Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-Protein C Antibody (CAB4532)
- SKU:
- CAB4532
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Protein C Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB4532 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
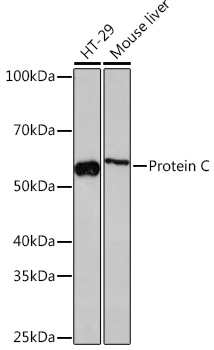
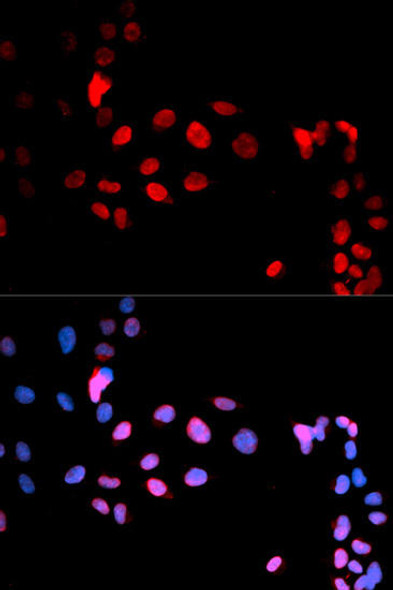
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Protein C |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | HT-29, Mouse liver |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Protein C |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5624 |
| Uniprot: | P04070 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 52kDa |
| Observed MW: | 52KDa |
| Synonyms: | APC, PC, PROC1, THPH3, THPH4 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein. The encoded protein is cleaved to its activated form by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. This activated form contains a serine protease domain and functions in degradation of the activated forms of coagulation factors V and VIII. Mutations in this gene have been associated with thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, neonatal purpura fulminans, and recurrent venous thrombosis.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PROC: Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent serine protease that regulates blood coagulation by inactivating factors Va and VIIIa in the presence of calcium ions and phospholipids. Defects in PROC are the cause of thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, autosomal dominant (THPH3). A hemostatic disorder characterized by impaired regulation of blood coagulation and a tendency to recurrent venous thrombosis. However, many adults with heterozygous disease may be asymptomatic. Individuals with decreased amounts of protein C are classically referred to as having type I protein C deficiency and those with normal amounts of a functionally defective protein as having type II deficiency. Defects in PROC are the cause of thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, autosomal recessive (THPH4). A hemostatic disorder characterized by impaired regulation of blood coagulation and a tendency to recurrent venous thrombosis. It results in a thrombotic condition that can manifest as a severe neonatal disorder or as a milder disorder with late-onset thrombophilia. The severe form leads to neonatal death through massive neonatal venous thrombosis. Often associated with ecchymotic skin lesions which can turn necrotic called purpura fulminans, this disorder is very rare. Belongs to the peptidase S1 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protease; Apoptosis; EC 3.4.21.69 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2q13-q14 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum lumen; Golgi lumen; extracellular region Molecular Function:protein binding; serine-type endopeptidase activity; calcium ion binding Biological Process: cellular protein metabolic process; negative regulation of blood coagulation; blood coagulation; proteolysis; post-translational protein modification; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation; leukocyte migration; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Thrombophilia Due To Protein C Deficiency, Autosomal Recessive; Thrombophilia Due To Protein C Deficiency, Autosomal Dominant |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein. The encoded protein is cleaved to its activated form by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. This activated form contains a serine protease domain and functions in degradation of the activated forms of coagulation factors V and VIII. Mutations in this gene have been associated with thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, neonatal purpura fulminans, and recurrent venous thrombosis.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P04070 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 131067 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5624 |
| NCBI Accession: | P04070.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P04070,Q15189, Q15190, Q16001, Q53S74, Q9UC55, B4DPQ7 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P04070 |
| Molecular Weight: | 461 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Vitamin K-dependent protein C |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein C (inactivator of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PROC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PC; APC; PROC1; THPH3; THPH4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | vitamin K-dependent protein C; prepro-protein C; autoprothrombin IIA; anticoagulant protein C; blood coagulation factor XIV |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Vitamin K-dependent protein C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Anticoagulant protein C; Autoprothrombin IIA; Blood coagulation factor XIVCleaved into the following 3 chains:Vitamin K-dependent protein C light chain; Vitamin K-dependent protein C heavy chain; Activation peptide |
| Protein Family: | Vitamin K-dependent protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PROC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PROC_HUMAN |
View AllClose