Description
| Product Name: | Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha (Phospho-Ser77) Transcription Factor Activity Assay |
| Product Code: | TFAB00048 |
| Target: | Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha (Phospho-Ser77) |
| Synonyms: | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1 |
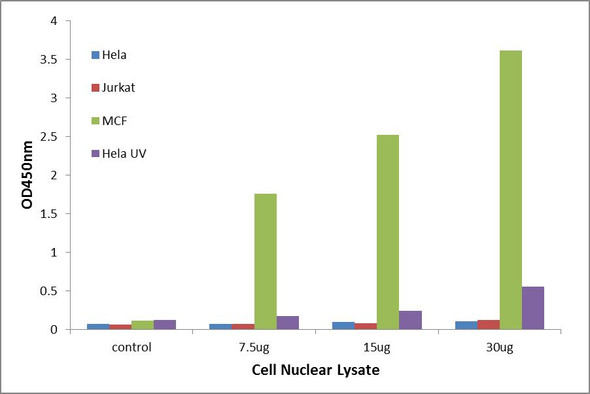
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Sample Types: | Nuclear or cell lysates |
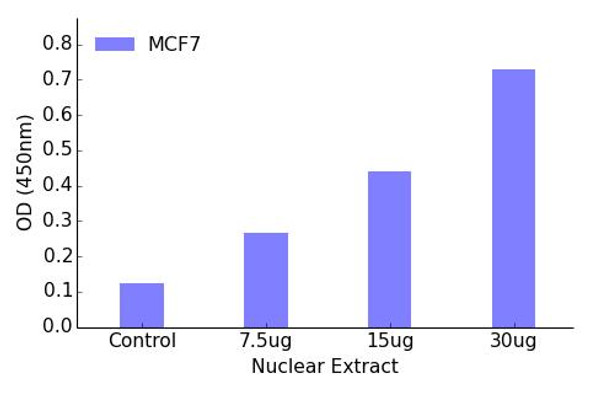
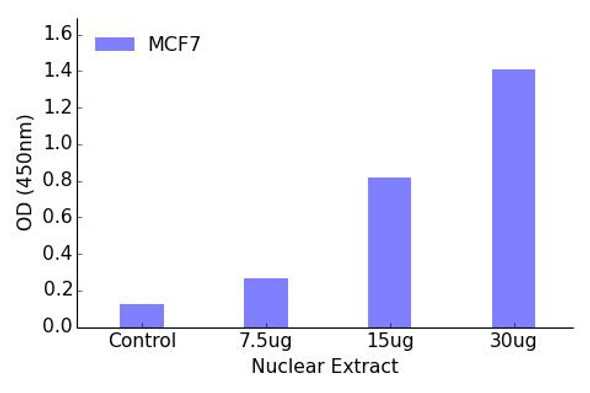
The Assay Genie Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha (Phospho-Ser77) transcription factor activity assay allows for the detection and qualitative analysis of Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha (Phospho-Ser77) active transcription factors in eukaryotic nuclear or cell lysates.
Assay Genie ELISA kits are designed to significantly reduce experiment time and ensure sensitivity and flexibility for high-throughput screening.
| Assay Time: | 4.5 hours |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nm |
| Size: | 12 x 8-Well Microstrips |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RARA: is a receptor for retinoic acid, a potent mammalian morphogen and teratogen that has profound effects on vertebrate development. RARA is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Controls cell function by directly regulating gene expression. Its phosphorylation is crucial for transcriptional activity. Aberrations involving RARA may be a cause of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Two splice-variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Oncoprotein; Transcription factor; Nuclear receptor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q21 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cell surface; cell soma; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; cytoplasm; dendrite; nuclear chromatin; nucleus; actin cytoskeleton Molecular Function:protein domain specific binding; protein kinase B binding; retinoic acid binding; zinc ion binding; chromatin DNA binding; translation repressor activity, nucleic acid binding; transcription coactivator activity; phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulator activity; drug binding; alpha-actinin binding; transcription factor binding; protein binding; enzyme binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein kinase A binding; steroid hormone receptor activity; mRNA 5'-UTR binding; retinoic acid receptor activity; transcription factor activity; transcription corepressor activity; receptor binding Biological Process: retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway; limb development; prostate gland development; negative regulation of translational initiation; regulation of myelination; estrogen receptor signaling pathway; glandular epithelial cell development; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation; regulation of synaptic plasticity; female pregnancy; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; signal transduction; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; response to estradiol stimulus; response to vitamin A; negative regulation of granulocyte differentiation; germ cell development; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production; negative regulation of cell proliferation; Sertoli cell fate commitment; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation; ureteric bud development; negative regulation of interferon-gamma production; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of interleukin-13 production; transmembrane transport; positive regulation of interleukin-5 production; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to retinoic acid; multicellular organism growth; positive regulation of cell cycle; positive regulation of binding; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; liver development; embryonic camera-type eye development; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; response to ethanol; response to cytokine stimulus; neural tube closure; gene expression; spermatogenesis; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; steroid hormone mediated signaling; positive regulation of neuron differentiation; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; apoptotic cell clearance; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene represents a nuclear retinoic acid receptor. The encoded protein, retinoic acid receptor alpha, regulates transcription in a ligand-dependent manner. This gene has been implicated in regulation of development, differentiation, apoptosis, granulopoeisis, and transcription of clock genes. Translocations between this locus and several other loci have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this locus.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P10276 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 133483 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5914 |
| NCBI Accession: | P10276.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P10276,P78456, Q13440, Q13441, Q96S41, Q9NQS0, B8Y636 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P10276 |
| Molecular Weight: | 39,700 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Retinoic acid receptor alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | retinoic acid receptor, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RARA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RAR; NR1B1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | retinoic acid receptor alpha; RAR-alpha; retinoic acid receptor, alpha polypeptide; nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1; retinoic acid nuclear receptor alpha variant 1; retinoic acid nuclear receptor alpha variant 2; nucleophosmin-retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein NPM-RAR long form |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Retinoic acid receptor alpha |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1 |
| Protein Family: | Retinoic acid receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RARA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RARA_HUMAN |