Human Cell Biology ELISA Kits 5
Human GJ beta1 (Gap Junction Protein Beta 1) CLIA Kit (HUES00847)
- SKU:
- HUES00847
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 37.5pg/mL
- Range:
- 62.5-4000pg/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 62.50-4000 pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 37.50 pg/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Human GJ beta1 in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Human GJ beta1 and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human GJ beta1. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Human GJ beta1 and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Human GJ beta1, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Human GJ beta1. The concentration of Human GJ beta1 in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | GJB1: One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell. Defects in GJB1 are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease X-linked type 1 (CMTX1); also designated CMT- X. CMTX1 is a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the most common inherited disorder of the peripheral nervous system. Charcot- Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies characterized by severely reduced motor nerve conduction velocities (NCVs) (less than 38m/s) and segmental demyelination and remyelination, and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies characterized by normal or mildly reduced NCVs and chronic axonal degeneration and regeneration on nerve biopsy. CMTX1 has both demyelinating and axonal features. Central nervous system involvement may occur. Defects in GJB1 may contribute to the phenotype of Dejerine-Sottas syndrome (DSS); also known as Dejerine-Sottas neuropathy (DSN) or hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy III (HMSN3). DSS is a severe degenerating neuropathy of the demyelinating Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease category, with onset by age 2 years. DSS is characterized by motor and sensory neuropathy with very slow nerve conduction velocities, increased cerebrospinal fluid protein concentrations, hypertrophic nerve changes, delayed age of walking as well as areflexia. There are both autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive forms of Dejerine- Sottas syndrome. Belongs to the connexin family. Beta-type (group I) subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral; Channel, misc. Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq13. 1 Cellular Component: connexon complex; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; integral to membrane Molecular Function:protein homodimerization activity Biological Process: nervous system development; gap junction assembly; cell-cell signaling; transport Disease: Charcot-marie-tooth Disease, X-linked Dominant, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junction proteins are membrane-spanning proteins that assemble to form gap junction channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene cause X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, an inherited peripheral neuropathy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P08034 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 117688 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2705 |
| NCBI Accession: | P08034. 1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P08034,Q5U0S4, B2R8R2, D3DVV2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P08034 |
| Molecular Weight: | 32,025 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Gap junction beta-1 protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | gap junction protein, beta 1, 32kDa |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GJB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CMTX; CX32; CMTX1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | gap junction beta-1 protein; connexin 32; connexin-32; GAP junction 28 kDa liver protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Gap junction beta-1 protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Connexin-32; Cx32; GAP junction 28 kDa liver protein |
| Protein Family: | Gap junction beta-1 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GJB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CXB1_HUMAN |
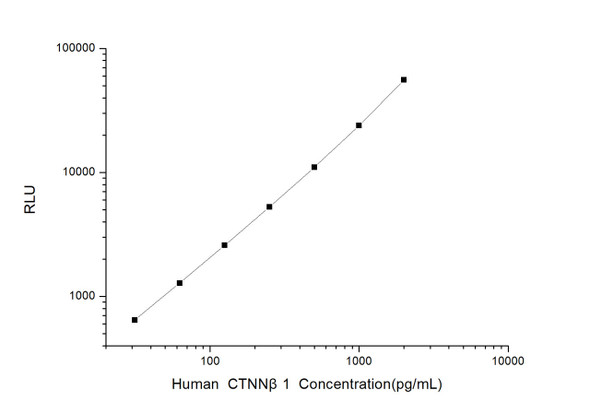
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 4000 | 57605 60557 | 59081 | 59046 |
| 2000 | 26234 29484 | 27859 | 27824 |
| 1000 | 14598 12370 | 13484 | 13449 |
| 500 | 6037 7173 | 6605 | 6570 |
| 250 | 3443 3043 | 3243 | 3208 |
| 125 | 1691 1471 | 1581 | 1546 |
| 62.50 | 708 802 | 755 | 720 |
| 0 | 33 37 | 35 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human GJ beta1 were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human GJ beta1 were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 196.14 | 533.30 | 1372.83 | 192.24 | 570.82 | 1434.80 |
| Standard deviation | 20.67 | 45.70 | 100.90 | 15.96 | 66.61 | 118.37 |
| C V (%) | 10.54 | 8.57 | 7.35 | 8.30 | 11.67 | 8.25 |
Recovery
The recovery of Human GJ beta1 spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 93-108 | 99 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 91-101 | 96 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 88-102 | 94 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Human GJ beta1 and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 98-115 | 90-103 | 87-100 |
| Average (%) | 106 | 97 | 93 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 90-103 | 101-114 | 91-103 |
| Average (%) | 97 | 108 | 97 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 101-117 | 102-114 | 95-106 |
| Average (%) | 109 | 108 | 101 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 94-104 | 93-109 | 96-110 |
| Average (%) | 99 | 100 | 103 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100µl of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100µl of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100µl of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37°C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.