Description
| Product Name: | Human Delta-like Recombinant Protein 1/DLL1 (C-Fc) |
| Product Code: | RPES6386 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | HEK293 Cells |
| Synonyms: | Delta-like protein 1, Drosophila Delta homolog 1, Delta1, H-Delta-1, DLL1 |
| Mol Mass: | 83.3 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 90-100 kDa |
| Tag: | C-Fc |
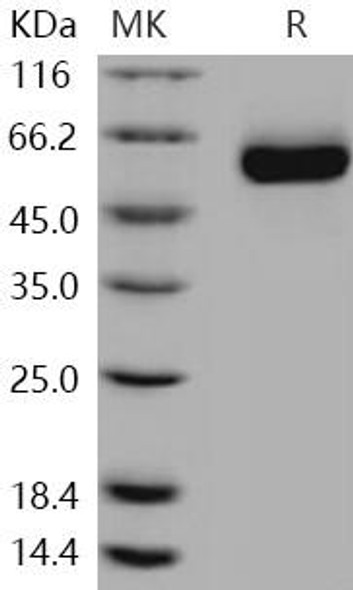
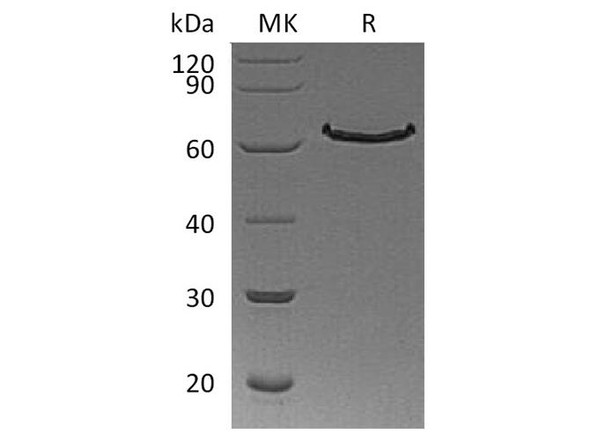
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Gln18-Gly540 |
| Accession: | O00548 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Hepes, 150mM NaCl, 1mM EDTA, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in th |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1) is a type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the Delta/Serrate/Lag2 (DSL) family of Notch ligands. Mature human DLL1 consists of a 528 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with one DSL domain and eight EGF-like repeats, a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 155 aa cytoplasmic domain. Within the ECD, human DLL1 shares 91% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat DLL1. The residual membranebound portion of DLL1 can be cleave by presenilin-dependent γ-secretase, enabling the cytoplasmic domain to migrate to the nucleus. DLL1 localizes to adherens junctions on neuronal processes through its association with the scaffolding protein MAGI1. DLL1 is widely expressed, and it plays an important role in embryonic somite formation, cochlear hair cell differentiation, plus B and T lymphocyte differentiation. The upregulation of DLL1 in arterial endothelial cells following injury or angiogenic stimulation is central to postnatal arteriogenesis. DLL1 is also overexpressed in cervical carcinoma and glioma and contributes to tumor progression. |