Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 4
Anti-FANCA Antibody (CAB7671)
- SKU:
- CAB7671
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-FANCA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7671 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
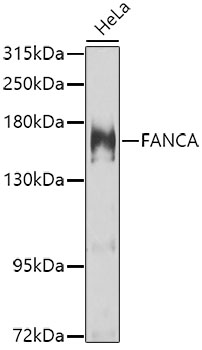
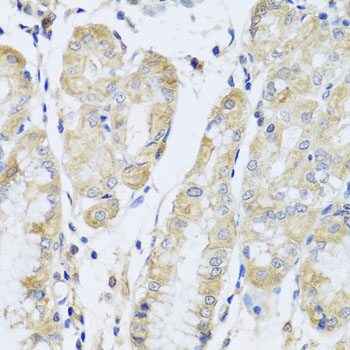
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-275 of human FANCA (NP_000126.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-275 of human FANCA (NP_000126.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSDS WVPN SASG QDPG GRRR AWAE LLAG RVKR EKYN PERA QKLK ESAV RLLR SHQD LNAL LLEV EGPL CKKL SLSK VIDC DSSE AYAN HSSS FIGS ALQD QASR LGVP VGIL SAGM VASS VGQI CTAP AETS HPVL LTVE QRKK LSSL LEFA QYLL AHSM FSRL SFCQ ELWK IQSS LLLE AVWH LHVQ GIVS LQEL LESH PDMH AVGS WLFR NLCC LCEQ MEAS CQHA DVAR AMLS DFVQ MFVL RGFQ KNSD LRRT VEPE KMPQ VTVD VLQR MLI |
| Gene ID: | 2175 |
| Uniprot: | O15360 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 32kDa/159kDa/162kDa |
| Observed MW: | 163kDa |
| Synonyms: | FANCA, FA, FA-H, FA1, FAA, FACA, FAH, FANCH |
| Background: | The Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCI, FANCJ (also called BRIP1), FANCL, FANCM and FANCN (also called PALB2). The previously defined group FANCH is the same as FANCA. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation group A. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene are the most common cause of Fanconi anemia. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FANCA: DNA repair protein that may operate in a postreplication repair or a cell cycle checkpoint function. May be involved in interstrand DNA cross-link repair and in the maintenance of normal chromosome stability. Defects in FANCA are a cause of Fanconi anemia (FA). FA is a genetically heterogeneous, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by progressive pancytopenia, a diverse assortment of congenital malformations, and a predisposition to the development of malignancies. At the cellular level it is associated with hypersensitivity to DNA-damaging agents, chromosomal instability (increased chromosome breakage), and defective DNA repair. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA repair, damage Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16q24.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: DNA repair; protein complex assembly Disease: Fanconi Anemia, Complementation Group A; Tracheoesophageal Fistula With Or Without Esophageal Atresia |
| NCBI Summary: | The Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCI, FANCJ (also called BRIP1), FANCL, FANCM and FANCN (also called PALB2). The previously defined group FANCH is the same as FANCA. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation group A. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene are the most common cause of Fanconi anemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O15360 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 147744560 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2175 |
| NCBI Accession: | O15360.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O15360,O75266, Q6PL10, Q92497, Q96H18, Q9UEA5, Q9UEL8 Q9UEL9, Q9UPK3, A5D923, B4DRI7, H3BSR5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O15360 |
| Molecular Weight: | 159,083 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fanconi anemia group A protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | Fanconi anemia complementation group A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FANCA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FA; FA1; FAA; FAH; FA-H; FACA; FANCH |
| NCBI Protein Information: | Fanconi anemia group A protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fanconi anemia group A protein |
| Protein Family: | Fanconi anemia group A protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FANCA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FANCA_HUMAN |
View AllClose