Cell Cytotoxicity Assay - Information
This Cytotoxicity Assay Kit (Luminescent) provides a rapid method to measure intracellular ATP, cell viability and cytotoxicity. The single working reagent lyses cells to release ATP, which, in the presence of luciferase, immediately reacts with the Substrate D-luciferin to produce light. The light intensity is a direct measure of intracellular ATP concentration and hence number of living cells. This non-radioactive, homogeneous cell-based assay can be conveniently performed in microplates. The reagent is compatible with all culture media and liquid handling systems for high-throughput screening applications in 96-well and 384-well plates.
Applications
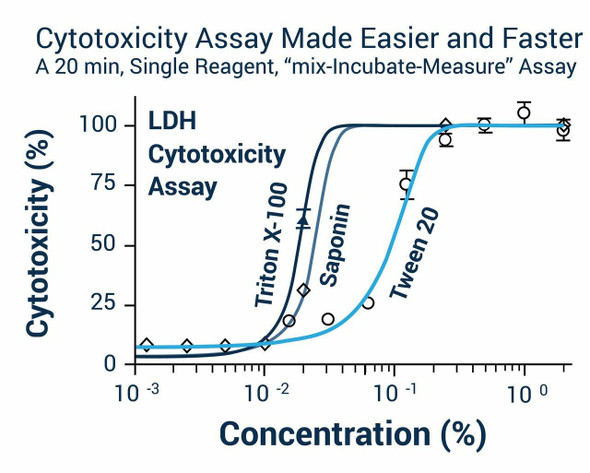
For rapid, bioluminescent luciferin/luciferase based assay for cell viability, proliferation, cytotoxcity and high-throughput screen for anticancer agents.
Cell Cytotoxcity Assay - Key Features
- Safe. Non-radioactive assay (cf. 3H-thymidine incorporation assay).
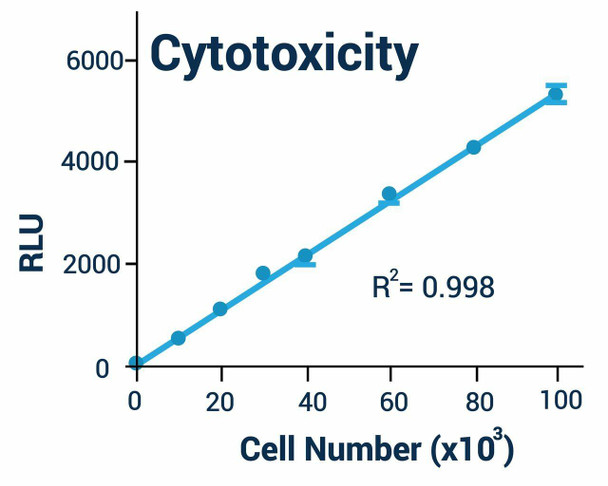
- Sensitive and accurate. As low as 50 cells can be quantified.
- Homogeneous and convenient. "Mix-incubate-measure" type assay. No wash and reagent transfer steps are involved.
- Robust and amenable to HTS: Z' factors of 0.6 to 0.7 are routinely observed in 96-well and 384-well plates. Can be readily automated on HTS liquid handling systems for processing thousands of samples per day.
Cell Cytotoxicty Assay - Data Sheet | |
| Includes | Assay Buffer: 10 mL Substrate: 120 mL ATP Enzyme: 120 mL |
| Method of Detection | Luminescence |
| Detection Limit | 50 cells |
| Samples | Cells |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 2 min |
| Size | 100 tests |
| Storage | Store all reagents at -20°C. |
| Shelf Life | 6 months |
More Details
Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) is the chemical energy for cellular metabolism and is often referred to as energy currency" of the cell. ATP is produced only in living cells during photosynthesis and cellular respiration and consumed in cellular processes including biosynthetic reactions, motility and cell division. It is a key indicator of cellular activity and has been utilized as a measure of cell viability and cytotoxicity in research and drug discovery.