Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 3
Anti-MED1 Antibody (CAB1724)
- SKU:
- CAB1724
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MED1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1724 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human MED1 (NP_004765.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
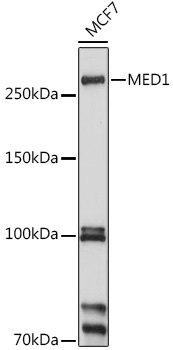
| Positive Samples: | MCF7 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human MED1 (NP_004765.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MKAQ GETE ESEK LSKM SSLL ERLH AKFN QNRP WSET IKLV RQVM EKRV VMSS GGHQ HLVS CLET LQKA LKVT SLPA MTDR LESI ARQN GLGS HLSA SGTE CYIT SDMF YVEV QLDP AGQL CDVK VAHH GENP VSCP ELVQ QLRE KNFD EFSK HLKG LVNL YNLP GDNK LKTK MYLA LQSL EQDL SKMA IMYW KATN AGPL DKIL HGSV GYLT PRSG GHLM NLKY YVSP SDLL DDKT ASPI ILHE NNVS RSLG MNAS VTIE GTSA VYKL PIAP LIMG SHPV DNKW TPSF SSIT SANS VDLP |
| Gene ID: | 5469 |
| Uniprot: | Q15648 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 61kDa/168kDa |
| Observed MW: | 250KDa |
| Synonyms: | MED1, CRSP1, CRSP200, DRIP205, DRIP230, PBP, PPARBP, PPARGBP, RB18A, TRAP220, TRIP2 |
| Background: | The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. It also regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and it is essential for adipogenesis. This protein is known to have the ability to self-oligomerize. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | MED1: a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. Also is a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor- (TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. May regulates p53-dependent apoptosis. Is essential for adipogenesis. This protein is known to have the ability to self-oligomerize. Two splice-variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transcription, coactivator/corepressor; Nuclear receptor co-regulator Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q12 Cellular Component: chromatin; membrane; nucleolus; nucleoplasm; nucleus; Srb-mediator complex; ubiquitin ligase complex Molecular Function:chromatin binding; chromatin DNA binding; estrogen receptor binding; LBD domain binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity; nuclear hormone receptor binding; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding; protein binding; receptor activity; retinoic acid receptor binding; thyroid hormone receptor binding; thyroid hormone receptor coactivator activity; transcription coactivator activity; transcription cofactor activity; transcription factor binding; vitamin D receptor binding Biological Process: androgen biosynthetic process; androgen receptor signaling pathway; angiogenesis; brain development; cell morphogenesis; cellular lipid metabolic process; embryonic heart tube development; embryonic hemopoiesis; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; embryonic placenta development; enucleate erythrocyte development; erythrocyte development; fat cell differentiation; gene expression; keratinocyte differentiation; lactation; lens development in camera-type eye; liver development; monocyte differentiation; mRNA transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of neuron differentiation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; organ regeneration; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation; positive regulation of estrogen receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; protein ubiquitination; regulation of cell cycle; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase I promoter; steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway; thyroid hormone generation; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter |
| NCBI Summary: | The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. It also regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and it is essential for adipogenesis. This protein is known to have the ability to self-oligomerize. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15648 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 158518535 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5469 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15648.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15648,O43810, O75447, Q6P9H7, Q6PK58, Q9HD39, A2RRQ6 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15648 |
| Molecular Weight: | 61,563 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mediator complex subunit 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MED1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PBP; CRSP1; RB18A; TRIP2; PPARBP; CRSP200; DRIP205; DRIP230; PPARGBP; TRAP220 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Activator-recruited cofactor 205 kDa component; ARC205; Mediator complex subunit 1; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein; PBP; PPAR-binding protein; Thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex 220 kDa component; Trap220; Thyroid receptor-interacting protein 2; TR-interacting protein 2; TRIP-2; Vitamin D receptor-interacting protein complex component DRIP205; p53 regulatory protein RB18A |
| Protein Family: | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MED1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MED1_HUMAN |