Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 2
Anti-FUBP1 Antibody (CAB5587)
- SKU:
- CAB5587
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-FUBP1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5587 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
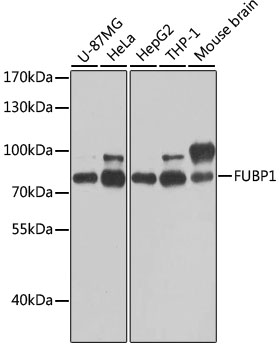
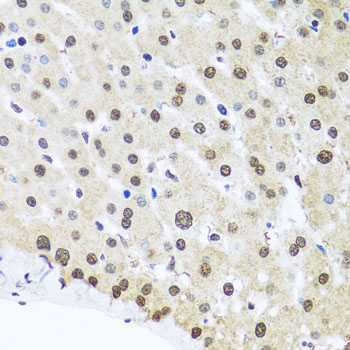
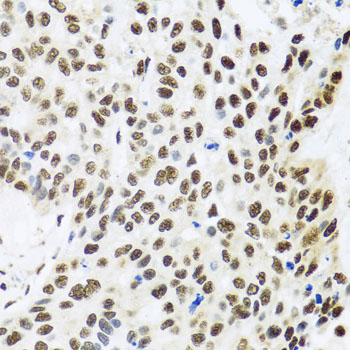
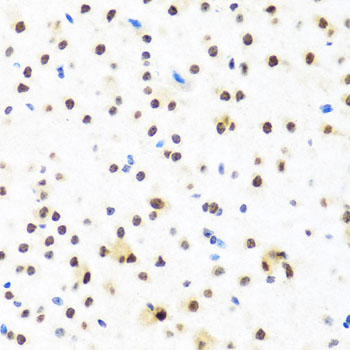
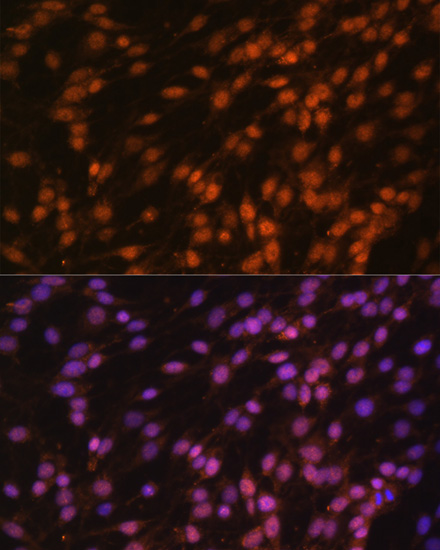
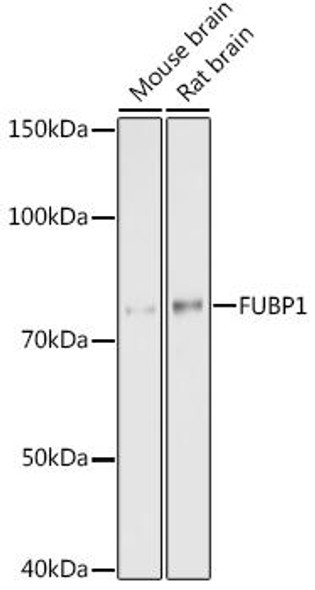
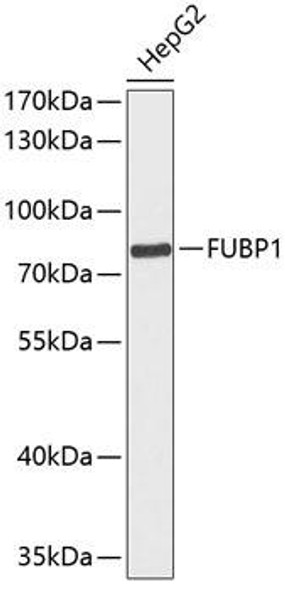
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 302-644 of human FUBP1 (NP_003893.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:100 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-87MG, HeLa, HepG2, THP-1, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 302-644 of human FUBP1 (NP_003893.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | QNDA GVRI QFKP DDGT TPER IAQI TGPP DRCQ HAAE IITD LLRS VQAG NPGG PGPG GRGR GRGQ GNWN MGPP GGLQ EFNF IVPT GKTG LIIG KGGE TIKS ISQQ SGAR IELQ RNPP PNAD PNMK LFTI RGTP QQID YARQ LIEE KIGG PVNP LGPP VPHG PHGV PGPH GPPG PPGP GTPM GPYN PAPY NPGP PGPA PHGP PAPY APQG WGNA YPHW QQQA PPDP AKAG TDPN SAAW AAYY AHYY QQQA QPPP AAPA GAPT TTQT NGQG DQQN PAPA GQVD YTKA WEEY YKKM GQAV PAPT GAPP GGQP DYSA AWAE YYRQ QAAY YAQT SPQG MPQH PPAP QGQ |
| Gene ID: | 8880 |
| Uniprot: | Q96AE4 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 67kDa/68kDa |
| Observed MW: | 79kDa |
| Synonyms: | FUBP1, FBP, FUBP, hDH V, hDHV |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FBP1: Regulates MYC expression by binding to a single-stranded far-upstream element (FUSE) upstream of the MYC promoter. May act both as activator and repressor of transcription. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor; RNA-binding; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; RNA splicing Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p31.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; transcription factor activity; single-stranded DNA binding Biological Process: transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q96AE4 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116241370 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8880 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q96AE4.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q96AE4,Q12828, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q96AE4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 653 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Far upstream element-binding protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FUBP1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FBP; FUBP; hDH V |
| NCBI Protein Information: | far upstream element-binding protein 1; DNA helicase V |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Far upstream element-binding protein 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | DNA helicase V; hDH V |
| Protein Family: | Far upstream element-binding protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FUBP1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FUBP1_HUMAN |
View AllClose


![FUBP1 Monoclonal Antibody [PAT14F5AT] (CPAB0640) FUBP1 Monoclonal Antibody [PAT14F5AT] (CPAB0640)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/58860/64042/fubp1-monoclonal-antibody-pat14f5at-cpab0640__50998__01809.1706535240.jpg?c=1)

