Description
| Antibody Name: | EPHB1/EPHB2/EPHB3 Antibody (PACO23432) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO23432 |
| Size: | 100ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:10000, IHC:1:50-1:100, IF:1:100-1:500 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human EPHB1/2/3. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
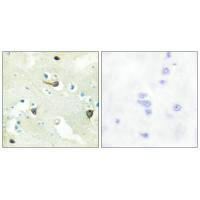 | Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue using EPHB1/2/3 antibody. |
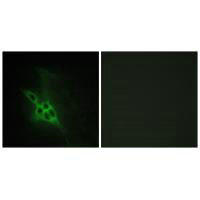 | Immunofluorescence analysis of NIH/3T3 cells, using EPHB1/2/3 antibody. |
| Background: | Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Cognate/functional ephrin ligands for this receptor include EFNB1, EFNB2 and EFNB3. During nervous system development, regulates retinal axon guidance redirecting ipsilaterally ventrotemporal retinal ganglion cells axons at the optic chiasm midline. This probably requires repulsive interaction with EFNB2. In the adult nervous system together with EFNB3, regulates chemotaxis, proliferation and polarity of the hippocampus neural progenitors. Beside its role in axon guidance plays also an important redundant role with other ephrin-B receptors in development and maturation of dendritic spines and synapse formation. May also regulate angiogenesis. More generally, may play a role in targeted cell migration and adhesion. Upon activation by EFNB1 and probably other ephrin-B ligands activates the MAPK/ERK and the JNK signaling cascades to regulate cell migration and adhesion respectively. |
| Synonyms: | EC 2.7.10.1; ELK; EPB1; EPHT2; EPTH2 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | EphB1: a receptor tyrosine kinase of the Eph family. Receptor for members of the ephrin-B family: ephrin-B1, -B2 and -B3. The Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family, the largest in the tyrosine kinase group, has fourteen members. They bind membrane-anchored ligands, ephrins, at sites of cell-cell contact, regulating the repulsion and adhesion of cells that underlie the establishment, maintenance, and remodeling of patterns of cellular organization. Eph signals are particularly important in regulating cell adhesion and cell migration during development, axon guidance, homeostasis and disease. EphA receptors bind to GPI-anchored ephrin-A ligands, while EphB receptors bind to ephrin-B proteins that have a transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain. Interactions between EphB receptor kinases and ephrin-B proteins transduce signals bidirectionally, signaling to both interacting cell types. Eph receptors and ephrins also regulate the adhesion of endothelial cells and are required for the remodeling of blood vessels. The ligand-activated form of EphB1 interacts with GRB2, GRB10 and NCK through their respective SH2 domains. Four alternatively spliced isoforms are known. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, TK; Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.10.1; Protein kinase, tyrosine (receptor); Membrane protein, integral; TK group; Eph family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3q21-q23 Cellular Component: cytosol; early endosome membrane; extracellular region; integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane Molecular Function:protein binding; transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity Biological Process: angiogenesis; axon guidance; cell-substrate adhesion; central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis; detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; establishment of cell polarity; neurogenesis; positive regulation of synaptogenesis; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; regulation of JNK cascade; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance |
| NCBI Summary: | Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for ephrin-B family members. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P54762 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1706663 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2047 |
| NCBI Accession: | P54762.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P54762,O43569, O95142, O95143, Q0VG87, A8K593, B3KTB2 B5A969, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P54762 |
| Molecular Weight: | 26,906 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | EPH receptor B1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EPHB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ELK; NET; Hek6; EPHT2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ephrin type-B receptor 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ELK; EPH tyrosine kinase 2; EPH-like kinase 6; EK6; hEK6; Neuronally-expressed EPH-related tyrosine kinase; NET; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor EPH-2 |
| Protein Family: | Ephrin type-B receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EPHB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EPHB1_HUMAN |






