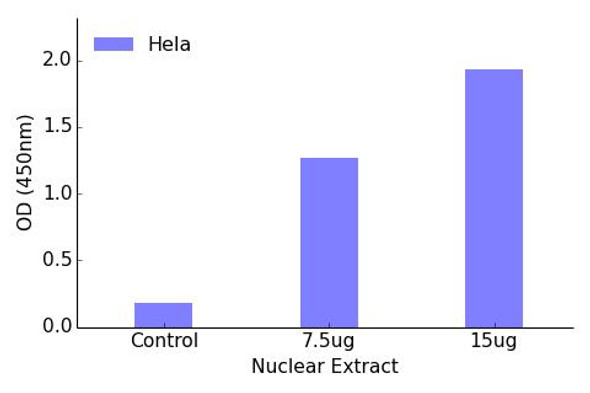
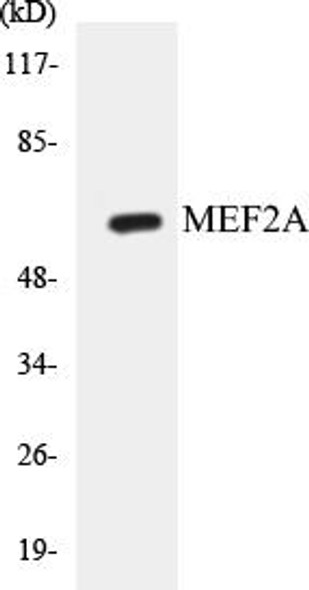
Cell Death Antibodies 2
Anti-MEF2A Antibody (CAB7911)
- SKU:
- CAB7911
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MEF2A Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7911 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MEF2A |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
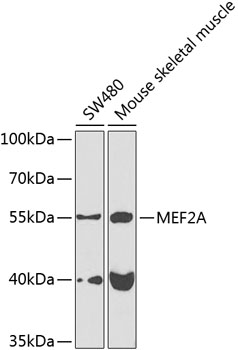
| Positive Samples: | SW480, Mouse skeletal muscle |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MEF2A |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 4205 |
| Uniprot: | Q02078 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 45kDa/46kDa/53kDa/54kDa |
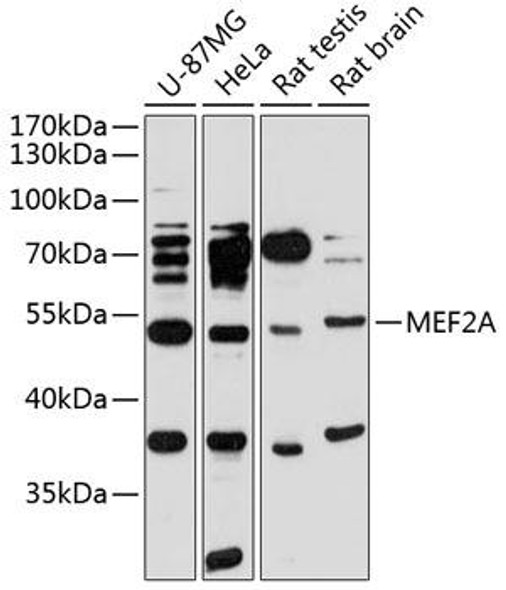
| Observed MW: | 55kDa |
| Synonyms: | MEF2A, ADCAD1, RSRFC4, RSRFC9, mef2 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding transcription factor that activates many muscle-specific, growth factor-induced, and stress-induced genes. The encoded protein can act as a homodimer or as a heterodimer and is involved in several cellular processes, including muscle development, neuronal differentiation, cell growth control, and apoptosis. Defects in this gene could be a cause of autosomal dominant coronary artery disease 1 with myocardial infarction (ADCAD1). Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | MEF2A: a myocyte-specific enhancing transcription factor which binds specifically to the MEF2 element present in the regulatory regions of many, if not all, muscle-specific genes. A member of the MADS gene family that also includes several homeotic genes and other transcription factors, all of which share a conserved DNA-binding domain. Five alternatively spliced isoforms have been reported. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 15q26 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nuclear chromatin; nucleoplasm; nucleus; transcription factor complex Molecular Function:chromatin binding; histone acetyltransferase binding; histone deacetylase binding; protein binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein kinase binding; RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; SMAD binding; transcription activator binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: apoptosis; dendrite morphogenesis; heart development; innate immune response; MAPKKK cascade; mitochondrial genome maintenance; mitochondrion distribution; muscle cell differentiation; muscle development; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; stress-activated MAPK cascade; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; transcription, DNA-dependent; ventricular cardiac myofibril development Disease: Coronary Artery Disease, Autosomal Dominant, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding transcription factor that activates many muscle-specific, growth factor-induced, and stress-induced genes. The encoded protein can act as a homodimer or as a heterodimer and is involved in several cellular processes, including muscle development, neuronal differentiation, cell growth control, and apoptosis. Defects in this gene could be a cause of autosomal dominant coronary artery disease 1 with myocardial infarction (ADCAD1). Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q02078 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1170908 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4205 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q02078.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q02078,O43814, Q14223, Q14224, Q59GX4, Q7Z6C9, Q96D14 B4DFQ7, F6XG23, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q02078 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45,570 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | myocyte enhancer factor 2A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MEF2A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | mef2; ADCAD1; RSRFC4; RSRFC9 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Serum response factor-like protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MEF2A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MEF2A_HUMAN |