Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-FGF1 Antibody (CAB5900)
- SKU:
- CAB5900
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-FGF1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5900 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
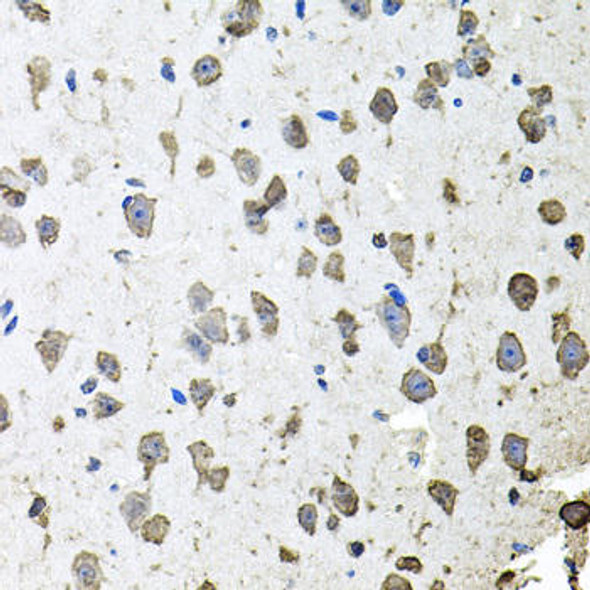
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF1 |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
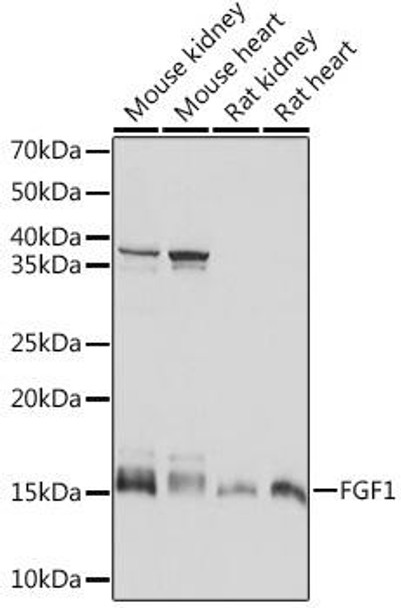
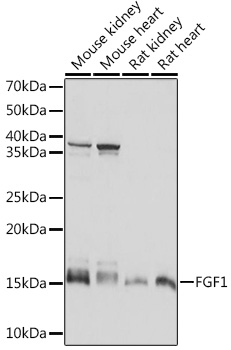
| Positive Samples: | Mouse kidney, Mouse heart, Rat kidney, Rat heart |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2246 |
| Uniprot: | P05230 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 17kDa |
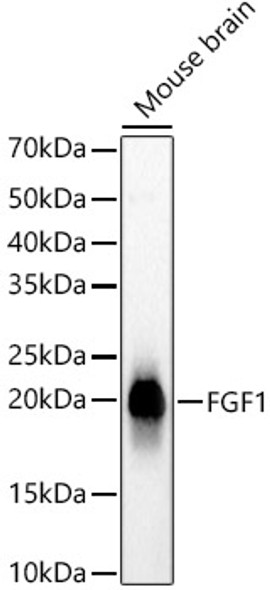
| Observed MW: | 17KDa |
| Synonyms: | AFGF, ECGF, ECGF-beta, ECGFA, ECGFB, FGF-1, FGF-alpha, FGFA, GLIO703, HBGF-1, HBGF1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein functions as a modifier of endothelial cell migration and proliferation, as well as an angiogenic factor. It acts as a mitogen for a variety of mesoderm- and neuroectoderm-derived cells in vitro, thus is thought to be involved in organogenesis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FGF1: Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, angiogenesis, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as potent mitogen in vitro. Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Affinity between fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors is increased by heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans that function as coreceptors. Found in a complex with FGFBP1, FGF1 and FGF2. Interacts with FGFBP1. Part of a Cu(2+)-dependent multiprotein aggregate containing FGF1, S100A13 and SYT1. Interacts with SYT1. Interacts with S100A13. Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Cell development/differentiation; Cytokine Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q31 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; extracellular space; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; nucleolus; extracellular region; cell cortex; cytosol Molecular Function:heparin binding; protein binding; growth factor activity; Hsp70 protein binding; fibroblast growth factor receptor binding Biological Process: epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; anatomical structure morphogenesis; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; multicellular organismal development; positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process; signal transduction; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; positive regulation of angiogenesis; induction of an organ; positive regulation of cell division; positive regulation of cell proliferation; insulin receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; angiogenesis; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of cell migration; lung development |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein functions as a modifier of endothelial cell migration and proliferation, as well as an angiogenic factor. It acts as a mitogen for a variety of mesoderm- and neuroectoderm-derived cells in vitro, thus is thought to be involved in organogenesis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P05230 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 122737 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2246 |
| NCBI Accession: | P05230.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P05230,P07502, Q16588, B2R5T0, D3DQF2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P05230 |
| Molecular Weight: | 6,698 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FGF1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AFGF; ECGF; FGFA; ECGFA; ECGFB; FGF-1; HBGF1; HBGF-1; GLIO703; ECGF-beta; FGF-alpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fibroblast growth factor 1; heparin-binding growth factor 1; beta-endothelial cell growth factor; endothelial cell growth factor, beta; endothelial cell growth factor, alpha |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Acidic fibroblast growth factor; aFGF; Endothelial cell growth factor; ECGF; Heparin-binding growth factor 1; HBGF-1 |
| Protein Family: | Fibroblast growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FGF1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FGF1_HUMAN |