Mouse Cell Signalling ELISA Kits 2
Mouse TNF- alpha (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) CLIA Kit (MOES00046)
- SKU:
- MOES00046
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 7.5pg/mL
- Range:
- 12.5-800pg/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- DIF, TNF-alpha, TNFA, TNFSF2
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 12.50-800 pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 7.50 pg/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Mouse TNF- alpha in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Mouse TNF- alpha and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Mouse TNF- alpha. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Mouse TNF- alpha and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Mouse TNF- alpha, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Mouse TNF- alpha. The concentration of Mouse TNF- alpha in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | TNF-a: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. It is mainly secreted by macrophages and can induce cell death of certain tumor cell lines. It is potent pyrogen causing fever by direct action or by stimulation of interleukin-1 secretion and is implicated in the induction of cachexia, Under certain conditions it can stimulate cell proliferation and induce cell differentiation. Homotrimer. Interacts with SPPL2B. Belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, integral; Apoptosis; Cytokine Cellular Component: extracellular space; cell surface; integral to plasma membrane; extracellular region; integral to membrane; lipid raft; secretory granule; recycling endosome; membrane; plasma membrane; intracellular; phagocytic cup; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; protease binding; cytokine activity; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding Biological Process: positive regulation of JNK activity; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; positive regulation of NFAT protein import into nucleus; activation of MAPK activity; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation; positive regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; multicellular organismal development; response to glucocorticoid stimulus; positive regulation of caspase activity; positive regulation of NF-kappaB import into nucleus; osteoclast differentiation; positive regulation of translational initiation by iron; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway; cellular extravasation; positive regulation of phagocytosis; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production; JNK cascade; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation; positive regulation of action potential; regulation of immunoglobulin secretion; negative regulation of protein complex disassembly; positive regulation of cytokine production; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of mitosis; response to virus; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production; positive regulation of interleukin-8 biosynthetic process; glucose metabolic process; positive regulation of chemokine production; negative regulation of cytokine secretion during immune response; positive regulation of protein transport; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain; cell activation; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium; organ morphogenesis; induction of apoptosis via death domain receptors; DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in induction of apoptosis; defense response to bacterium; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of L-glutamate transport; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; leukocyte migration; sequestering of triacylglycerol; apoptosis; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of JNK cascade; defense response; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production; signal transduction; chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus; positive regulation of synaptic transmission; positive regulation of hair follicle development; negative regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of protein secretion; regulation of osteoclast differentiation; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process; positive regulation of neuron apoptosis; positive regulation of cell proliferation; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; protein kinase B signaling cascade; positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; inflammatory response; caspase activation; positive regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin; regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein complex disassembly; transformed cell apoptosis; calcium-mediated signaling; MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; humoral immune response; regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; cell proliferation; positive regulation of interferon-gamma production; negative regulation of glucose import; positive regulation of programmed cell death; positive regulation of chemokine biosynthetic process; positive regulation of protein complex assembly; negative regulation of viral genome replication; protein import into nucleus, translocation; positive regulation of protein kinase activity; activation of MAPKKK activity; positive regulation of fever; immune response; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; receptor biosynthetic process; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation; leukocyte tethering or rolling; regulation of insulin secretion; positive regulation of cytokine secretion; positive regulation of inflammatory response |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a multifunctional proinflammatory cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. Members of this family are classified based on primary sequence, function, and structure. This protein is synthesized as a type-II transmembrane protein and is reported to be cleaved into products that exert distinct biological functions. It plays an important role in the innate immune response as well as regulating homeostasis but is also implicated in diseases of chronic inflammation. In mouse deficiency of this gene is associated with defects in response to bacterial infection, with defects in forming organized follicular dendritic cell networks and germinal centers, and with a lack of primary B cell follicles. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | P06804 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 135935 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 21926 |
| NCBI Accession: | P06804. 2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P06804,O35853, Q62326, Q91VF3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P06804 |
| Molecular Weight: | 25,896 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Tumor necrosis factor |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | tumor necrosis factor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Tnf |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DIF; Tnfa; TNF-a; TNFSF2; Tnfsf1a; TNFalpha; TNF-alpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | tumor necrosis factor; cachectin; tumor necrosis factor-alpha; tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Tumor necrosis factor |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cachectin; TNF-alpha; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 2; TNF-a |
| Protein Family: | Tumor necrosis factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Tnf |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TNFA_MOUSE |
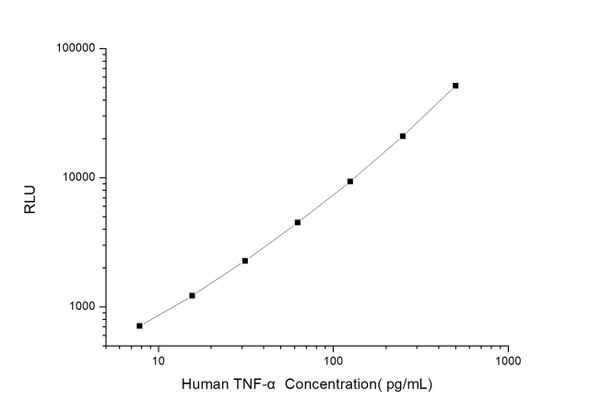
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 800 | 52589 52695 | 52642 | 52616 |
| 400 | 19695 23773 | 21734 | 21708 |
| 200 | 9903 9513 | 9708 | 9682 |
| 100 | 4223 4881 | 4552 | 4526 |
| 50 | 2308 2068 | 2188 | 2162 |
| 25 | 1106 1014 | 1060 | 1034 |
| 12.50 | 474 544 | 509 | 483 |
| 0 | 25 27 | 26 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse TNF- alpha were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse TNF- alpha were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 42.22 | 117.24 | 278.12 | 41.21 | 125.30 | 276.40 |
| Standard deviation | 5.19 | 11.06 | 27.45 | 4.52 | 11.16 | 26.70 |
| C V (%) | 12.29 | 9.43 | 9.87 | 10.97 | 8.91 | 9.66 |
Recovery
The recovery of Mouse TNF- alpha spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 96-112 | 103 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 88-100 | 93 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 86-98 | 93 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Mouse TNF- alpha and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 101-119 | 98-115 | 96-114 |
| Average (%) | 109 | 106 | 104 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 88-104 | 93-105 | 92-103 |
| Average (%) | 95 | 100 | 97 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 99-113 | 89-102 | 86-100 |
| Average (%) | 105 | 95 | 92 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 97-112 | 90-102 | 94-112 |
| Average (%) | 102 | 97 | 102 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100 µL of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100 µL of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100 µL of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37 °C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100 µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37 °C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350 µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100 µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37 °C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100 µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37 °C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.