CD Antigens Recombinant Proteins
Human CD59 Recombinant Protein (RPPB3084)
- SKU:
- RPPB3084
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P13987
- Research Area:
- CD Antigens
Description
| Product Name: | Human CD59 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3084 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | CD59 |
| Synonyms: | CD59 Molecule Complement Regulatory Protein, CD59 Antigen P18-20, CD59 Glycoprotein, Surface Anitgen Recognized By Monoclonal Antibody 16.3A5, Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) Inhibition Factor, Lymphocytic Antigen CD59/MEM43, Human Leukocyte Antigen MIC11, Membrane Attack Complex Inhibition Factor, 20 KDa Homologous Restriction Factor, Membrane Inhibitor Of Reactive Lysis, MAC-Inhibitory Protein, T Cell-Activating Protein, Ly-6-Like Protein, Protectin, MIC11, MSK21, MEM43, MIN1/2/3, MIRL, MAC-IP, MACIF, HRF-20, G344, EJ16/30/32, 1F5. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The CD59 solution (0.5mg/ml) contains 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0), 0.15M NaCl, 1mM DTT and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks.�Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time.�For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
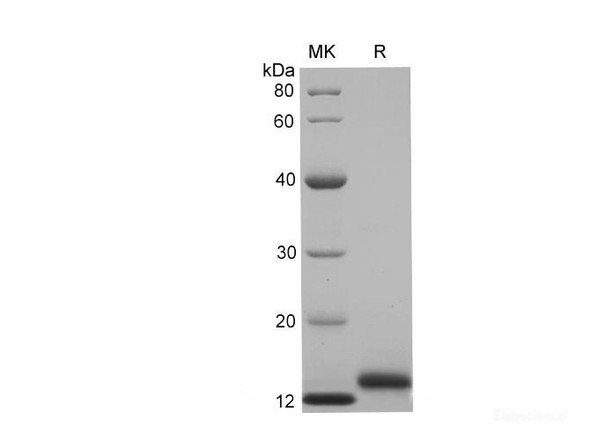
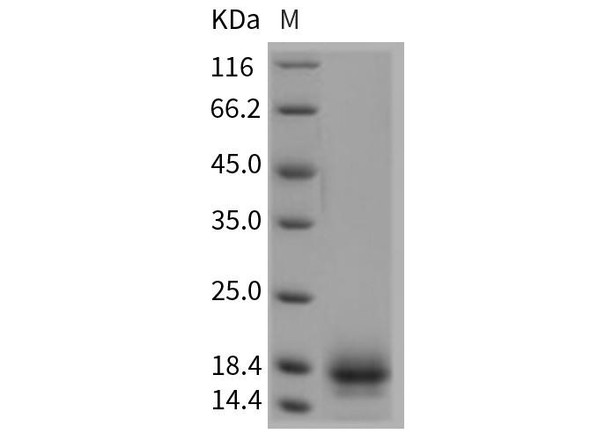
| Purity: | Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSLQCYNCP NPTADCKTAV NCSSDFDACL ITKAGLQVYN KCWKFEHCNF NDVTTRLREN ELTYYCCKKD LCNFNEQLEN� |
CD59 is a cell surface glycoprotein which regulates complement-mediated cell lysis, and it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction. CD59 is an effective inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex, whereby it binds complement C8 and/or C9 during the compilation of this complex, thus inhibiting the incorporation of multiple copies of C9 into the complex, which is essential for osmolytic pore formation. In addition, CD59 has a role in signal transduction pathways in the activation of T cells. CD59 gene mutations cause CD59 deficiency, a disease resulting in hemolytic anemia and thrombosis, and which causes cerebral infarction.
CD59 Human Recombinant produced in E.coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 100 amino acids (26-102) and having a molecular mass of 11.3kDa.CD59 is fused to a 23 amino acid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CD59: Potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex (MAC) action. Acts by binding to the C8 and/or C9 complements of the assembling MAC, thereby preventing incorporation of the multiple copies of C9 required for complete formation of the osmolytic pore. This inhibitor appears to be species-specific. Involved in signal transduction for T-cell activation complexed to a protein tyrosine kinase. Defects in CD59 are the cause of CD59 deficiency (CD59D). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, GPI anchor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11p13 Cellular Component: anchored to external side of plasma membrane; cell surface; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; ER-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane; extracellular space; focal adhesion; Golgi membrane; membrane; plasma membrane; vesicle Molecular Function:complement binding; protein binding Biological Process: blood coagulation; cell activation; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; COPII coating of Golgi vesicle; ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport; neutrophil degranulation; regulation of complement activation Disease: Hemolytic Anemia, Cd59-mediated, With Or Without Immune-mediated Polyneuropathy |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that regulates complement-mediated cell lysis, and it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex, whereby it binds complement C8 and/or C9 during the assembly of this complex, thereby inhibiting the incorporation of multiple copies of C9 into the complex, which is necessary for osmolytic pore formation. This protein also plays a role in signal transduction pathways in the activation of T cells. Mutations in this gene cause CD59 deficiency, a disease resulting in hemolytic anemia and thrombosis, and which causes cerebral infarction. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode the same protein, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P13987 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116021 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 966 |
| NCBI Accession: | P13987.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P13987 |
| Molecular Weight: | 14kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | CD59 glycoprotein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | CD59 molecule (CD59 blood group) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CD59�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | 1F5; EJ16; EJ30; EL32; G344; MIN1; MIN2; MIN3; MIRL; HRF20; MACIF; MEM43; MIC11; MSK21; 16.3A5; HRF-20; MAC-IP; p18-20�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | CD59 glycoprotein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | CD59 glycoprotein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 1F5 antigen; 20 kDa homologous restriction factor; HRF-20; HRF20; MAC-inhibitory protein; MAC-IP; MEM43 antigen; Membrane attack complex inhibition factor; MACIF; Membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis; MIRL; Protectin; CD_antigen: CD59 |
| Protein Family: | CD59 glycoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CD59�� |