Description
| Product Name: | Human FGF23 Recombinant Protein (SUMO,His tag) |
| Product Code: | RPES5455 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | E.coli |
| Synonyms: | FGF-23, Fgf23, ADHR, FGF23, fibroblast growth factor 23, HPDR2, HYPF, phosphatonin, PHPTC |
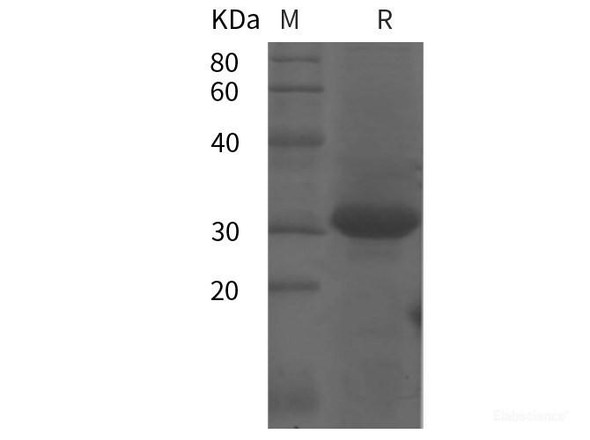
| Mol Mass: | 31.22 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 32 kDa |
| Tag: | N-SUMO-His |
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | Please contact us for more information. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Ala 24-Val 126 |
| Accession: | Q9GZV9 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF‑23) is a 30‑32 kDa member of the FGF family, within a subfamily that also includes FGF‑19 and FGF‑21. FGF proteins contain a 120 amino acid (aa) core FGF domain that exhibits a beta ‑trefoil structure. FGF‑19 subfamily members are highly diffusible molecules owing to their poor ECM/heparin sulfate binding and plasma‑stabilizing intramolecular folds. FGF‑23 is produced by osteocytes and osteoblasts in response to high circulating phosphate levels, elevated parathyroid hormone, and circulatory volume loading. It functions as an endocrine phosphatonin by suppressing circulating phosphate levels . FGF‑23 interaction with renal proximal tubular epithelium decreases the renal resorption of phosphate by down‑regulating phosphate transporters and by suppressing vitamin D production. It also decreases the intestinal absorption of phosphate. |