Description
| Product Name: | Human SIGLEC2/CD22 Recombinant Protein (His Tag) |
| Product Code: | RPES5953 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 Cells |
| Synonyms: | B-cell receptor CD22, BL-CAM, B-lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule, CD22 antigenMGC130020, CD22 molecule, CD22, sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 2, Siglec-2, SIGLEC2FLJ22814, T-cell surface antigen Leu-14, SIGLEC-2, Siglec-2 |
| Mol Mass: | 76.2 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 100-140 kDa |
| Tag: | C-His |
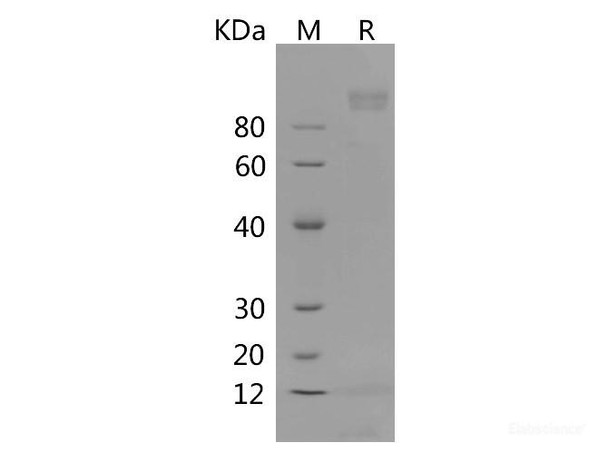
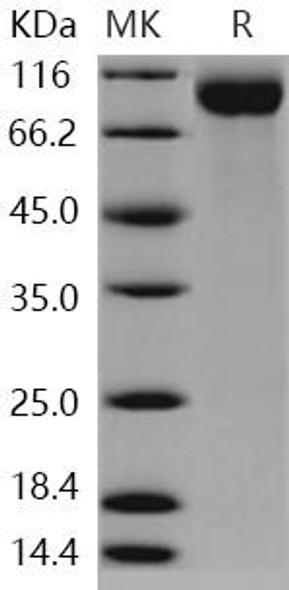
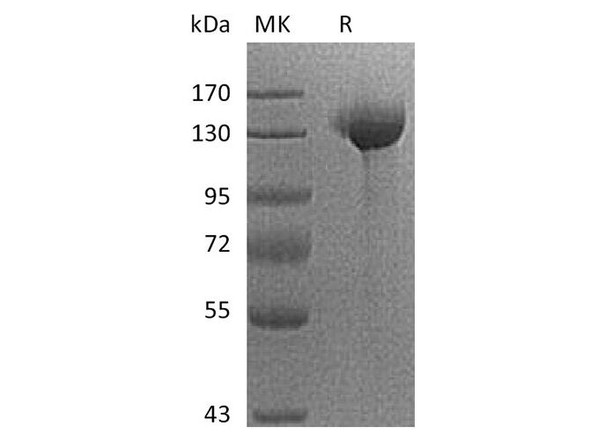
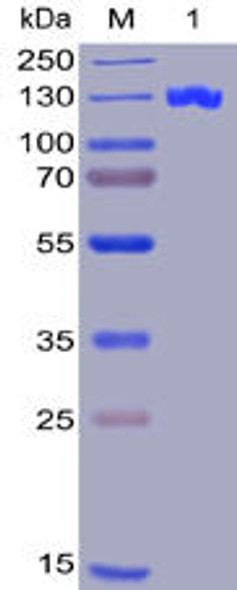
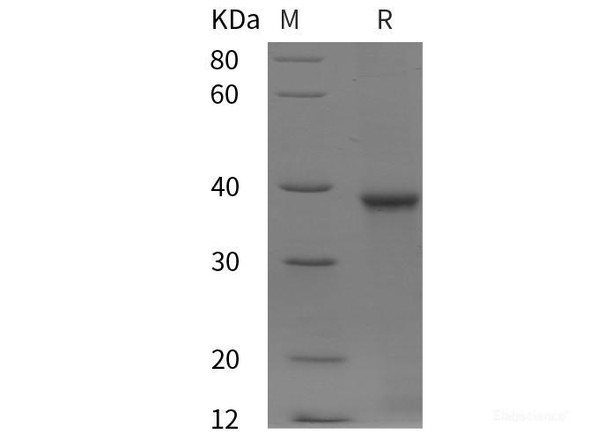
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Asp20-Arg687 |
| Accession: | P20273 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | Mediates B-cell B-cell interactions. May be involved in the localization of B-cells in lymphoid tissues. Binds sialylated glycoproteins; one of which is CD45. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site can be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. Upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the immune response seems to be involved in regulation of B-cell antigen receptor signaling. Plays a role in positive regulation through interaction with Src family tyrosine kinases and may also act as an inhibitory receptor by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatases via their SH2 domains that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. |