Human Cell Biology ELISA Kits 5
Human DMD (Dystrophin) CLIA Kit (HUES00814)
- SKU:
- HUES00814
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- ELISA Type:
- CLIA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Sensitivity:
- 18.75pg/mL
- Range:
- 31.25-2000pg/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Detection method: | Chemiluminescence |
| Detection range: | 31.25-2000 pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 18.75 pg/mL |
| Sample volume: | 100µL |
| Sample type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Repeatability: | CV < 15% |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Human DMD in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Human DMD and analogues was observed. |
This kit uses Sandwich-CLIA as the method. The micro CLIA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human DMD. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro CLIA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Human DMD and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Human DMD, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear fluorescence. The Relative light unit (RLU) value is measured spectrophotometrically by the Chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. The RLU value is positively associated with the concentration of Human DMD. The concentration of Human DMD in the samples can be calculated by comparing the RLU of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | dystrophin: Anchors the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton via F-actin. Ligand for dystroglycan. Component of the dystrophin- associated glycoprotein complex which accumulates at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and at a variety of synapses in the peripheral and central nervous systems and has a structural function in stabilizing the sarcolemma. Also implicated in signaling events and synaptic transmission. Defects in DMD are the cause of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). DMD is the most common form of muscular dystrophy; a sex-linked recessive disorder. It typically presents in boys aged 3 to 7 year as proximal muscle weakness causing waddling gait, toe-walking, lordosis, frequent falls, and difficulty in standing up and climbing up stairs. The pelvic girdle is affected first, then the shoulder girdle. Progression is steady and most patients are confined to a wheelchair by age of 10 or 12. Flexion contractures and scoliosis ultimately occur. About 50% of patients have a lower IQ than their genetic expectations would suggest. There is no treatment. Defects in DMD are the cause of Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). BMD resembles DMD in hereditary and clinical features but is later in onset and more benign. Defects in DMD are a cause of cardiomyopathy dilated X- linked type 3B (CMD3B); also known as X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy (XLCM). Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death. 6 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Cytoskeletal Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xp21. 2 Cellular Component: filopodium membrane; cell surface; protein complex; costamere; syntrophin complex; Z disc; cytosol; cell-matrix junction; lipid raft; actin cytoskeleton; dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex; postsynaptic membrane; cytoskeleton; plasma membrane; synapse; nucleus; sarcolemma; lateral plasma membrane; filopodium Molecular Function:protein binding; myosin binding; zinc ion binding; structural constituent of cytoskeleton; structural constituent of muscle; nitric-oxide synthase binding; actin binding; vinculin binding Biological Process: regulation of skeletal muscle contraction via regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion; muscle development; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; regulation of heart rate; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptide biosynthetic process; muscle filament sliding; muscle maintenance; cellular protein complex assembly; regulation of skeletal muscle contraction; muscle fiber development; positive regulation of neuron differentiation; cardiac muscle contraction Disease: Cardiomyopathy, Dilated, 3b; Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Type; Muscular Dystrophy, Duchenne Type |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene spans a genomic range of greater than 2 Mb and encodes a large protein containing an N-terminal actin-binding domain and multiple spectrin repeats. The encoded protein forms a component of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC), which bridges the inner cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. Deletions, duplications, and point mutations at this gene locus may cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), or cardiomyopathy. Alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing result in numerous distinct transcript variants and protein isoforms for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | P11532 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 313104240 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1756 |
| NCBI Accession: | P11532. 3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P11532,P11531, P11530, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P11532 |
| Molecular Weight: | 427kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Dystrophin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | dystrophin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DMD |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BMD; CMD3B; MRX85; DXS142; DXS164; DXS206; DXS230; DXS239; DXS268; DXS269; DXS270; DXS272 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | dystrophin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Dystrophin |
| Protein Family: | Dystrophin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DMD |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DMD_HUMAN |
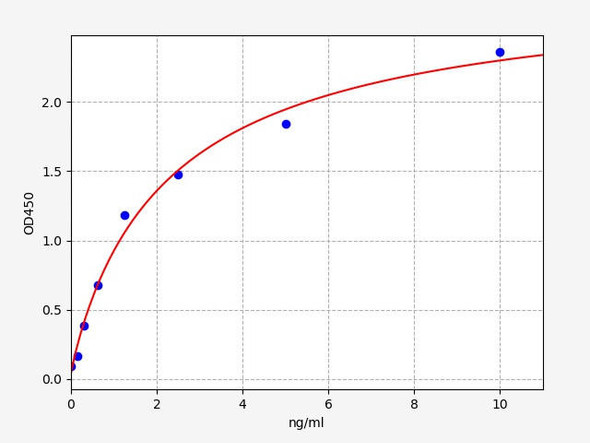
As the RLU values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU | Average | Corrected |
| 2000 | 51744 59698 | 55721 | 55693 |
| 1000 | 23924 24024 | 23974 | 23946 |
| 500 | 11531 10533 | 11032 | 11004 |
| 250 | 4990 5598 | 5294 | 5266 |
| 125 | 2800 2416 | 2608 | 2580 |
| 62.5 | 1337 1285 | 1311 | 1283 |
| 31.25 | 650 698 | 674 | 646 |
| 0 | 27 29 | 28 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human DMD were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Human DMD were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (pg/mL) | 104.54 | 224.07 | 923.09 | 105.32 | 227.03 | 876.23 |
| Standard deviation | 11.04 | 23.17 | 92.03 | 9.26 | 21.61 | 95.42 |
| C V (%) | 10.56 | 10.34 | 9.97 | 8.79 | 9.52 | 10.89 |
Recovery
The recovery of Human DMD spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 97-113 | 105 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 100-114 | 108 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 90-106 | 96 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Human DMD and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 95-111 | 87-98 | 99-114 |
| Average (%) | 102 | 92 | 104 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 95-108 | 86-98 | 90-105 |
| Average (%) | 101 | 92 | 96 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 97-109 | 97-110 | 102-115 |
| Average (%) | 103 | 104 | 108 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 95-109 | 100-111 | 94-110 |
| Average (%) | 102 | 106 | 102 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro CLIA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent A | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Substrate Reagent B | 1 vial, 5 mL | 4°C (shading light) |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100µl of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100µl of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100µl of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids. ) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 100µL of Substrate mixture solution to each well. Cover with a new plate seal andincubate for no more than 5 min at 37°C. Protect the plate from light.
- Determine the RLU value of each well immediately.