Microbiology Recombinant Proteins
S. Aureus GLU-C Recombinant Protein (RPPB1706)
- SKU:
- RPPB1706
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Uniprot:
- P0C1U8
- Research Area:
- Microbiology
Description
| Product Name: | S. Aureus GLU-C Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1706 |
| Size: | 250µg |
| Species: | S. Aureus |
| Target: | GLU-C |
| Synonyms: | Glutamyl endopeptidase (EC:3.4.21.19), Endoproteinase Glu-C, Staphylococcal serine proteinase, V8 protease, V8 proteinase, sspA. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered lyophilized powder. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a sterile (0.2�m) filtered aqueous solution containing 10mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.5. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized GLU-C� in sterile 18M-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized GLU-C although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution GLU-C should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
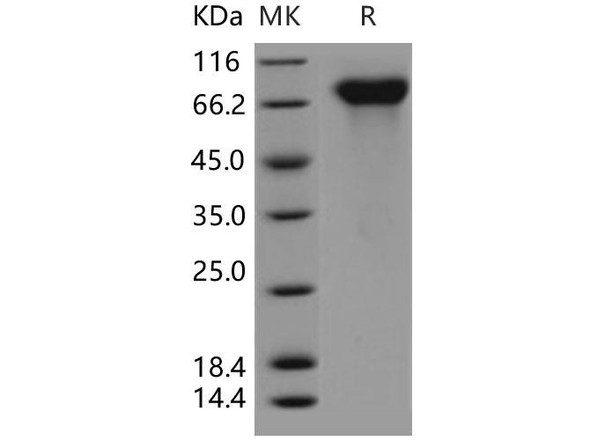
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MLPNNDRHQI TDTTNGHYAP VTYIQVEAPT GTFIASGVVV GKDTLLTNKH VVDATHGDPH ALKAFPSAIN QDNYPNGGFT AEQITKYSGE GDLAIVKFSP NEQNKHIGEV VKPATMSNNA ETQVNQNITV TGYPGDKPVA TMWESKGKIT YLKGEAMQYD LSTTGGNSGS PVFNEKNEVI GIHWGGVPNE FNGAVFINEN VRNFLKQNIE DIHFANDDQP NNPDNPDNPN NPDNPNNPDE PNNPDNPNNP DNPDNGDNNN SDNPDAA |
| UniProt Code: | P0C1U8 |
Glutamyl endopeptidase (GLU-C) is an enzyme which cleaves peptide bonds on the carboxyl-terminal side of glutamic acid and, less frequently, aspartic acid (for example: Glu-|-Xaa, Asp-|-Xaa). GLU-C is a pathogenic factor involved in the adherence and colonization of human tissue. GLU-C preferentially cleaves peptide bonds on the carboxyl-terminal side of aspartate and glutamate. GLU-C is required for proteolytic maturation of thiol protease SspB and inactivation of SspC, an inhibitor of SspB. GLU-C is the most important protease for degradation of fibronectin-binding protein (FnBP) and surface protein A, which are involved in adherence to host cells. Furthermore, GLU-C protects bacteria against host defense mechanism by cleaving the immunoglobulin classes IgG, IgA and IgM. GLU-C may also be involved in the stability of secreted lipases.
Recombinant Staphylococcal GLU-C produced in E.coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing a total of 267 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 28.9kDa.