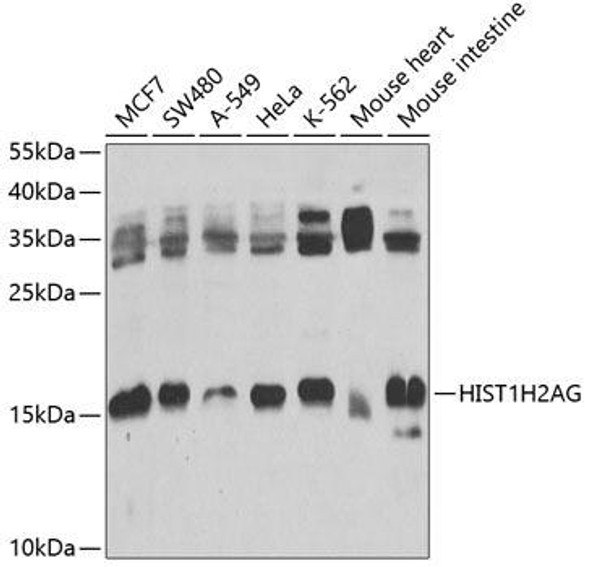
Description
| Antibody Name: | Histone H2A Antibody (PACO21619) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO21619 |
| Size: | 100ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:10000, IHC:1:50-1:100 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthesized peptide derived from Internal of human Histone H2A. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
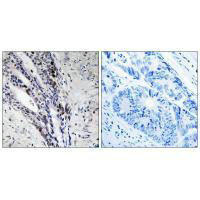 | Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma tissue using Histone H2A antibody. |
| Background: | Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Albig W., Biol. Chem. 380:7-18(1999). |
| Synonyms: | H2A.1b; H2A/c; H2A/d; H2A/i; H2A/n |
| UniProt Protein Function: | H2A.1: Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. The octamer wraps approximately 147 bp of DNA. Belongs to the histone H2A family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6p22.1 Cellular Component: nuclear chromatin; nucleus Molecular Function:DNA binding; enzyme binding; protein binding Biological Process: chromatin silencing |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. The linker histone, H1, interacts with linker DNA between nucleosomes and functions in the compaction of chromatin into higher order structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-dependent histone that is a member of the histone H2A family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails but instead contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in the histone microcluster on chromosome 6p21.33. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P0C0S8 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 83288406 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8969 |
| NCBI Accession: | P0C0S8.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P0C0S8,P02261, Q2M1R2, Q76PA6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P0C0S8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 14kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone H2A type 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | histone cluster 1 H2A family member g |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HIST1H2AG |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H2AG; H2A/p; H2AFP; H2A.1b; pH2A/f |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone H2A type 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone H2A type 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Histone H2A/p |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HIST1H2AG |