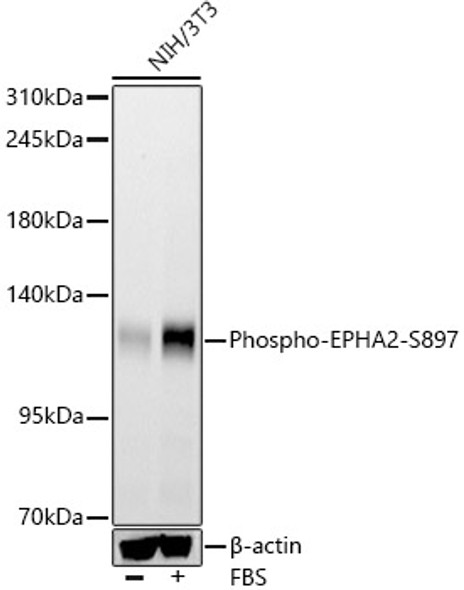
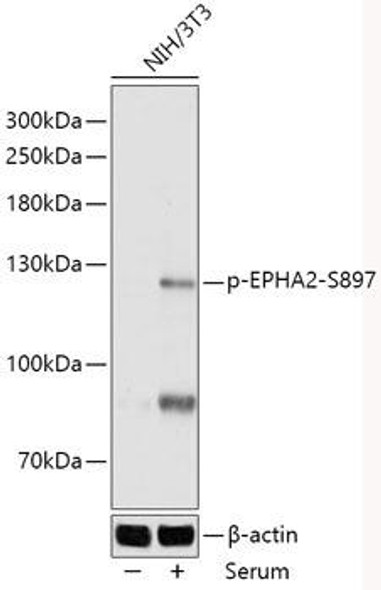
Description
| Antibody Name: | Phospho-EPHA2/EPHA5 (Tyr594) Antibody (PACO24176) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO24176 |
| Size: | 100ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:10000, WB:1:500-1:1000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of tyrosine 594 (H-T-Y(p)-E-D) derived from Human EPHA2/5. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy using non-phosphopeptide. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
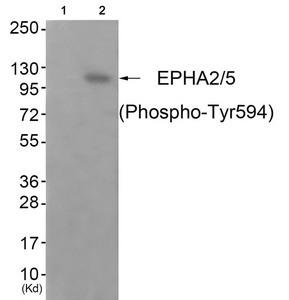 | Western blot analysis of extracts from JK cells (Lane 2), using EPHA2/5 (Phospho-Tyr594) Antibody. The lane on the left is treated with antigen-specific peptide. |
| Background: | Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously membrane-bound ephrin-A family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Activated by the ligand ephrin-A1/EFNA1 regulates migration, integrin-mediated adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of cells. Regulates cell adhesion and differentiation through DSG1/desmoglein-1 and inhibition of the ERK1/ERK2 (MAPK3/MAPK1, respectively) signaling pathway. |
| Synonyms: | ARCC2; ECK; EPHA2; |
| UniProt Protein Function: | EphA2: a receptor tyrosine kinase. Receptor for members of the ephrin-A family. Binds to ephrin-A1, -A3, -A4 AND -A5. The Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family, the largest in the tyrosine kinase group, has fourteen members. They bind membrane-anchored ligands, ephrins, at sites of cell-cell contact, regulating the repulsion and adhesion of cells that underlie the establishment, maintenance, and remodeling of patterns of cellular organization. Eph signals are particularly important in regulating cell adhesion and cell migration during development, axon guidance, homeostasis and disease. EphA receptors bind to GPI-anchored ephrin-A ligands, while EphB receptors bind to ephrin-B proteins that have a transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain. Interactions between EphB receptor kinases and ephrin-B proteins transduce signals bidirectionally, signaling to both interacting cell types. Eph receptors and ephrins also regulate the adhesion of endothelial cells and are required for the remodeling of blood vessels. Overexpressed in many cancers including aggressive ovarian, cervical and breast carcinomas, and lung cancer. Expression correlates with degree of angiogenesis, metastasis and xenograft tumor growth. Soluble receptor inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in mice. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, TK; Membrane protein, integral; Protein kinase, tyrosine (receptor); Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.10.1; TK group; Eph family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p36 Cellular Component: cell surface; focal adhesion; integral to plasma membrane; intracellular; plasma membrane Molecular Function:ATP binding; ephrin receptor activity; protein binding; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity Biological Process: angiogenesis; axial mesoderm formation; axon guidance; bone remodeling; cell adhesion; cell migration; DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in induction of apoptosis; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; keratinocyte differentiation; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation; multicellular organismal development; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; neural tube development; notochord cell development; notochord formation; osteoblast differentiation; osteoclast differentiation; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; protein kinase B signaling cascade; regulation of angiogenesis; regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin; skeletal development; vasculogenesis; viral reproduction Disease: Cataract 6, Multiple Types |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. This gene encodes a protein that binds ephrin-A ligands. Mutations in this gene are the cause of certain genetically-related cataract disorders.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P29317 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 229462861 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1969 |
| NCBI Accession: | P29317.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P29317,Q8N3Z2, B5A968, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P29317 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | EPH receptor A2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EPHA2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ECK; CTPA; ARCC2; CTPP1; CTRCT6 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Epithelial cell kinase; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor ECK |
| Protein Family: | Ephrin type-A receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EPHA2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EPHA2_HUMAN |