Cytokines Recombinant Proteins
Human APOB Recombinant Protein (RPPB0051)
- SKU:
- RPPB0051
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P04114
- Research Area:
- Cytokines
Description
| Product Name: | Human APOB Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0051 |
| Size: | 1mg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | APOB |
| Synonyms: | APOB, APO-B, Apolipoprotein B. |
| Source: | Human Plasma |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | The protein was lyophilized from a 0.5mg/ml solution of 50mM Na2CO3 pH-10 containing 50mM NaCl and 10mM sodium deoxycholate. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized APOB in sterile 18M-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized APOB although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution, APOB should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C. For long-term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).�Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
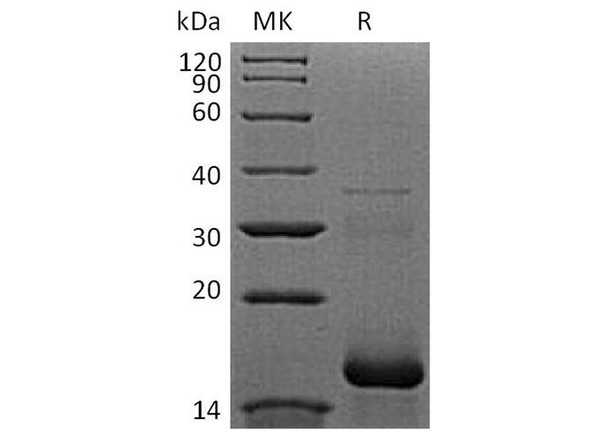
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0%. |
ApoB is the main apolipoprotein of LDL, IDL, VLDL and chylomicrons particles that serves as the carrier of lipids (fat molecules), as well as cholesterol, in the water surrounding the cells within every tissue across the body. Though all the functional aspects of Apolipoprotein B within the LDL and other elements are considered to be rather uncertain, it serves as the key organizing protein of all other carriers of lipids. across LDL membranes, apolipoprotein B also serves as a ligand for LDL receptors in many cells across the body, meaning, it shows that lipid carriers that are set to cross into cells with Apolipoprotein B receptors, this is the way that lipids are transported within and into cells.
Human APOB produced from Human plasma having a molecular mass of 550 kDa.����� � � � � � � � �
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Apolipoprotein B is a major protein constituent of chylomicrons (apo B-48), LDL (apo B-100) and VLDL (apo B-100). Apo B-100 functions as a recognition signal for the cellular binding and internalization of LDL particles by the apoB/E receptor. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Subcellular location: Secreted. Induction: Up-regulated in response to enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection (at protein level). Ref.34 Post-translational modification: Palmitoylated; structural requirement for proper assembly of the hydrophobic core of the lipoprotein particle. Ref.31 Involvement in Disease: Defects in APOB are a cause of hypobetalipoproteinemia familial type 1 (FHBL1) [ MIM:107730]. A disorder characterized by highly reduced plasma concentrations of low density lipoproteins, and dietary fat malabsorption. Clinical presentation may vary from no symptoms to severe gastrointestinal and neurological dysfunction similar to abetalipoproteinemia. Ref.46Defects in APOB are a cause of familial ligand-defective apolipoprotein B-100 (FDB) [ MIM:144010]. FDB is a dominantly inherited disorder of lipoprotein metabolism leading to hypercholesterolemia and increased proneness to coronary artery disease (CAD). The plasma cholesterol levels are dramatically elevated due to impaired clearance of LDL particles by defective APOB/E receptors. Ref.40 Ref.42 Ref.44Note=Defects in APOB associated with defects in other genes (polygenic) can contribute to hypocholesterolemia. Sequence similarities: Contains 1 vitellogenin domain. RNA editing: Edited at position 2180.The stop codon (UAA) at position 2180 is created by RNA editing. Apo B-48, derived from the fully edited RNA, is produced only in the intestine and is found in chylomicrons. Apo B-48 is a shortened form of apo B-100 which lacks the LDL-receptor region. The unedited version (apo B-100) is produced by the liver and is found in the VLDL and LDL. Sequence caution: The sequence AAA51752.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at positions 942, 951, 1139, 1165, 1164, 1371 and 1385. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene product is the main apolipoprotein of chylomicrons and low density lipoproteins. It occurs in plasma as two main isoforms, apoB-48 and apoB-100: the former is synthesized exclusively in the gut and the latter in the liver. The intestinal and the hepatic forms of apoB are encoded by a single gene from a single, very long mRNA. The two isoforms share a common N-terminal sequence. The shorter apoB-48 protein is produced after RNA editing of the apoB-100 transcript at residue 2180 (CAA->UAA), resulting in the creation of a stop codon, and early translation termination. Mutations in this gene or its regulatory region cause hypobetalipoproteinemia, normotriglyceridemic hypobetalipoproteinemia, and hypercholesterolemia due to ligand-defective apoB, diseases affecting plasma cholesterol and apoB levels. [provided by RefSeq] |
| UniProt Code: | P04114 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 114014 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 338 |
| NCBI Accession: | P04114.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P04114,O00502, P78479, P78480, P78481, Q13779, Q13785 Q13786, Q13787, Q13788, Q4ZG63, Q53QC8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P04114,P78482,Q13789,Q13828,Q59HB3,Q7Z7Q0,Q9UE51,Q9UE52,Q9UE53 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Apolipoprotein B-100 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | apolipoprotein B (including Ag(x) antigen) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | APOB�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FLDB; LDLCQ4�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | apolipoprotein B-100; apoB-48; apoB-100; apo B-100; mutant Apo B 100; OTTHUMP00000115994; apolipoprotein B48 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Apolipoprotein B-100 |
| Protein Family: | Apolipoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | APOB�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | APOB_HUMAN |