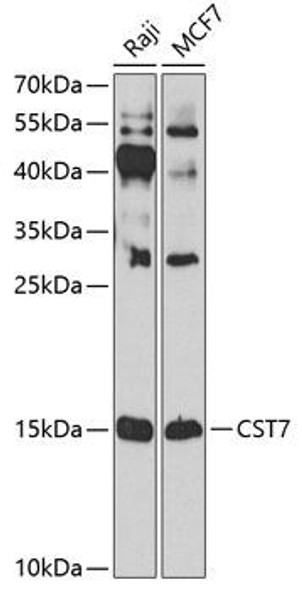
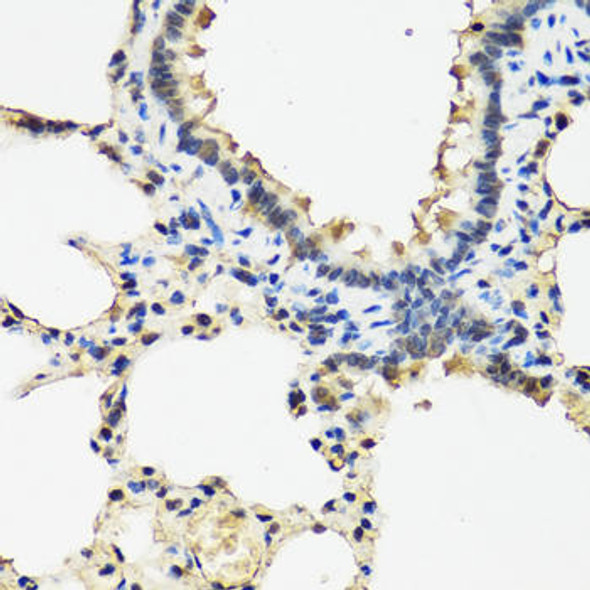
Description
| Antibody Name: | F Antibody (PACO34134) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO34134 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA |
| Recommended Dilutions: | |
| Species Reactivity: | Canine distemper virus |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Canine distemper virus Fusion glycoprotein F0 protein (136-608AA) |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 |
| Purification Method: | >95%, Protein G purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Background: | Class I viral fusion protein. Under the current model, the protein has at least 3 conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and plasma cell membrane fusion, the heptad repeat (HR) regions assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of viral and plasma cell membranes. Directs fusion of viral and cellular membranes leading to delivery of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. This fusion is pH independent and occurs directly at the outer cell membrane. The trimer of F1-F2 (F protein) probably interacts with H at the virion surface. Upon HN binding to its cellular receptor, the hydrophobic fusion peptide is unmasked and interacts with the cellular membrane, inducing the fusion between cell and virion membranes. Later in infection, F proteins expressed at the plasma membrane of infected cells could mediate fusion with adjacent cells to form syncytia, a cytopathic effect that could lead to tissue necrosis. |
| Synonyms: | Fusion glycoprotein F0 [Cleaved into: Fusion glycoprotein F2; Fusion glycoprotein F1], F |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Class I viral fusion protein. Under the current model, the protein has at least 3 conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and plasma cell membrane fusion, the heptad repeat (HR) regions assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of viral and plasma cell membranes. Directs fusion of viral and cellular membranes leading to delivery of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. This fusion is pH independent and occurs directly at the outer cell membrane. The trimer of F1-F2 (F protein) probably interacts with H at the virion surface. Upon HN binding to its cellular receptor, the hydrophobic fusion peptide is unmasked and interacts with the cellular membrane, inducing the fusion between cell and virion membranes. Later in infection, F proteins expressed at the plasma membrane of infected cells could mediate fusion with adjacent cells to form syncytia, a cytopathic effect that could lead to tissue necrosis (). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | |
| UniProt Code: | P12569 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 138249 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | |
| NCBI Accession: | P12569.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P12569,Q65991 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P12569 |
| Molecular Weight: | 67.5 kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fusion glycoprotein F0 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | |
| NCBI Protein Information: | |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fusion glycoprotein F0 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | |
| Protein Family: | |
| UniProt Gene Name: | F |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FUS_CDVO |