Description
| Product Name: | Human FABP5 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3499 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | FABP5 |
| Synonyms: | Fatty acid-binding protein epidermal, E-FABP, Fatty acid-binding protein 5, Psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding protein homolog, PA-FABP, FABP5, EFABP, PAFABP. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | Sterile filtered and lyophilized from 0.5 mg/ml in phosphate buffered saline. |
| Solubility: | Add 0.2 ml of dH20 and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. |
| Stability: | Store lyophilized protein at -20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reconstituted protein can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show any change after two weeks at 4°C. |
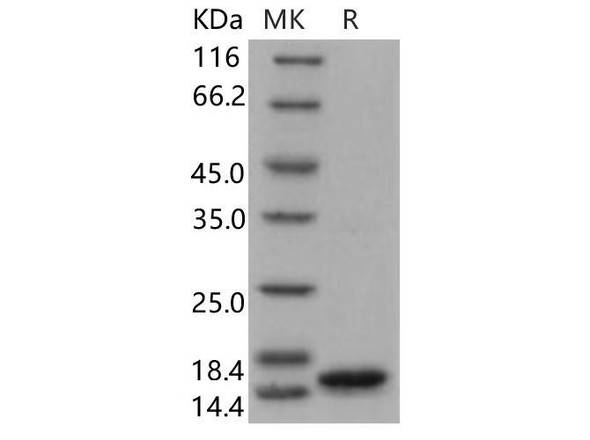
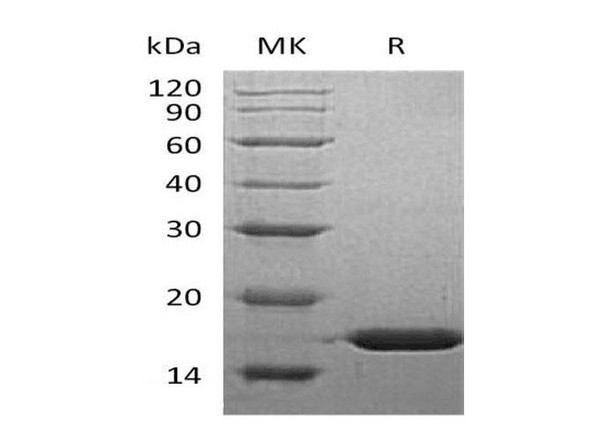
| Purity: | Greater than 90% as determined by SDS PAGE. |
Human Fatty Epidermal Acid Binding Protein FABP also called FABP-5 is a 15 kD member of the intracellular fatty acid binding protein (FABP) family, which is known for the ability to bind fatty acids and related compounds ( bile acids or retinoids). In an internal cavity. The fatty acid binding proteins aP2 (fatty acid binding protein [FABP]-4) and mal1 (EFABP) are closely related and both are expressed in adipocytes.�
Recombinant Human Epidermal Fatty Acid Binding Protein (FABP-5) is a monomeric, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 135 amino acids and having a total molecular mass of 15200 Daltons.
| UniProt Protein Function: | FABP5: High specificity for fatty acids. Highest affinity for C18 chain length. Decreasing the chain length or introducing double bonds reduces the affinity. May be involved in keratinocyte differentiation. Belongs to the calycin superfamily. Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q21.13 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cytoplasm; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; transporter activity; fatty acid binding; lipid binding Biological Process: epidermis development; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process; glucose metabolic process; lipid metabolic process; glucose transport |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the fatty acid binding protein found in epidermal cells, and was first identified as being upregulated in psoriasis tissue. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. FABPs may play roles in fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. Polymorphisms in this gene are associated with type 2 diabetes. The human genome contains many pseudogenes similar to this locus.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q01469 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 232081 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2171 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q01469.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q01469,B2R4K0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q01469 |
| Molecular Weight: | 15,164 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fatty acid binding protein 5 (psoriasis-associated) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FABP5�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | EFABP; KFABP; E-FABP; PAFABP; PA-FABP�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal; epidermal-type fatty acid-binding protein; psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding protein homolog |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Epidermal-type fatty acid-binding protein; E-FABP; Fatty acid-binding protein 5; Psoriasis-associated fatty acid-binding protein homolog |
| Protein Family: | Fatty acid-binding protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FABP5�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FABP5_HUMAN |