Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 5
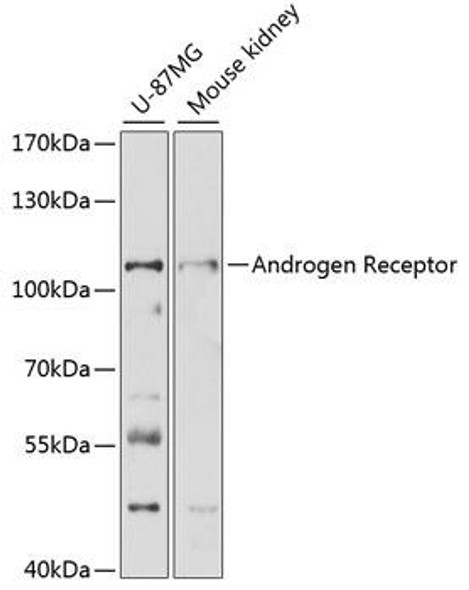
Anti-Androgen Receptor Antibody (CAB19611)
- SKU:
- CAB19611
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Androgen Receptor Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19611 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Androgen Receptor. |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse testis |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Androgen Receptor. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 367 |
| Uniprot: | P10275 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 110kDa |
| Observed MW: | 110KDa |
| Synonyms: | AIS, AR8, DHTR, HUMARA, HYSP1, KD, NR3C4, SBMA, SMAX1, TFM, AR |
| Background: | The androgen receptor gene is more than 90 kb long and codes for a protein that has 3 major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and androgen-binding domain. The protein functions as a steroid-hormone activated transcription factor. Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. This gene contains 2 polymorphic trinucleotide repeat segments that encode polyglutamine and polyglycine tracts in the N-terminal transactivation domain of its protein. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract from the normal 9-34 repeats to the pathogenic 38-62 repeats causes spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA, also known as Kennedy's disease). Mutations in this gene are also associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | AR: a nuclear hormone receptor and transcription factor. Regulates gene expression and affects cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Two splice-variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transcription factor; Nuclear receptor; DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq12 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; protein complex; cytoplasm; nuclear chromatin; nucleus Molecular Function:protein dimerization activity; protein binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor activity; androgen receptor activity; enzyme binding; DNA binding; androgen binding; zinc ion binding; beta-catenin binding; chromatin binding; transcription factor binding; transcription factor activity; receptor binding Biological Process: prostate gland development; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway; transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; signal transduction; protein oligomerization; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; negative regulation of integrin biosynthetic process; cell proliferation; cell-cell signaling; transport; androgen receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase III promoter; gene expression; steroid hormone mediated signaling; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of integrin biosynthetic process; cell growth; sex differentiation; positive regulation of phosphorylation Disease: Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome; Prostate Cancer; Androgen Insensitivity, Partial; Hypospadias 1, X-linked; Spinal And Bulbar Muscular Atrophy, X-linked 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | The androgen receptor gene is more than 90 kb long and codes for a protein that has 3 major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and androgen-binding domain. The protein functions as a steroid-hormone activated transcription factor. Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. This gene contains 2 polymorphic trinucleotide repeat segments that encode polyglutamine and polyglycine tracts in the N-terminal transactivation domain of its protein. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract causes spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease). Mutations in this gene are also associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). Two alternatively spliced variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P10275 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 113830 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 367 |
| NCBI Accession: | P10275.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P10275,Q9UD95, A2RUN2, B1AKD7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P10275 |
| Molecular Weight: | 44,643 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Androgen receptor |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | androgen receptor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | AR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KD; AIS; TFM; DHTR; SBMA; HYSP1; NR3C4; SMAX1; HUMARA |
| NCBI Protein Information: | androgen receptor; androgen nuclear receptor variant 2; dihydrotestosterone receptor; nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Androgen receptor |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Dihydrotestosterone receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 4 |
| Protein Family: | Allatostatin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | AR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ANDR_HUMAN |