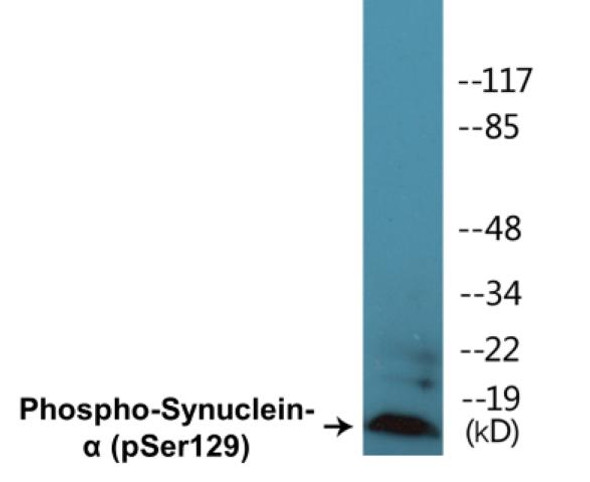
Description
Synuclein-pan Cell-Based ELISA
| Product Description: | The Synuclein-pan Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA allows for qualitative detection of Synuclein-pan in plated and fixed cells. |
| Target Synonyms: | Alpha-synuclein; Non-A beta component of AD amyloid; Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor; NACP; SNCA; NACP; PARK1 |
| Detection Target: | Phospho-IRAK1(Thr209) |
| Reactivity: | H, M, R |
| Pack Size: | 1 x 96 assays |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nm |
| Format: | Cell-Based ELISA/In-Cell ELISA |
| Storage and Stability Guarantee: | 4°C/6 Months |
| Sample Type: | Plated & fixed cells |
| Range: | 5000 cells/well minimum |
| Time: | 4.5 hours |
Synuclein-pan Cell-Based ELISA Protein Information
| UniProt Protein Function: | SNCA: a member of the synuclein family. Abundantly expressed in the brain. Inhibits phospholipase D2 selectively. May integrate presynaptic signaling and membrane trafficking. Implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. A major component of amyloid plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Two alternatively spliced isoforms transcripts have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Adaptor/scaffold Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q21 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; nuclear outer membrane; mitochondrion; rough endoplasmic reticulum; lysosome; extracellular region; fibril; terminal button; inclusion body; cell cortex; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I; cytosol; actin cytoskeleton; synaptic vesicle; platelet alpha granule membrane; growth cone; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; axon; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; ribosome; cell junction; nucleus Molecular Function:protein domain specific binding; identical protein binding; histone binding; zinc ion binding; kinesin binding; ferrous iron binding; microtubule binding; caspase inhibitor activity; beta-tubulin binding; magnesium ion binding; phosphoprotein binding; protein N-terminus binding; oxidoreductase activity; Hsp70 protein binding; calcium ion binding; dynein binding; protein binding; copper ion binding; phospholipase binding; phospholipid binding; tau protein binding; fatty acid binding; alpha-tubulin binding Biological Process: regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity; negative regulation of serotonin uptake; regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process; adult locomotory behavior; positive regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake; mitochondrial membrane organization and biogenesis; microglial cell activation; response to lipopolysaccharide; positive regulation of endocytosis; dopamine biosynthetic process; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of caspase activity; negative regulation of monooxygenase activity; fatty acid metabolic process; positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion; regulation of dopamine secretion; negative regulation of dopamine uptake; negative regulation of histone acetylation; calcium ion homeostasis; negative regulation of exocytosis; response to magnesium ion; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; behavioral response to cocaine; receptor internalization; phospholipid metabolic process; fibril organization and biogenesis; synapse organization and biogenesis; dopamine uptake; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; response to iron(II) ion; positive regulation of receptor recycling; aging; caspase activation; response to drug; neutral lipid metabolic process; protein destabilization; regulation of macrophage activation; regulation of glutamate secretion; negative regulation of microtubule polymerization; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process; organelle ATP synthesis coupled electron transport; regulation of locomotion; synaptic vesicle endocytosis; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential; negative regulation of transporter activity; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Parkinson Disease 4, Autosomal Dominant; Dementia, Lewy Body; Parkinson Disease 1, Autosomal Dominant |
| NCBI Summary: | Alpha-synuclein is a member of the synuclein family, which also includes beta- and gamma-synuclein. Synucleins are abundantly expressed in the brain and alpha- and beta-synuclein inhibit phospholipase D2 selectively. SNCA may serve to integrate presynaptic signaling and membrane trafficking. Defects in SNCA have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. SNCA peptides are a major component of amyloid plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Four alternatively spliced transcripts encoding two different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P37840 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 586067 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6622 |
| NCBI Accession: | P37840.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P37840,Q13701, Q4JHI3, Q6IAU6, A8K2A4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P37840 |
| Molecular Weight: | 140 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Alpha-synuclein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | synuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SNCA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PD1; NACP; PARK1; PARK4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | alpha-synuclein; synuclein alpha-140; non A-beta component of AD amyloid |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Alpha-synuclein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Non-A beta component of AD amyloid; Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor; NACP |
| Protein Family: | Alpha-synuclein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SNCA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SYUA_HUMAN |