Creatine Kinase Activity Assay Kit - Information
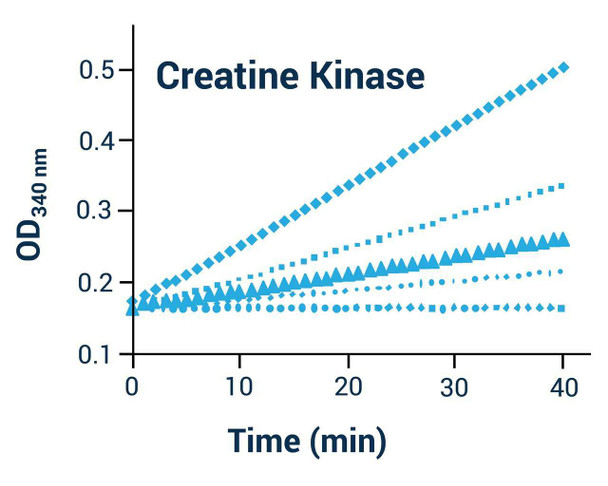
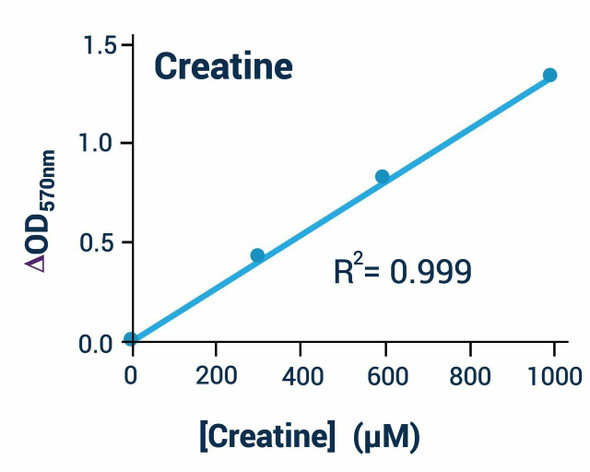
Assay Genie's creatine kinase activity assay kit is based on enzyme coupled reactions in which creatine phosphate and ADP is converted to creatine and ATP by CK, the generated ATP is used to phosphorylate glucose by hexokinase to generate glucose-6-phosphate, which is then oxidized by NADP in the presence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. The produced NADPH, measured at 340 nm, is proportionate to the CK activity in the sample.
Applications
For quantitative determination of creatine kinase activity and evaluation of drug effects on CK activity.
Creatine Kinase Activity Assay Kit - Key Features
- Sensitive and accurate. Detection range: 5 to 300 U/L creatine kinase in 96-well plate assay.
- Convenient. The procedure involves adding a single working reagent, and reading the optical density at 20 min and 40 min at room temperature or 37°C.
- High-throughput. Can be readily automated as a high-throughput 96-well plate assay for thousands of samples per day.
Creatine Kinase Activity Assay Kit - Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Assay Buffer: 12 mL Substrate Solution: 1.0 mL Enzyme Mix: 120 mL Calibrator: 150 mL |
| Kit Requires | Pipeting (multi-channel) devices. Clear-bottom 96-well plates and plate reader. |
| Method of Detection | OD340nm |
| Detection Limit | 5 U/L |
| Samples | Serum, plasma etc |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 5 min |
| Size | 100 tests |
| Storage | Store all reagents at -20°C |
| Shelf Life | 6 months |
More Details
CREATINE KINASE (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK), is an enzyme (EC 2.7.3.2) expressed predominantly in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and the brain. The CK enzyme consists of two subunits, which can be either B (brain type) or M (muscle type), and hence three different isoenzymes: CK-MM, CK-BB and CK-MB. CK catalyzes the conversion of creatine to phosphocreatine, consuming adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and generating adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and the reverse reaction. CK is often determined routinely in emergency patients with chest pain and acute renal failure. Elevation of CK is an indication of damage to muscle and has been associated with injury, rhabdomyolysis, myocardial infarction, myositis, myocarditis, malignant hyperthermia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, etc. Lower levels can be an indication of alcoholic liver disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Simple, direct and automation-ready procedures for measuring CK activity are very desirable.