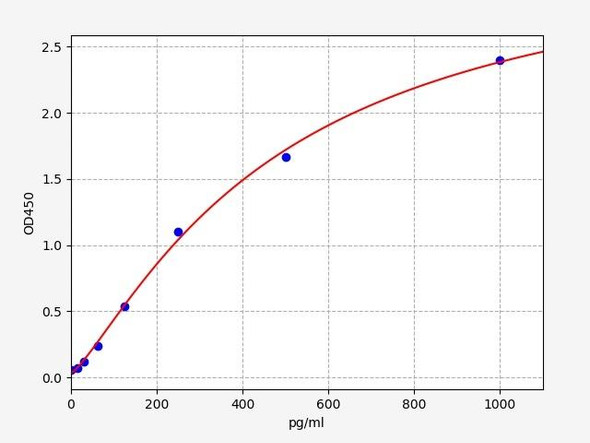
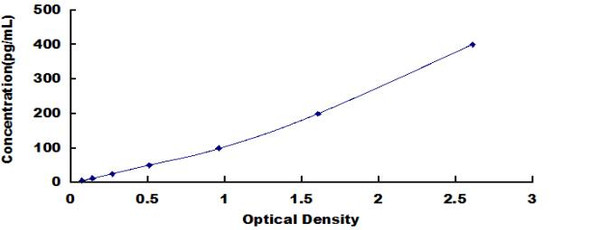
Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Assay Kit - Information
Assay Genie's non-radioactive, colorimetric G6PDH assay is based on the reduction of the tetrazolium salt MTT in a NADPH-coupled enzymatic reaction to a reduced form of MTT which exhibits an absorption maximum at 565 nm. The increase in absorbance at 565 nm is proportional to the enzyme activity.
Applications
For quantitative colorimetric determination of Glucose-6-Phosphate concentration and evaluation of drug effects on its metabolism.
Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Assay Kit -Key Features
- Fast and sensitive. Linear detection range (20 sample): 0.2 to 100 U/L for 15 min reaction.
- Convenient and high-throughput. Homogeneous "mix-incubate-measure" type assay. Can be readily automated on HTS liquid handling systems for processing thousands of samples per day.
Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Assay Kit - Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Assay Buffer: 10 mL Diaphorase: 120 uL NADP/MTT: 1 mL Calibrator: 10 mL Substrate: 1 mL |
| Kit Requires | Pipetting devices and accessories (e.g. multi-channel pipettor), clear flat- bottom 96-well plates, centrifuge tubes and plate reader |
| Method of Detection | OD460nm |
| Detection Limit | 0.2 U/L |
| Samples | Plasma, serum, tissue and culture media, etc |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 20 min |
| Size | 100 tests |
| Shelf Life | 6 months |
| Storage | Store all components at -20°C upon receiving |
More Details
GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (G6PDH) is a cytosolic enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway which supplies reducing energy to cells by maintaining the level of the co-enzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). G6PDH reduces nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) to NADPH while oxidizing glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). Humans with a genetic deficiency of G6PDH are predisposed to non-immune hemolytic anemia.
Aliases for G6PD Gene
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
- EC 1.1.1.49
- Glucose-6-Phosphate 1-Dehydrogenase
- G6PD1
Entrez Gene Summary for G6PD Gene
This gene encodes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This protein is a cytosolic enzyme encoded by a housekeeping X-linked gene whose main function is to produce NADPH, a key electron donor in the defense against oxidizing agents and in reductive biosynthetic reactions. G6PD is remarkable for its genetic diversity. Many variants of G6PD, mostly produced from missense mutations, have been described with wide ranging levels of enzyme activity and associated clinical symptoms. G6PD deficiency may cause neonatal jaundice, acute hemolysis, or severe chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot for G6PD Gene
G6PD_HUMAN,P11413Catalyzes the rate-limiting step of the oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway, which represents a route for the dissimilation of carbohydrates besides glycolysis. The main function of this enzyme is to provide reducing power (NADPH) and pentose phosphates for fatty acid and nucleic acid synthesis.
Protein details for G6PD Gene (UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot)
Protein Symbol:P11413-G6PD_HUMANRecommended name:Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase
Protein Accession:P11413
Secondary Accessions:D3DWX9, Q16000, Q16765, Q8IU70, Q8IU88, Q8IUA6, Q96PQ2
Protein attributes for G6PD Gene
Size:515 amino acids
Molecular mass:59257 Da
Quaternary structure:Homotetramer; dimer of dimers. Interacts with SIRT2; the interaction is enhanced by H(2)O(2) treatment.
Miscellaneous:Binds two molecules of NADP. The first one is a cosubstrate (bound to the N-terminal domain), the second is bound to the C-terminal domain and functions as a structural element.
SequenceCaution:Sequence=AAA63175.1; Type=Erroneous initiation; Note=Translation N-terminally extended.; Evidence={ECO:0000305};
Post-translational modifications for G6PD Gene
- Acetylated by ELP3 at Lys-403; acetylation inhibits its homodimerization and enzyme activity. Deacetylated by SIRT2 at Lys-403; deacetylation stimulates its enzyme activity.
- Ubiquitination at Lys 97, Lys 171, and Lys 403
- Modification sites at PhosphoSitePlus
- P11413