Description
| Product Name: | QuickStep Human IgA (Immunoglobulin A) ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | AEES00643 |
| Assay Type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96 Assays |
| Assay Time: | 2.5h |
| Reactivity: | Human |
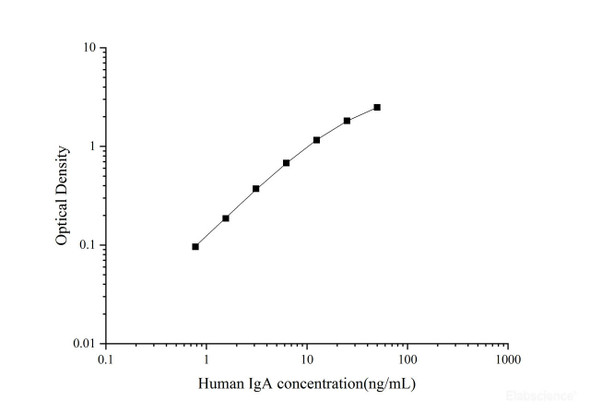
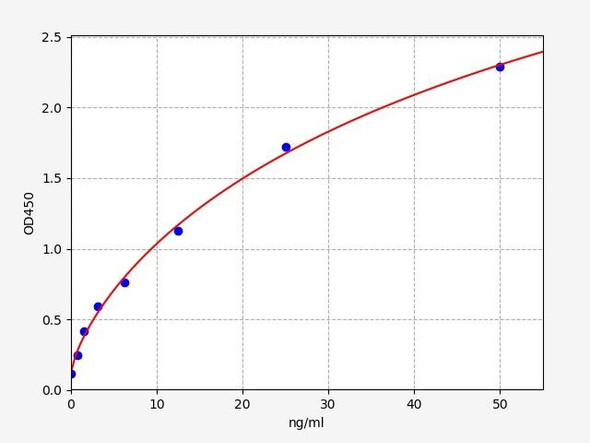
| Detection Range: | 6.25-400 ng/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 1.19 ng/mL |
| Sample Type & Sample Volume: | Serum, plasma, urine, saliva, 50μL |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Human IgA in samples. No significant or interference between Human IgA and analogues was observed. |
| Reproducibility: | Both intra-CV and inter-CV are < 10%. |
| Application: | This ELISA kit applies to the in vitro quantitative determination of Human IgA concentrations in serum, plasma, urine, saliva.Please consult technical support for the applicability if other biological fluids need to be tested. |
This ELISA kit uses the Sandwich-ELISA principle. The micro ELISA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human IgA. Samples (or Standards) and biotinylated detection antibody specific for Human IgA are added to the micro ELISA plate wells. Human IgA would combine with the specific antibody. Then Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added successively to each micro plate well and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Human IgA, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear blue in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of stop solution and the color turns yellow. The optical density (OD) is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450 ± 2 nm. The OD value is proportional to the concentration of Human IgA. You can calculate the concentration of Human IgA in the samples by comparing the OD of the samples to the standard curve.
| Kit Components: | An unopened kit can be stored at 2-8℃ for six months. After test, the unused wells and reagents should be stored according to the table below.
|
| 1. | Add 50μL standard or sample to the wells, immediately add 50μL Biotinylated Detection Ab working solution to each well. Incubate for 90 min at 37°C |
| 2. | Aspirate and wash the plate for 3 times |
| 3. | Add 100μL HRP conjugate working solution. Incubate for 30 min at 37°C. Aspirate and wash the plate for 5 times |
| 4. | Add 90μL Substrate Reagent. Incubate for 15 min at 37°C |
| 5. | Add 50μL Stop Solution |
| 6. | Read the plate at 450nm immediately. Calculation of the results |
First described in serum in 1953, IgA is the second dominant isotype in the blood circulation following IgG. It can be found in both monomeric and polymeric forms. Circulating IgA is in monomeric form, whereas secretory IgA, in the mucosal secretions of respiratory, intestinal, and genitourinary systems, is dimeric. In humans, there are two subclasses of IgA: IgA1 and IgA2, constant heavy chains of which are encoded by two separate α1 and α2 genes on chromosome 14 [1]. The main structural difference between them is that IgA2 has a shorter hinge region which may render this isotype more resistant to bacterial proteases in the lumen of gastrointestinal or respiratory systems. In the blood, IgA interacts with an Fc receptor called FcαRⅠ(or CD89), which is expressed on immune effector cells, to initiate inflammatory reactions[2]. Ligation of FcαRⅠ by IgA containing immune complexes causes antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), degranulation of eosinophils and basophils, phagocytosis by monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, and triggering of respiratory burst activity by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. IgA nephropathy is caused by IgA deposits in the kidneys, it is not yet known why IgA deposits occur in this chronic disease. Some theories suggest an abnormality of the immune system results in these deposits.