Cell Death Antibodies 1
Anti-E2F1 Antibody (CAB16720)
- SKU:
- CAB16720
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-E2F1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16720 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
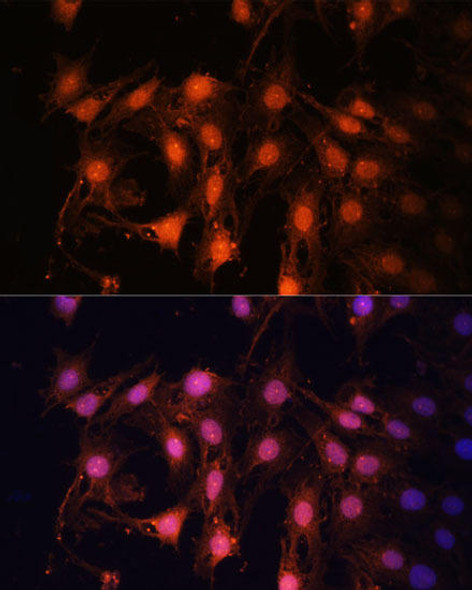
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human E2F1 |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:1000 IF 1:20 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
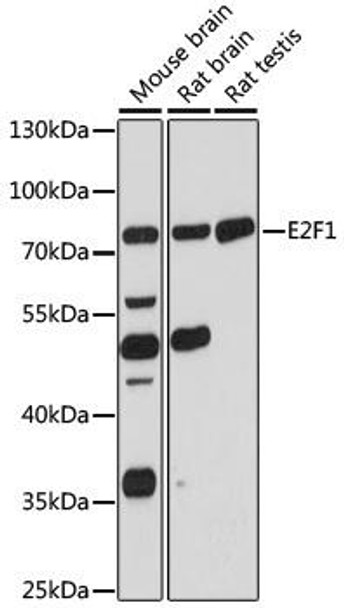
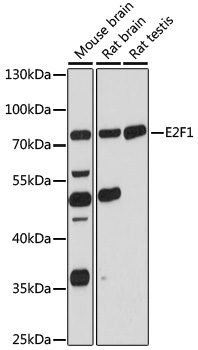
| Positive Samples: | mouse brain, rat brain, rat testis |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human E2F1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1869 |
| Uniprot: | Q01094 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 46kDa |
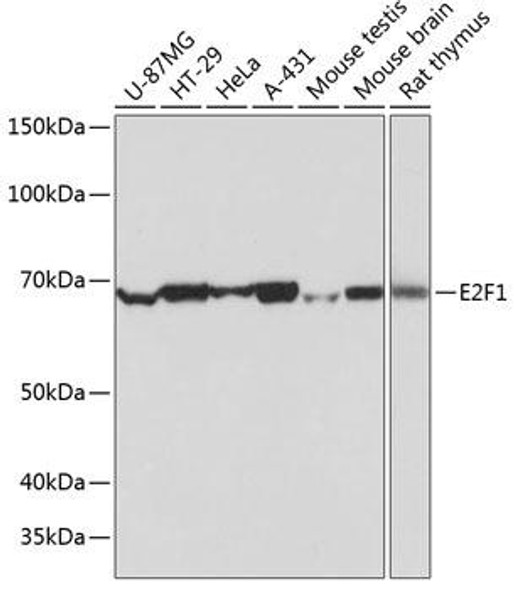
| Observed MW: | 70kDa |
| Synonyms: | E2F-1, RBAP1, RBBP3, RBP3, E2F1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. The E2F proteins contain several evolutionally conserved domains found in most members of the family. These domains include a DNA binding domain, a dimerization domain which determines interaction with the differentiation regulated transcription factor proteins (DP), a transactivation domain enriched in acidic amino acids, and a tumor suppressor protein association domain which is embedded within the transactivation domain. This protein and another 2 members, E2F2 and E2F3, have an additional cyclin binding domain. This protein binds preferentially to retinoblastoma protein pRB in a cell-cycle dependent manner. It can mediate both cell proliferation and p53-dependent/independent apoptosis. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | E2F1: a member of the E2F/DP family of transcription factors.The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. Binds DNA cooperatively with Dp transcription factors in the promoter region of a number of genes whose products are involved in cell cycle regulation or in DNA replication.The Dp-1/E2F complex functions in the control of cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. The E2F-1 complex binds specifically hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma protein RB1. During the cell cycle, RB1 becomes phosphorylated in mid-to-late G1 phase, detaches from the DRTF1/E2F complex, rendering E2F transcriptionally active. Phosphorylated by CDK2 and cyclin A-CDK2 in the S-phase. It can mediate both cell proliferation and p53-dependent apoptosis. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transcription factor; DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q11.2 Cellular Component: mitochondrion; nuclear chromatin; nucleoplasm; nucleus; Rb-E2F complex Molecular Function:DNA binding; protein binding; protein kinase binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: anoikis; DNA damage checkpoint; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in induction of apoptosis; forebrain development; mRNA stabilization; negative regulation of DNA binding; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; spermatogenesis; transcription, DNA-dependent |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. The E2F proteins contain several evolutionally conserved domains found in most members of the family. These domains include a DNA binding domain, a dimerization domain which determines interaction with the differentiation regulated transcription factor proteins (DP), a transactivation domain enriched in acidic amino acids, and a tumor suppressor protein association domain which is embedded within the transactivation domain. This protein and another 2 members, E2F2 and E2F3, have an additional cyclin binding domain. This protein binds preferentially to retinoblastoma protein pRB in a cell-cycle dependent manner. It can mediate both cell proliferation and p53-dependent/independent apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q01094 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 400928 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1869 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q01094.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q01094,Q13143, Q92768, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q01094 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,920 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transcription factor E2F1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | E2F transcription factor 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | E2F1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RBP3; E2F-1; RBAP1; RBBP3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transcription factor E2F1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transcription factor E2F1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | PBR3; Retinoblastoma-associated protein 1; RBAP-1; Retinoblastoma-binding protein 3; RBBP-3; pRB-binding protein E2F-1 |
| Protein Family: | Transcription factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | E2F1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | E2F1_HUMAN |