Human Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling ELISA Kits
Human UBA52 (Ubiquitin A 52 Residue Ribosomal Protein Fusion Product 1) CLIA Kit (HUES01222)
- SKU:
- HUES01222
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 37.5pg/mL
- Range:
- 62.5-4000pg/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 62.50-4000 pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 37.50 pg/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Human UBA52 in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Human UBA52 and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human UBA52. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Human UBA52 and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Human UBA52, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Human UBA52. The concentration of Human UBA52 in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | UBA52: the gene (UBA52) that encodes this protein is one of four that encode for ubiquitin: UBC, UBB, UBA52 and RPS27A. UBB and UBC genes code for a polyubiquitin precursor with exact head to tail repeats, the number of repeats differ between species and strains. UBA52 and RPS27A genes code for a single copy of ubiquitin fused to the ribosomal proteins L40 and S27a, respectively. The RPS27A gene product is cleaved into the following 2 chains: ubiquitin (amino acids 1-76) and the 60S ribosomal protein L40 (77 ? 128). Ubiquitin is a peptide 76 amino acids in length that can be covalently attached to target lysines either as a monomer or as a lysine-linked polymer. Hundreds of ubiquitin ligases and hydrolases have been identified, implicating ubiquitin as a major regulatory element in many crucial cellular systems. It can be covalently bound to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B. Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling. Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed. When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling. At the protein level, it is not possible to easily determine which of the four genes encoded a given ubiquitin chain. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ribosomal; Translation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19p13. 1-p12 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; lysosomal membrane; plasma membrane; ribosome; endosome membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; structural constituent of ribosome Biological Process: circadian rhythm; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; protein polyubiquitination; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; viral reproduction; activation of MAPK activity; positive regulation of apoptosis; stress-activated MAPK cascade; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; endosome transport; T cell receptor signaling pathway; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; regulation of apoptosis; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; translational initiation; JNK cascade; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I; viral transcription; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; regulation of interferon type I production; glycogen biosynthetic process; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; transcription, DNA-dependent; glucose metabolic process; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I, TAP-dependent; Notch receptor processing; virus assembly; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; translational elongation; carbohydrate metabolic process; viral protein processing; mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; negative regulation of interferon type I production; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; translation; apoptosis; pathogenesis; translational termination; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; viral infectious cycle; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; positive regulation of interferon type I production; transmembrane transport; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; Notch signaling pathway; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; protein modification process; DNA repair; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; cellular protein metabolic process; regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; gene expression; mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | Ubiquitin is a highly conserved nuclear and cytoplasmic protein that has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome. It is also involved in the maintenance of chromatin structure, the regulation of gene expression, and the stress response. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin moiety fused to an unrelated protein. This gene encodes a fusion protein consisting of ubiquitin at the N terminus and ribosomal protein L40 at the C terminus, a C-terminal extension protein (CEP). Multiple processed pseudogenes derived from this gene are present in the genome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P62987 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 302393718 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7311 |
| NCBI Accession: | P62987. 2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P62987,P02248, P02249, P02250, P14793, P62988, Q29120 Q6LBL4, Q6LDU5, Q8WYN8, Q91887, Q91888, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P62987 |
| Molecular Weight: | 14,728 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ubiquitin A-52 residue ribosomal protein fusion product 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | UBA52 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | L40; CEP52; RPL40; HUBCEP52 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40; ubiquitin-CEP52; ubiquitin-52 amino acid fusion protein; ubiquitin carboxyl extension protein 52 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | CEP52; Ubiquitin A-52 residue ribosomal protein fusion product 1Cleaved into the following 2 chains:Ubiquitin; 60S ribosomal protein L40 |
| Protein Family: | Ubiquitin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | UBA52 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RL40_HUMAN |
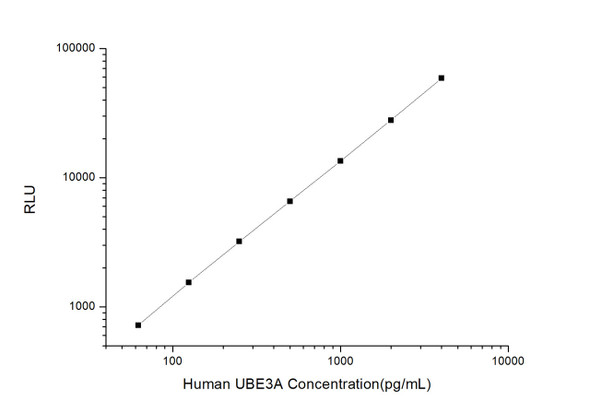
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 4000 | 53212 64950 | 59081 | 59046 |
| 2000 | 27523 28195 | 27859 | 27824 |
| 1000 | 13700 13268 | 13484 | 13449 |
| 500 | 6434 6776 | 6605 | 6570 |
| 250 | 3361 3125 | 3243 | 3208 |
| 125 | 1646 1516 | 1581 | 1546 |
| 62.50 | 733 777 | 755 | 720 |
| 0 | 34 36 | 35 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human UBA52 were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human UBA52 were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 206.43 | 617.17 | 1877.26 | 190.28 | 606.66 | 2035.73 |
| Standard deviation | 24.07 | 61.41 | 121.08 | 20.30 | 69.64 | 216.40 |
| C V (%) | 11.66 | 9.95 | 6.45 | 10.67 | 11.48 | 10.63 |
Recovery
The recovery of Human UBA52 spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 96-109 | 104 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 99-116 | 106 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 97-112 | 103 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Human UBA52 and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 95-107 | 101-113 | 90-103 |
| Average (%) | 102 | 107 | 96 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 96-110 | 88-98 | 96-109 |
| Average (%) | 103 | 93 | 104 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 98-114 | 93-106 | 88-103 |
| Average (%) | 105 | 99 | 96 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 97-113 | 92-104 | 89-99 |
| Average (%) | 104 | 99 | 94 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100 µL of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100 µL of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100 µL of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37 °C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100 µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37 °C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350 µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100 µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37 °C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100 µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37 °C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.