regulation of protein sumoylation; chromatin remodeling; negative regulation of cell proliferation; B cell differentiation; regulation of protein binding; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; negative regulation of glycolysis; inflammatory response; skeletal development |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class II of the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. This protein does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P56524 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 259016348 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 9759 |
| NCBI Accession: | P56524.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P56524,Q86YH7, Q9UND6, E9PGB9, F5GX36, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P56524 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated MW: 106kDa/119kDaObserved MW: 117kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone deacetylase 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | histone deacetylase 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HDAC4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HD4; AHO3; BDMR; HDACA; HA6116; HDAC-4; HDAC-A |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone deacetylase 4; histone deacetylase A |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone deacetylase 4 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HDAC4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HDAC4_HUMAN |