Cytokines Recombinant Proteins
Mouse SHH Recombinant Protein (RPPB0905)
- SKU:
- RPPB0905
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Mouse
- Uniprot:
- Q62226
- Research Area:
- Cytokines
Description
| Product Name: | Mouse SHH Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0905 |
| Size: | 25µg |
| Species: | Mouse |
| Target: | SHH |
| Synonyms: | SHH, HHG-1, HHG1, Sonic hedgehog protein, TPT, HLP3, HPE3, SMMCI, TPTPS, MCOPCB5. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | SHH Mouse His Tag solution containing 20mM Trsi HCL pH-8, 1mM DTT, and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time.�For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).�Please prevent freeze thaw cycles. |
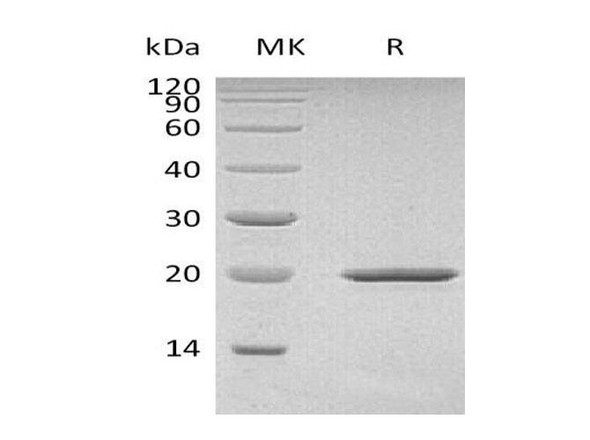
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MCGPGRGFGK RRHPKKLTPL AYKQFIPNVA EKTLGASGRY EGKITRNSER FKELTPNYNP DIIFKDEENT GADRLMTQRC KDKLNALAIS VMNQWPGVKL RVTEGWDEDG HHSEESLHYE GRAVDITTSD RDRSKYGMLA RLAVEAGFDW VYYESKAHIH CSVKAENSVA AKSGGLEHHH HHH |
Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog is part of a small group of secreted proteins that are vital for development in both vertebrates and invertebrates. 3 mammalian hedgehog genes (sonic, desert, Indian) share about 60% homology. The Human Sonic Hedgehog is 99% homologous to the mouse gene. Sonic HedgeHog is a protein that is vital in guding the early embryo. It has been associated as the major inductive signal in patterning of the ventral neural tube, the anterior-posterior limb axis, and the ventral somites. Sonic HedgeHog binds to the patched receptor, which functions in association with smoothened, to activate the transcription of target genes. In the absence of sonic HedgeHog, patched receptor represses the constitutive signaling activity of smoothened. Sonic HedgeHog also regulates another factor, the gli oncogene. Sonic HedgeHog intercellular signal is essential for a various patterning events during development: signal produced by the notochord that induces ventral cell fate in the neural tube and somites, and the polarizing signal for patterning of the anterior-posterior axis of the developing limb bud. Sonic HedgeHog exhibits both floor plate- and motor neuron-inducing activity. Mutations in a long-range Sonic HedgeHog enhancer located in an intron of the limb region 1 gene result in preaxial polydactyly.
SHH Mouse Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated,polypeptide chain containing 183 amino acids (25-198 a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 20.8 kDa. SHH protein is fused to a 8 amino acid His-Tag at C-terminus and purified by standard chromatography.
