Cell Biology Antibodies 10
Anti-COCH Antibody (CAB6562)
- SKU:
- CAB6562
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-COCH Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB6562 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
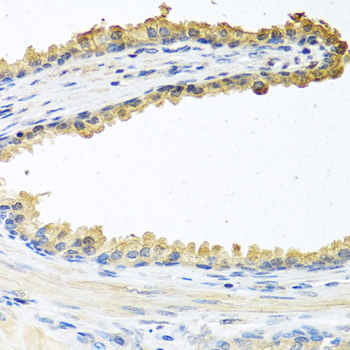
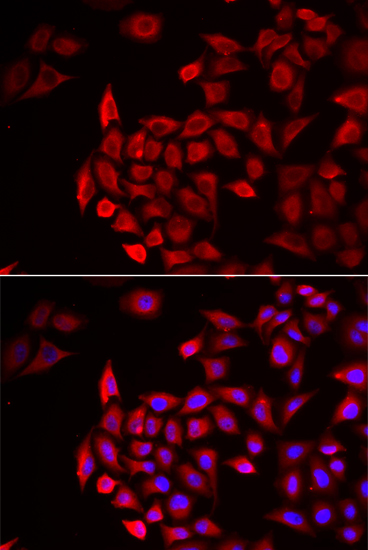
| Application: | IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-260 of human COCH (NP_001128530.1). |
| Application: | IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IHC 1:50 - 1:100 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-260 of human COCH (NP_001128530.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GPAG SEGA APIA ITCF TRGL DIRK EKAD VLCP GGCP LEEF SVYG NIVY ASVS SICG AAVH RGVI SNSG GPVR VYSL PGRE NYSS VDAN GIQS QMLS RWSA SFTV TKGK SSTQ EATG QAVS TAHP PTGK RLKK TPEK KTGN KDCK ADIA FLID GSFN IGQR RFNL QKNF VGKV ALML GIGT EGPH VGLV QASE HPKI EFYL KNFT SAKD VLFA IKEV GFRG GNSN TGKA LKHT AQKF FTVD A |
| Gene ID: | 1690 |
| Uniprot: | O43405 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted, extracellular matrix, extracellular space |
| Calculated MW: | 53kDa/59kDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to Figures |
| Synonyms: | COCH, COCH-5B2, COCH5B2, DFNA9, cochlin |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively. Hybridization to this gene was detected in spindle-shaped cells located along nerve fibers between the auditory ganglion and sensory epithelium. These cells accompany neurites at the habenula perforata, the opening through which neurites extend to innervate hair cells. This and the pattern of expression of this gene in chicken inner ear paralleled the histologic findings of acidophilic deposits, consistent with mucopolysaccharide ground substance, in temporal bones from DFNA9 (autosomal dominant nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness 9) patients. Mutations that cause DFNA9 have been reported in this gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. Additional splice variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described but their biological validities have not been demonstrated. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | COCH: Plays a role in the control of cell shape and motility in the trabecular meshwork. Defects in COCH are the cause of deafness autosomal dominant type 9 (DFNA9). DFNA9 is a form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. DFNA9 is characterized by onset in the fourth or fifth decade of life and initially involves the high frequencies. Deafness is progressive and usually complete by the sixth decade. In addition to cochlear involvement, DFNA9 patients also exhibit a spectrum of vestibular dysfunctions. Penetrance of the vestibular symptoms is often incomplete, and some patients are minimally affected, whereas others suffer from severe balance disturbances and episodes of vertigo. Affected individuals have mucopolysaccharide depositions in the channels of the cochlear and vestibular nerves. These depositions apparently cause strangulation and degeneration of dendritic fibers. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide; Extracellular matrix Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q11.2-q13 Cellular Component: extracellular matrix Molecular Function:collagen binding; protein binding Biological Process: regulation of cell shape Disease: Deafness, Autosomal Dominant 9 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively. Hybridization to this gene was detected in spindle-shaped cells located along nerve fibers between the auditory ganglion and sensory epithelium. These cells accompany neurites at the habenula perforata, the opening through which neurites extend to innervate hair cells. This and the pattern of expression of this gene in chicken inner ear paralleled the histologic findings of acidophilic deposits, consistent with mucopolysaccharide ground substance, in temporal bones from DFNA9 (autosomal dominant nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness 9) patients. Mutations that cause DFNA9 have been reported in this gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. Additional splice variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described but their biological validities have not been demonstrated. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O43405 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 7387582 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1690 |
| NCBI Accession: | O43405.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O43405,Q96IU6, A8K9K9, D3DS84, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O43405 |
| Molecular Weight: | 53,230 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cochlin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cochlin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COCH |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DFNA9; COCH5B2; COCH-5B2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cochlin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cochlin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | COCH-5B2 |
| Protein Family: | Cochlin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COCH |
| UniProt Entry Name: | COCH_HUMAN |
View AllClose