Growth Factors & Cytokines Recombinant Proteins
Human FGF 2 Recombinant Protein (RPPB0209)
- SKU:
- RPPB0209
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P09038
- Research Area:
- Growth Factors & Cytokines
Description
| Product Name: | Human FGF 2 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0209 |
| Size: | 50µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | FGF 2 |
| Synonyms: | Prostatropin, HBGH-2, HBGF-2, FGF-2, FGF-b, Fibroblast growth factor 2, Basic fibroblast growth factor, Heparin-binding growth factor 2. |
| Source: | Rice Grain (Oryza Sativa) |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | FGF-b was lyophilized from a concentrated solution without any additives. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Fibroblast Growth Factor Basic in sterile 18M?-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution FGF-b should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
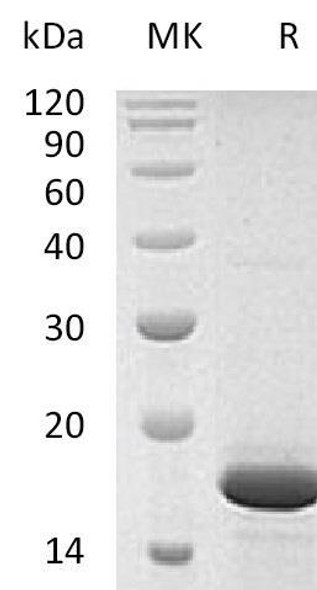
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Biological Activity: | The ED50, as calculated by the dose-dependent proliferation of Balb/c 3T3 cells expressing FGF receptors is <1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of >1 x106 Units/mg. |
Basic fibroblast growth factor is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein functions as a modifier of endothelial cell migration and proliferation, as well as an angiogenic factor. It acts as a mitogen for a variety of mesoderm- and neuroectoderm-derived cells in vitro, thus is thought to be involved in organogenesis. Three alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been described. The heparin-binding growth factors are angiogenic agents in vivo and are potent mitogens for a variety of cell types in vitro. There are differences in the tissue distribution and concentration of these 2 growth factors.
FGF-2 Human Recombinant produced in rice is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 146 amino acids and having a molecular mass of ~17kDa.The FGF-b protein is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | FGF2: Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, angiogenesis, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as potent mitogen in vitro. Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Affinity between fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors is increased by heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans that function as coreceptors. Interacts with CSPG4, FGFBP1 and TEC. Found in a complex with FGFBP1, FGF1 and FGF2. Expressed in granulosa and cumulus cells. Expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not in non- cancerous liver tissue. Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative initiation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Activator; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q26 Cellular Component: extracellular space; extracellular region; nucleus Molecular Function:heparin binding; protein binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity; growth factor activity; cytokine activity; chemoattractant activity; fibroblast growth factor receptor binding Biological Process: extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; wound healing; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; somatic stem cell maintenance; activation of MAPK activity; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; chemotaxis; signal transduction; hyaluronan catabolic process; growth factor dependent regulation of satellite cell proliferation; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; positive chemotaxis; positive regulation of cell proliferation; embryonic morphogenesis; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; nervous system development; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cell fate specification; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; regulation of angiogenesis; positive regulation of angiogenesis; organ morphogenesis; cell migration during sprouting angiogenesis; ureteric bud branching; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol; positive regulation of cell division; Ras protein signal transduction; insulin receptor signaling pathway; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process; innate immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; inositol phosphate biosynthetic process |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members bind heparin and possess broad mitogenic and angiogenic activities. This protein has been implicated in diverse biological processes, such as limb and nervous system development, wound healing, and tumor growth. The mRNA for this gene contains multiple polyadenylation sites, and is alternatively translated from non-AUG (CUG) and AUG initiation codons, resulting in five different isoforms with distinct properties. The CUG-initiated isoforms are localized in the nucleus and are responsible for the intracrine effect, whereas, the AUG-initiated form is mostly cytosolic and is responsible for the paracrine and autocrine effects of this FGF. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P09038 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 261260095 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2247 |
| NCBI Accession: | P09038.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P09038,O00527, P78443, Q16443, Q5PY50, Q7KZ11, Q7KZ72 Q9UC54, Q9UCS5, Q9UCS6, A4LBB8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P09038 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FGF2�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BFGF; FGFB; FGF-2; HBGF-2�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fibroblast growth factor 2; prostatropin; heparin-binding growth factor 2; basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Basic fibroblast growth factor; bFGF; Heparin-binding growth factor 2; HBGF-2 |
| Protein Family: | Fibroblast growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FGF2�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FGF2_HUMAN |