| UniProt Protein Function: | SHH: Binds to the patched (PTC) receptor, which functions in association with smoothened (SMO), to activate the transcription of target genes. In the absence of SHH, PTC represses the constitutive signaling activity of SMO. Also regulates another target, the gli oncogene. Intercellular signal essential for a variety of patterning events during development: signal produced by the notochord that induces ventral cell fate in the neural tube and somites, and the polarizing signal for patterning of the anterior-posterior axis of the developing limb bud. Displays both floor plate- and motor neuron-inducing activity. The threshold concentration of N-product required for motor neuron induction is 5-fold lower than that required for floor plate induction. Interacts with HHATL/GUP1 which negatively regulates HHAT-mediated palmitoylation of the SHH N-terminus. N-product is active as a multimer. Expressed in fetal intestine, liver, lung, and kidney. Not expressed in adult tissues. Belongs to the hedgehog family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oncoprotein; Cell development/differentiation; Cell cycle regulation; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Cellular Component: axon; cell soma; cell surface; dendrite; endoplasmic reticulum; extracellular space; Golgi apparatus; lipid raft; membrane; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; transport vesicle Molecular Function:calcium ion binding; glycoprotein binding; glycosaminoglycan binding; hydrolase activity; laminin-1 binding; patched binding; protein binding; zinc ion binding Biological Process: activation of hh target transcription factor; anatomical structure development; anatomical structure formation; androgen metabolic process; angiogenesis; anterior/posterior pattern formation; axon guidance; Bergmann glial cell differentiation; blood coagulation; branching morphogenesis of a tube; camera-type eye development; CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment; cell development; cell fate commitment; cell fate specification; cell proliferation; cell proliferation in the external granule layer; cell-cell signaling; central nervous system development; determination of left/right symmetry; developmental growth; digestive tract morphogenesis; dorsal/ventral pattern formation; dorsoventral neural tube patterning; ectoderm development; embryonic development; embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis; embryonic digit morphogenesis; embryonic foregut morphogenesis; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; embryonic limb morphogenesis; embryonic morphogenesis; embryonic organ development; embryonic skeletal development; endocytosis; establishment of cell polarity; forebrain development; forebrain regionalization; formation of anatomical boundary; granule cell precursor proliferation; gut mesoderm development; hair follicle development; hair follicle morphogenesis; heart development; heart looping; hindbrain development; hindgut morphogenesis; inner ear development; intermediate filament organization; kidney development; limb bud formation; limb development; lung development; lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation; male genitalia development; male genitalia morphogenesis; mesenchymal cell proliferation; metanephros development; midbrain development; myoblast differentiation; myotube differentiation; negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of cell differentiation; negative regulation of cell migration; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; negative regulation of protein catabolic process; negative regulation of T cell proliferation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of Wnt receptor signaling pathway; negative thymic T cell selection; neural crest cell migration; neural tube formation; neuroblast proliferation; neuron fate commitment; odontogenesis; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; oligodendrocyte development; oligodendrocyte differentiation; organ formation; osteoblast development; palate development; pancreas development; pattern specification process; patterning of blood vessels; polarity specification of anterior/posterior axis; positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation; positive regulation of cell differentiation; positive regulation of cell division; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of granule cell precursor proliferation; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in the thymus; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation; positive regulation of neuron differentiation; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus; positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of skeletal muscle development; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway; positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in the thymus; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of Wnt receptor signaling pathway; positive thymic T cell selection; prostate gland development; regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of gene expression; regulation of odontogenesis; regulation of proteolysis; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; respiratory tube development; response to axon injury; response to ethanol; signal transduction; skin development; smoothened signaling pathway; smoothened signaling pathway in regulation of granule cell precursor cell proliferation; spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning; spinal cord motor neuron differentiation; stem cell development; striated muscle cell differentiation; striated muscle development; T cell differentiation in the thymus; telencephalon regionalization; thalamus development; thymus development; thyroid gland development; tongue development; tongue morphogenesis; ureteric bud branching; vasculature development; vasculogenesis; ventral spinal cord interneuron specification; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin |
| UniProt Code: | Q62226 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6094284 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 20423 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q62226.2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q62226 |
| Molecular Weight: | 47,773 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Sonic hedgehog protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | sonic hedgehog |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Shh�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | Hx; Dsh; Hhg1; Hxl3; M100081; 9530036O11Rik�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | sonic hedgehog protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Sonic hedgehog protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | HHG-1 |
| Protein Family: | Sonic hedgehog protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Shh�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SHH_MOUSE |