Cytokines Recombinant Proteins
Human Clusterin Recombinant Protein (RPPB0060)
- SKU:
- RPPB0060
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P10909
- Research Area:
- Cytokines
Description
| Product Name: | Human Clusterin Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0060 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | Clusterin |
| Synonyms: | CLI, AAG4, KUB1, SGP2, SGP-2, SP-40, TRPM2, MGC24903, Clusterin, Apolipoprotein J, Apo-J. |
| Source: | Plasma |
| Physical Appearance: | Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | Human native Clusterin was filtered (0.4�m) and lyophilized from 0.5mg/ml in 0.1M phosphate buffer, 0.15M NaCl pH 7.5. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to add deionized H2O to prepare a working stock solution of 0.5mg/ml and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. Product is not sterile! Please filter the product by an appropriate sterile filter before using it in the cell culture. |
| Stability: | Store lyophilized Clusterin at -20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid repeated freezing/thawing cycles. Reconstituted protein can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show any change after two weeks at 4°C. |
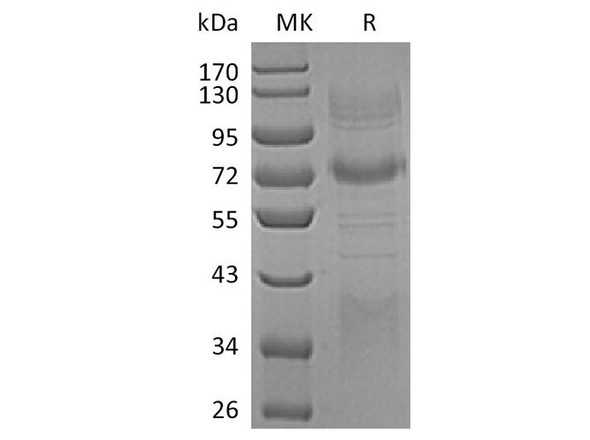
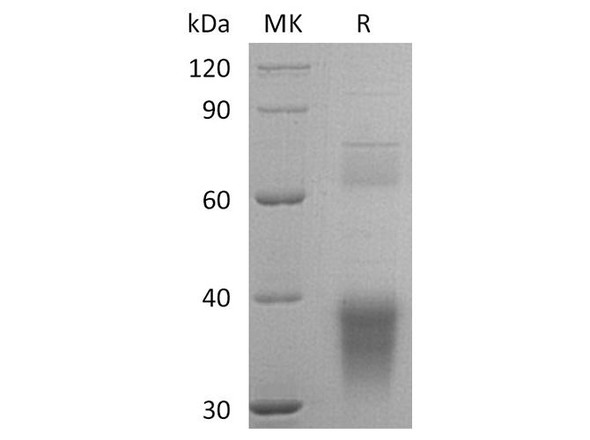
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS PAGE. |
Clusterin also named Apolipoprotein J (APO-J) is a 75-80 kD disulfide-linked heterodimeric protein containing about 30% of N-linked carbohydrate rich in sialic acid but truncated forms targeted to the nucleus have also been identified.The precursor polypeptide chain is cleaved proteolytically to remove the 22-mer secretory signal peptide and subsequently between residues 227/228 to generate the a and b chains. These are assembled in anti-parallel to give a heterodimeric molecule in which the cysteine-rich centers are linked by five disulfide bridges and are flanked by two predicted coiled-coil a-helices and three predicted amphipathic a-helices.Across a broad range of species clusterin shows a high degree of sequence homology ranging from 70% to 80%. It is nearly ubiquitously expressed in most mammalian tissues and can be found in plasma, milk, urine, cerebrospinal fluid and semen.It is able to bind and form complexes with numerous partners such as immunoglobulins, lipids, heparin, bacteria, complement components, paraoxonase, beta amyloid, leptin and others. Clusterin has been ascribed a plethora of functions such as phagocyte recruitment, aggregation induction, complement attack prevention, apoptosis inhibition, membrane remodeling, lipid transport, hormone transport and/or scavenging, matrix metalloproteinase inhibition.A genuine function of clusterin has not been defined. One tempting hypothesis says that clusterin is an extracellular chaperone protecting cells from stress induced insults caused by degraded and misfolded protein precipitates.Clusterin is up- or down regulated on the mRNA or protein level in many pathological and clinically relevant situations including cancer, organ regeneration, infection, Alzheimer disease, retinitis pigmentosa, myocardial infarction, renal tubular damage, autoimmunity and others.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CLU: Isoform 1 functions as extracellular chaperone that prevents aggregation of nonnative proteins. Prevents stress- induced aggregation of blood plasma proteins. Inhibits formation of amyloid fibrils by APP, APOC2, B2M, CALCA, CSN3, SNCA and aggregation-prone LYZ variants (in vitro). Does not require ATP. Maintains partially unfolded proteins in a state appropriate for subsequent refolding by other chaperones, such as HSPA8/HSC70. Does not refold proteins by itself. Binding to cell surface receptors triggers internalization of the chaperone-client complex and subsequent lysosomal or proteasomal degradation. Secreted isoform 1 protects cells against apoptosis and against cytolysis by complement. Intracellular isoforms interact with ubiquitin and SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes and promote the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Promotes proteasomal degradation of COMMD1 and IKBKB. Modulates NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity. Nuclear isoforms promote apoptosis. Mitochondrial isoforms suppress BAX-dependent release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm and inhibit apoptosis. Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation. Belongs to the clusterin family. 5 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Apoptosis; Mitochondrial; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8p21-p12 Cellular Component: extracellular matrix; Golgi apparatus; extracellular space; mitochondrion; endoplasmic reticulum; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; mitochondrial membrane; cytoplasm; extracellular region; nucleus; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; chaperone binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; ATPase activity; misfolded protein binding Biological Process: platelet activation; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria; response to misfolded protein; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; protein stabilization; positive regulation of apoptosis; response to virus; cell morphogenesis; microglial cell activation; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; negative regulation of protein homooligomerization; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; complement activation; reverse cholesterol transport; platelet degranulation; myelin maintenance in the central nervous system; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; protein import; innate immune response; lipid metabolic process; blood coagulation; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly; complement activation, classical pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted chaperone that can under some stress conditions also be found in the cell cytosol. It has been suggested to be involved in several basic biological events such as cell death, tumor progression, and neurodegenerative disorders. Alternate splicing results in both coding and non-coding variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | P10909 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116533 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1191 |
| NCBI Accession: | P10909.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P10909,P11380, P11381, Q2TU75, Q5HYC1, Q7Z5B9, B2R9Q1 B3KSE6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P10909,AAB25217 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated: 32kDa/48kDa/52kDa/53kDa/57kDaObserved: 40kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Clusterin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | clusterin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CLU�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CLI; AAG4; APOJ; CLU1; CLU2; KUB1; SGP2; APO-J; SGP-2; SP-40; TRPM2; TRPM-2; NA1/NA2�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | clusterin; apolipoprotein J; ku70-binding protein 1; sulfated glycoprotein 2; aging-associated protein 4; complement lysis inhibitor; complement cytolysis inhibitor; complement-associated protein SP-40,40; testosterone-repressed prostate message 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Clusterin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Aging-associated gene 4 protein; Apolipoprotein J; Apo-J; Complement cytolysis inhibitor; CLI; Complement-associated protein SP-40,40; Ku70-binding protein 1; NA1/NA2; Testosterone-repressed prostate message 2; TRPM-2 |
| Protein Family: | Clusterin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CLU�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CLUS_HUMAN |