Description
| Product Name: | Mouse Pentraxin-related Recombinant Protein PTX3 (N-6His) |
| Product Code: | RPES6675 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Mouse |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 Cells |
| Synonyms: | alpha-induced protein 5, pentaxin-related gene, rapidly induced by IL-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor, Pentaxin-related protein PTX3, Pentraxin 3, pentraxin 3, long, pentraxin-3, pentraxin-related gene, rapidly induced by IL-1 beta, pentraxin-related protein PTX3, PTX3, TNF alpha-induced protein 5, TNFAIP5, TSG14, TSG-14 |
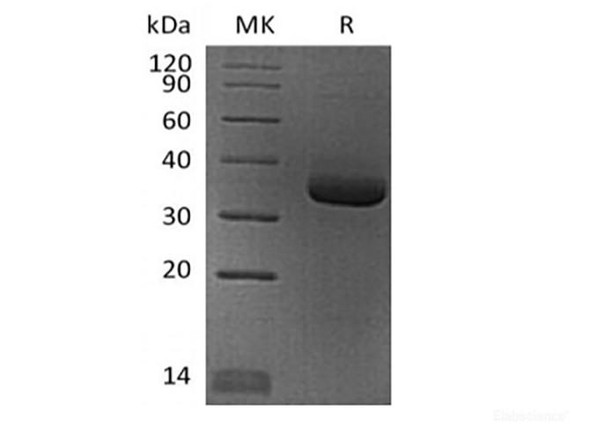
| Mol Mass: | 41 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 54 kDa |
| Tag: | N-6His |
| Purity: | > 90 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | His18-Ser381 |
| Accession: | P48759 |
| Storage: | Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as liquid. It is shipped at frozen temperature with blue ice/gel packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at < - 20°C. |
| Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Not Applicable |
| Background: | Pentraxin-related protein PTX3, also known as Tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 14 protein (TSG-14), belongs to the pentraxin family. PTX3 plays a role in the regulation of innate resistance to pathogens, inflammatory reactions, possibly clearance of self-components and female fertility. It’s subunit is a disulfide-linked homooctamer that binds to C1q. PTX3 concentration is elevated in the joint fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), indicating that PTX3 may be a potential mediator of immune response. PTX3 may also function in the regulation of the uptake and clearance of apoptotic cells by dendritic cells. An in vivo study showed that PTX3 transgenic mice are more resistant to sepsis and endotoxemia compared to wild-type during inflammatory injury. |