Description
| Antibody Name: | FPR3 Antibody (PACO19675) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO19675 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:1000-1:2000, IHC:1:25-1:100 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human FPR3 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
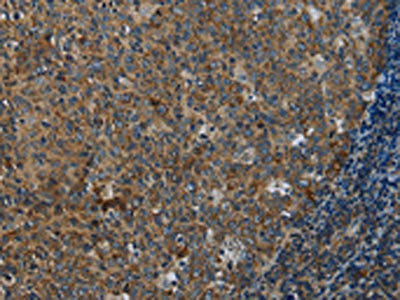 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human tonsil tissue using PACO19675(FPR3 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
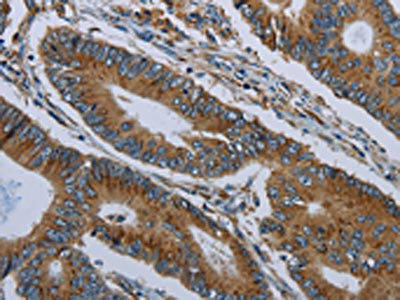 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human colon cancer tissue using PACO19675(FPR3 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | The N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR) family is comprised of three members, FPR, FPR3 (also designated FPRL1, lipoxin A4 receptor, FPRH1 or FPR2) and FPR like-2 (FPRL2), all of which are chemotactic G protein-coupled receptors that contain seven transmembrane domains. These receptors are found on the surface of phagocytic leukocytes, such as neutrophils and monocytes, and each family member contains specific residues, which are responsible for determining its ligand specificity. FPR3 is a promiscuous receptor that binds to several ligands, including lipoxin A4, N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP), serum amyloid A (SAA), prion peptide and the 42 amino acid, form of β amyloid. Upon activation, FPR3 induces migration and calcium mobilization in human monocytes and neutrophils and is involved in inflammatory and host defense responses. FPR3 may mediate inflammation in prion and Alzheimers diseases, which makes it a potential target for therapeutic agents. |
| Synonyms: | formyl peptide receptor 3 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FPR3: Low affinity receptor for N-formyl-methionyl peptides, which are powerful neutrophils chemotactic factors. Binding of FMLP to the receptor causes activation of neutrophils. This response is mediated via a G-protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family.Protein type: Receptor, GPCR; GPCR, family 1; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integralChromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19q13.3-q13.4Cellular Component: plasma membraneBiological Process: cell motility; signal transduction |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | |
| UniProt Code: | P25089 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 38258904 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2359 |
| NCBI Accession: | P25089.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P25089 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P25089 |
| Molecular Weight: | 39,965 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | N-formyl peptide receptor 3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | formyl peptide receptor 3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FPR3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FMLPY; FPRH1; FPRH2; FPRL2; RMLP-R-I; FMLP-R-II; FML2_HUMAN |
| NCBI Protein Information: | N-formyl peptide receptor 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | N-formyl peptide receptor 3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | FMLP-related receptor II; FMLP-R-II; Formyl peptide receptor-like 2 |
| Protein Family: | FK506-binding protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FPR3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FPR3_HUMAN |






