Human Cell Biology ELISA Kits 4
Human SPC (Pulmonary Surfactant Associated Protein C) CLIA Kit (HUES00725)
- SKU:
- HUES00725
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 0.56ng/mL
- Range:
- 0.94-60ng/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 0.94-60 ng/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 0.56 ng/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Human SPC in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Human SPC and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human SPC. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Human SPC and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Human SPC, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Human SPC. The concentration of Human SPC in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | SFTPC: Pulmonary surfactant associated proteins promote alveolar stability by lowering the surface tension at the air- liquid interface in the peripheral air spaces. Defects in SFTPC are the cause of pulmonary surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 2 (SMDP2); also called pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to surfactant protein C deficiency. A rare disease associated with progressive respiratory insufficiency and lung disease with a variable clinical course, due to impaired surfactant homeostasis. It is characterized by alveolar filling with floccular material that stains positive using the periodic acid-Schiff method and is derived from surfactant phospholipids and protein components. Excessive lipoproteins accumulation in the alveoli results in severe respiratory distress. Genetic variations in SFTPC are a cause of susceptibility to respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants (RDS); also known as RDS in prematurity. RDS is a lung disease affecting usually premature newborn infants. It is characterized by deficient gas exchange, diffuse atelectasis, high-permeability lung edema and fibrin-rich alveolar deposits called 'hyaline membranes'. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8p21 Cellular Component: multivesicular body; extracellular space Molecular Function:protein binding; protein homodimerization activity Biological Process: circadian rhythm; response to cAMP; response to hyperoxia; response to retinoic acid; response to glucocorticoid stimulus; response to glucose stimulus; response to lipopolysaccharide; respiratory gaseous exchange; protein homooligomerization; response to vitamin A Disease: Pulmonary Fibrosis, Idiopathic; Surfactant Metabolism Dysfunction, Pulmonary, 2 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the pulmonary-associated surfactant protein C (SPC), an extremely hydrophobic surfactant protein essential for lung function and homeostasis after birth. Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active lipoprotein complex composed of 90% lipids and 10% proteins which include plasma proteins and apolipoproteins SPA, SPB, SPC and SPD. The surfactant is secreted by the alveolar cells of the lung and maintains the stability of pulmonary tissue by reducing the surface tension of fluids that coat the lung. Multiple mutations in this gene have been identified, which cause pulmonary surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 2, also called pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to surfactant protein C deficiency, and are associated with interstitial lung disease in older infants, children, and adults. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P11686 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 131425 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6440 |
| NCBI Accession: | P11686. 2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P11686 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein C |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | surfactant protein C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SFTPC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SP-C; PSP-C; SFTP2; SMDP2; BRICD6 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | pulmonary surfactant-associated protein C |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Val); SP5 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SFTPC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PSPC_HUMAN |
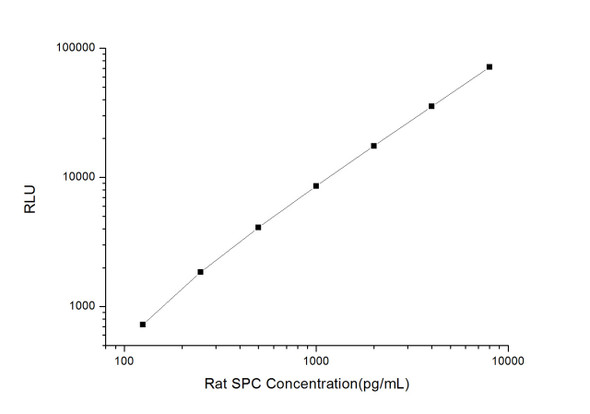
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (ng/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 60 | 37088 37238 | 37163 | 37138 |
| 30 | 15822 16136 | 15979 | 15954 |
| 15 | 7616 7126 | 7371 | 7346 |
| 7.5 | 3245 3881 | 3563 | 3538 |
| 3.75 | 1810 1756 | 1783 | 1758 |
| 1.88 | 947 901 | 924 | 899 |
| 0.94 | 491 513 | 502 | 477 |
| 0 | 25 25 | 25 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human SPC were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human SPC were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (ng/mL) | 3.21 | 7.45 | 20.26 | 3.05 | 7.39 | 18.94 |
| Standard deviation | 0.38 | 0.82 | 1.89 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 1.31 |
| C V (%) | 11.84 | 11.01 | 9.33 | 11.80 | 7.98 | 6.92 |
Recovery
The recovery of Human SPC spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 99-114 | 105 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 96-109 | 102 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 100-117 | 107 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Human SPC and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 93-106 | 89-101 | 97-112 |
| Average (%) | 98 | 96 | 103 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 98-111 | 96-111 | 86-99 |
| Average (%) | 105 | 104 | 91 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 96-111 | 90-103 | 86-99 |
| Average (%) | 103 | 97 | 92 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 95-108 | 97-113 | 98-110 |
| Average (%) | 103 | 105 | 105 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100µl of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100µl of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100µl of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37°C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.