Description
| Product Name: | Human EFNA5 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3410 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | EFNA5 |
| Synonyms: | EFNA5, AF1, EFL5, EPLG7, GLC1M, LERK7, RAGS, Ephrin-A5,AL-1, EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 7. |
| Source: | Sf9 Insect cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | EFNA5 protein solution (0.5mg/ml) contains PhosphateBuffered Saline (pH 7.4) and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time.�For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).�Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
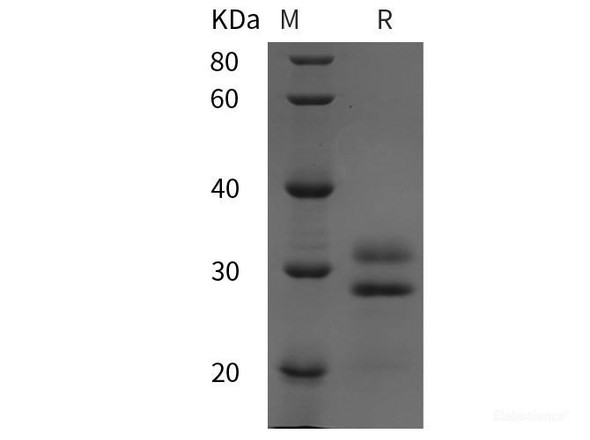
| Purity: | Greaterthan 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | QDPGSKAVADRYAVYWNSSN PRFQRGDYHI DVCINDYLDV FCPHYEDSVP EDKTERYVLY MVNFDGYSAC DHTSKGFKRWECNRPHSPNG PLKFSEKFQL FTPFSLGFEF RPGREYFYIS SAIPDNGRRS CLKLKVFVRP TNSCMKTIGVHDRVFDVNDK VENSLEPADD TVHESAEPSR GENLEPKSCD KTHTCPPCPA PELLGGPSVF LFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTC VVVDVSHEDP EVKFNWYVDG VEVHNAKTKP REEQYNSTYR VVSVLTVLHQ DWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAP IEKTISKAKG QPREPQVYTL PPSRDELTKN QVSLTCLVKG FYPSDIAVEW ESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSD GSFFLYSKLT VDKSRWQQGN VFSCSVMHEA LHNHYTQKSL SLSPGKHHHH HH |
Ephrin A5 (EFNA5) is a partof the ephrin ligand family which binds the members of ephrin receptorsubfamily of tyrosine kinases and stimulatescontact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. EFNA5is mainly expressed in human adult brain, heart, spleen, andovary and human fetal brain, lung, and kidney.
EFNA5 produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylatedpolypeptide chain containing 422 amino acids (21-203 a.a.) and having amolecular mass of 48.1kDa. (Migrates at 40-57kDa on SDS-PAGE under reducingconditions).EFNA5 is expressed with a 239 amino acid hIgG-His-tag atC-Terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | EFNA5: Cell surface GPI-bound ligand for Eph receptors, a family of receptor tyrosine kinases which are crucial for migration, repulsion and adhesion during neuronal, vascular and epithelial development. Binds promiscuously Eph receptors residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Induces compartmentalized signaling within a caveolae-like membrane microdomain when bound to the extracellular domain of its cognate receptor. This signaling event requires the activity of the Fyn tyrosine kinase. Activates the EPHA3 receptor to regulate cell-cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. With the receptor EPHA2 may regulate lens fiber cells shape and interactions and be important for lens transparency maintenance. May function actively to stimulate axon fasciculation. The interaction of EFNA5 with EPHA5 also mediates communication between pancreatic islet cells to regulate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Cognate/functional ligand for EPHA7, their interaction regulates brain development modulating cell-cell adhesion and repulsion. Belongs to the ephrin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell development/differentiation; Ligand, receptor tyrosine kinase; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, GPI anchor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q21 Cellular Component: anchored to external side of plasma membrane; extracellular region; plasma membrane; caveola Molecular Function:ephrin receptor binding; chemorepellent activity Biological Process: nervous system development; axon guidance; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; regulation of cell-cell adhesion; apoptosis; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of focal adhesion formation; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; negative chemotaxis; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance |
| NCBI Summary: | Ephrin-A5, a member of the ephrin gene family, prevents axon bundling in cocultures of cortical neurons with astrocytes, a model of late stage nervous system development and differentiation. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. EPH receptors typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin ligands and receptors have been named by the Eph Nomenclature Committee (1997). Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are similarly divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P52803 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1706678 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1946 |
| NCBI Accession: | P52803.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P52803 |
| Molecular Weight: | 26,297 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ephrin-A5 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ephrin-A5 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EFNA5�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AF1; EFL5; RAGS; EPLG7; GLC1M; LERK7�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ephrin-A5; AL-1; LERK-7; eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 7 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ephrin-A5 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | AL-1; EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 7; LERK-7 |
| Protein Family: | Ephrin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EFNA5�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EFNA5_HUMAN |