Description
| Antibody Name: | GNAS Antibody (PACO14434) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO14434 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:1000-1:5000, WB:1:200-1:1000, IHC:1:25-1:100 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen: | Fusion protein of human GNAS |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
 | Gel: 10%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 30 μg, Lane: Mouse brain tissue, Primary antibody: PACO14434(GNAS Antibody) at dilution 1/500, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 5 seconds. |
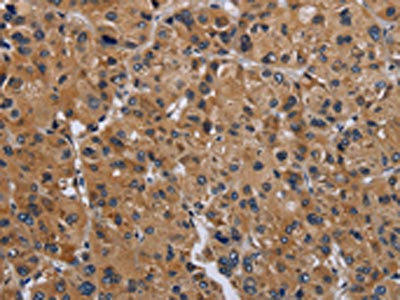 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using PACO14434(GNAS Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | This locus has a highly complex imprinted expression pattern. It gives rise to maternally, paternally, and biallelically expressed transcripts that are derived from four alternative promoters and 5' exons. Some transcripts contain a differentially methylated region (DMR) at their 5' exons, and this DMR is commonly found in imprinted genes and correlates with transcript expression. An antisense transcript is produced from an overlapping locus on the opposite strand. One of the transcripts produced from this locus, and the antisense transcript, are paternally expressed noncoding RNAs, and may regulate imprinting in this region. In addition, one of the transcripts contains a second overlapping ORF, which encodes a structurally unrelated protein - Alex. Alternative splicing of downstream exons is also observed, which results in different forms of the stimulatory G-protein α subunit, a key element of the classical signal transduction pathway linking receptor-ligand interactions with the activation of adenylyl cyclase and a variety of cellular reponses. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene result in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a, pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1b, Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism, McCune-Albright syndrome, progressive osseus heteroplasia, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone, and some pituitary tumors. |
| Synonyms: | GNAS complex locus |
| UniProt Protein Function: | G-alpha(s): a guanine nucleotide-binding protein of the G12 class of G-alpha proteins. Agonist binding to Gq-coupled receptors may block Akt activation via the release of active G-alpha(q) subunits that inhibit phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Heterotrimeric G proteins are composed of 3 units; alpha, beta and gamma. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oncoprotein; G protein; G protein, heterotrimeric alpha G(s); G protein, heterotrimeric; Vesicle; Membrane protein, peripheral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q13.3 Cellular Component: dendrite; extracellular region; cytosol; ruffle; transport vesicle; membrane; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; heterotrimeric G-protein complex; trans-Golgi network membrane; intrinsic to membrane; nucleus Molecular Function:GTPase activity; corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding; signal transducer activity; protein binding; GTP binding; mu-type opioid receptor binding; metal ion binding; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit binding; beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding; D1 dopamine receptor binding; adenylate cyclase activity Biological Process: developmental growth; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation; water transport; protein secretion; female pregnancy; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; G-protein signaling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway; intracellular transport; positive regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process; DNA methylation; tissue homeostasis; transmembrane transport; endochondral ossification; post-embryonic body morphogenesis; dopamine receptor, adenylate cyclase activating pathway; response to drug; sensory perception of chemical stimulus; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth; multicellular organism growth; adenylate cyclase activation; sensory perception of smell; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation; cartilage development; energy reserve metabolic process; renal water homeostasis; cAMP biosynthetic process; blood coagulation; cognition; regulation of insulin secretion Disease: Osseous Heteroplasia, Progressive; Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Type Ic; Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism; Mccune-albright Syndrome; Acth-independent Macronodular Adrenal Hyperplasia; Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Type Ia; Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Type Ib; Pituitary Adenoma, Growth Hormone-secreting |
| NCBI Summary: | This locus has a highly complex imprinted expression pattern. It gives rise to maternally, paternally, and biallelically expressed transcripts that are derived from four alternative promoters and 5' exons. Some transcripts contain a differentially methylated region (DMR) at their 5' exons, and this DMR is commonly found in imprinted genes and correlates with transcript expression. An antisense transcript is produced from an overlapping locus on the opposite strand. One of the transcripts produced from this locus, and the antisense transcript, are paternally expressed noncoding RNAs, and may regulate imprinting in this region. In addition, one of the transcripts contains a second overlapping ORF, which encodes a structurally unrelated protein - Alex. Alternative splicing of downstream exons is also observed, which results in different forms of the stimulatory G-protein alpha subunit, a key element of the classical signal transduction pathway linking receptor-ligand interactions with the activation of adenylyl cyclase and a variety of cellular reponses. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene result in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a, pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1b, Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism, McCune-Albright syndrome, progressive osseus heteroplasia, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone, and some pituitary tumors. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | P63092 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 52000961 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2778 |
| NCBI Accession: | P63092.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P63092,P04895, Q12927, Q14433, Q32P26, Q5JWD2, Q5JWD4 Q5JWD5, Q6NR75, Q6NXS0, A6NI00, E1P5G5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O95467,P63092,P84996,Q5JWF2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 626 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha isoforms short |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | GNAS complex locus |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GNAS |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AHO; GSA; GSP; POH; GPSA; NESP; GNAS1; PHP1A; PHP1B; PHP1C; C20orf45 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein ALEX; protein GNAS; protein NESP55; secretogranin VI; extra large alphas protein; neuroendocrine secretory protein; guanine nucleotide regulatory protein; alternative gene product encoded by XL-exon; adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein; |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha isoforms short |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein |
| Protein Family: | Protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GNAS |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GNAS2_HUMAN |






