Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-VWF Antibody (CAB13523)
- SKU:
- CAB13523
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-VWF Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB13523 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human VWF |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
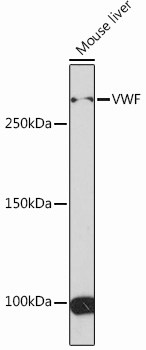
| Positive Samples: | Mouse liver |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human VWF |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 7450 |
| Uniprot: | P04275 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 309kDa |
| Observed MW: | 309KDa |
| Synonyms: | F8VWF, VWD |
| Background: | This gene encodes a glycoprotein involved in hemostasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed following assembly into large multimeric complexes. These complexes function in the adhesion of platelets to sites of vascular injury and the transport of various proteins in the blood. Mutations in this gene result in von Willebrand disease, an inherited bleeding disorder. An unprocessed pseudogene has been found on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | VWF: Important in the maintenance of hemostasis, it promotes adhesion of platelets to the sites of vascular injury by forming a molecular bridge between sub-endothelial collagen matrix and platelet-surface receptor complex GPIb-IX-V. Also acts as a chaperone for coagulation factor VIII, delivering it to the site of injury, stabilizing its heterodimeric structure and protecting it from premature clearance from plasma. Defects in VWF are the cause of von Willebrand disease type 1 (VWD1). A common hemorrhagic disorder due to defects in von Willebrand factor protein and resulting in impaired platelet aggregation. Von Willebrand disease type 1 is characterized by partial quantitative deficiency of circulating von Willebrand factor, that is otherwise structurally and functionally normal. Clinical manifestations are mucocutaneous bleeding, such as epistaxis and menorrhagia, and prolonged bleeding after surgery or trauma. Defects in VWF are the cause of von Willebrand disease type 2 (VWD2). A hemorrhagic disorder due to defects in von Willebrand factor protein and resulting in impaired platelet aggregation. Von Willebrand disease type 2 is characterized by qualitative deficiency and functional anomalies of von Willebrand factor. It is divided in different subtypes including 2A, 2B, 2M and 2N (Normandy variant). The mutant VWF protein in types 2A, 2B and 2M are defective in their platelet- dependent function, whereas the mutant protein in type 2N is defective in its ability to bind factor VIII. Clinical manifestations are mucocutaneous bleeding, such as epistaxis and menorrhagia, and prolonged bleeding after surgery or trauma. Defects in VWF are the cause of von Willebrand disease type 3 (VWD3). A severe hemorrhagic disorder due to a total or near total absence of von Willebrand factor in the plasma and cellular compartments, also leading to a profound deficiency of plasmatic factor VIII. Bleeding usually starts in infancy and can include epistaxis, recurrent mucocutaneous bleeding, excessive bleeding after minor trauma, and hemarthroses. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell adhesion; Secreted, signal peptide; Extracellular matrix; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Secreted Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12p13.3 Cellular Component: extracellular matrix; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; endoplasmic reticulum; extracellular region; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:integrin binding; collagen binding; identical protein binding; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; protease binding; chaperone binding; immunoglobulin binding; protein N-terminus binding; glycoprotein binding Biological Process: platelet activation; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; platelet degranulation; hemostasis; response to wounding; liver development; blood coagulation; cell adhesion; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway; protein homooligomerization; cell-substrate adhesion; placenta development Disease: Von Willebrand Disease, Type 3; Von Willebrand Disease, Type 1; Von Willebrand Disease, Type 2 |
| NCBI Summary: | The glycoprotein encoded by this gene functions as both an antihemophilic factor carrier and a platelet-vessel wall mediator in the blood coagulation system. It is crucial to the hemostasis process. Mutations in this gene or deficiencies in this protein result in von Willebrand's disease. An unprocessed pseudogene has been found on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P04275 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 317373549 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7450 |
| NCBI Accession: | P04275.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P04275,Q8TCE8, Q99806, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P04275 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated MW: 38kDa/309kDaObserved MW: Refer to figures |
| NCBI Full Name: | von Willebrand factor |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | von Willebrand factor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | VWF |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | VWD; F8VWF |
| NCBI Protein Information: | von Willebrand factor; coagulation factor VIII VWF |
| UniProt Protein Name: | von Willebrand factor |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | von Willebrand antigen II |
| Protein Family: | von Willebrand factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | VWF |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VWF_HUMAN |