Description
| Product Name: | Human Transthyretin Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB4289 |
| Size: | 25µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | Transthyretin |
| Synonyms: | TTHY, TTR, ATTR, TBPA, Transthyretin, Prealbumin, PALB, HsT2651. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The Transthyertin protein solution contains 1x PBS, pH-7.4, and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
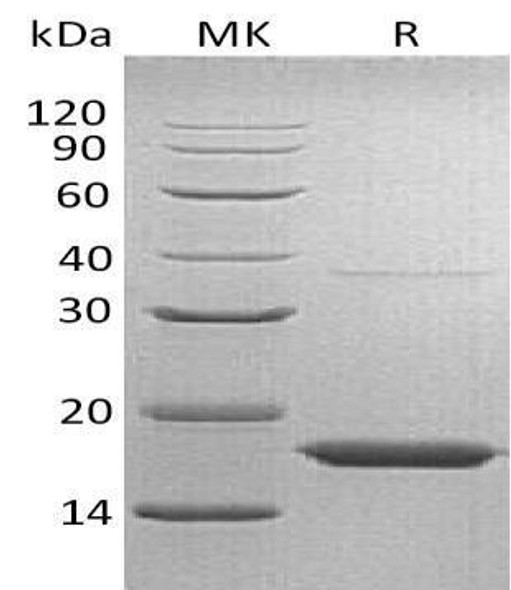
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGPTGTGESK CPLMVKVLDA VRGSPAINVA VHVFRKAADD TWEPFASGKT SESGELHGLT TEEEFVEGIY KVEIDTKSYW KALGISPFHEHAEVVFTAND SGPRRYTIAA LLSPYSYSTT AVVTNPKE |
Prealbumin is a thyroid hormone-binding protein that transports thyroxine from the bloodstream to the brain. Prealbumin is a carrier protein which transports thyroid hormones in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, and also transports retinol (vitamin A) in the plasma. Transthyretin consists of a tetramer of identical subunits and is dominantly produced in the liver. Mutations in Prealbumin are related to amyloid deposition, affecting predominantly peripheral nerve and/or the heart. The diseases caused by mutations include amyloidotic polyneuropathy, euthyroid hyperthyroxinaemia, amyloidotic vitreous opacities, cardiomyopathy, oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis, meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Prealbumin is an indicator of protein-energy malnutrition since it has a circulating half life of 2 days and reacts swiftly to changes in nutritional status.
Transthyertin Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 128 amino acids (21-147 a.a.) and having a molecular weight of 13.8kDa. The Transthyertin is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | TTR: Thyroid hormone-binding protein. Probably transports thyroxine from the bloodstream to the brain. Defects in TTR are the cause of amyloidosis transthyretin-related (AMYL-TTR). A hereditary generalized amyloidosis due to transthyretin amyloid deposition. Protein fibrils can form in different tissues leading to amyloid polyneuropathies, amyloidotic cardiomyopathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, systemic senile amyloidosis. The disease includes leptomeningeal amyloidosis that is characterized by primary involvement of the central nervous system. Neuropathologic examination shows amyloid in the walls of leptomeningeal vessels, in pia arachnoid, and subpial deposits. Some patients also develop vitreous amyloid deposition that leads to visual impairment (oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis). Clinical features include seizures, stroke-like episodes, dementia, psychomotor deterioration, variable amyloid deposition in the vitreous humor. Defects in TTR are a cause of hyperthyroxinemia dystransthyretinemic euthyroidal (HTDE). It is a condition characterized by elevation of total and free thyroxine in healthy, euthyroid persons without detectable binding protein abnormalities. Defects in TTR are a cause of carpal tunnel syndrome type 1 (CTS1). It is a condition characterized by entrapment of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Symptoms include burning pain and paresthesias involving the ventral surface of the hand and fingers which may radiate proximally. Impairment of sensation in the distribution of the median nerve and thenar muscle atrophy may occur. This condition may be associated with repetitive occupational trauma, wrist injuries, amyloid neuropathies, rheumatoid arthritis. Belongs to the transthyretin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 18q12.1 Cellular Component: extracellular space; protein complex; cytoplasm; extracellular region Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; protein heterodimerization activity; hormone activity Biological Process: phototransduction, visible light; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; retinol metabolic process; transport; retinoid metabolic process Disease: Hyperthyroxinemia, Dystransthyretinemic; Carpal Tunnel Syndrome; Amyloidosis, Hereditary, Transthyretin-related |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes transthyretin, one of the three prealbumins including alpha-1-antitrypsin, transthyretin and orosomucoid. Transthyretin is a carrier protein; it transports thyroid hormones in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, and also transports retinol (vitamin A) in the plasma. The protein consists of a tetramer of identical subunits. More than 80 different mutations in this gene have been reported; most mutations are related to amyloid deposition, affecting predominantly peripheral nerve and/or the heart, and a small portion of the gene mutations is non-amyloidogenic. The diseases caused by mutations include amyloidotic polyneuropathy, euthyroid hyperthyroxinaemia, amyloidotic vitreous opacities, cardiomyopathy, oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis, meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, etc. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P02766 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 136464 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7276 |
| NCBI Accession: | P02766.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P02766,Q549C7, Q6IB96, Q9UBZ6, Q9UCM9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P02766 |
| Molecular Weight: | 55,000 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transthyretin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | transthyretin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TTR�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CTS; CTS1; PALB; TBPA; HEL111; HsT2651�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transthyretin; ATTR; carpal tunnel syndrome 1; thyroxine-binding prealbumin; epididymis luminal protein 111; prealbumin, amyloidosis type I |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transthyretin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ATTR; Prealbumin; TBPA |
| Protein Family: | Transthyretin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TTR�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TTHY_HUMAN |