Description
| Product Name: | Recombinant Human Ephrin B Receptor 1/EphB1 (C-Fc) |
| Product Code: | RPES6387 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 Cells |
| Synonyms: | Ephrin Type-B Receptor 1, ELK, EPH Tyrosine Kinase 2, EPH-Like Kinase 6, EK6, hEK6, Neuronally-Expressed EPH, Related Tyrosine Kinase, NET, Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Receptor EPH-2, EPHB1, ELK, EPHT2, HEK6 |
| Mol Mass: | 85.6 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 85-100 kDa |
| Tag: | C-Fc |
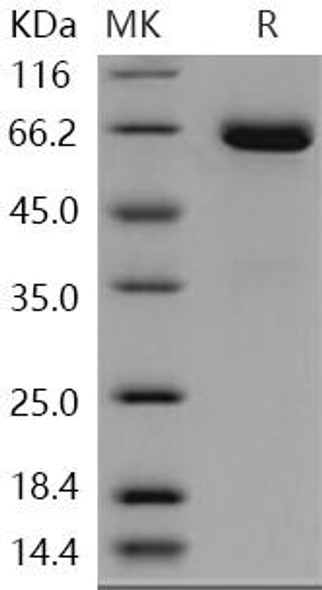
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Met18-Pro540 |
| Accession: | P54762 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the print |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | Ephrin Type-B Receptor 1 (EPHB1) is a single-pass type I membrane protein that belongs to the Ephrin-B family of receptor tyrosine kinases that is involved in embryonic nervous and vascular system development. EPHB1/EPHT2 contains two fibronectin type-III domains, one protein kinase domain and one SAM (sterile α motif) domain. EPHB1 could stimulate fibroblast motility on extracellular matrix in a kinase-dependent manner, which also correlated with its association with Grb7, an adaptor molecule implicated in the regulation of cell migration. It binds to ephrin-B1, ephrin-B2 and ephrin-B3. EPHB1 plays an important roles in diverse biological processes including nervous system development, angiogenesis, and neural synapsis formation and maturation and may be involved in cell-cell interactions in the nervous system. |