Description
| Antibody Name: | CACNA1G Antibody (PACO19378) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO19378 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:1000-1:2000, IHC:1:15-1:50 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human CACNA1G |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
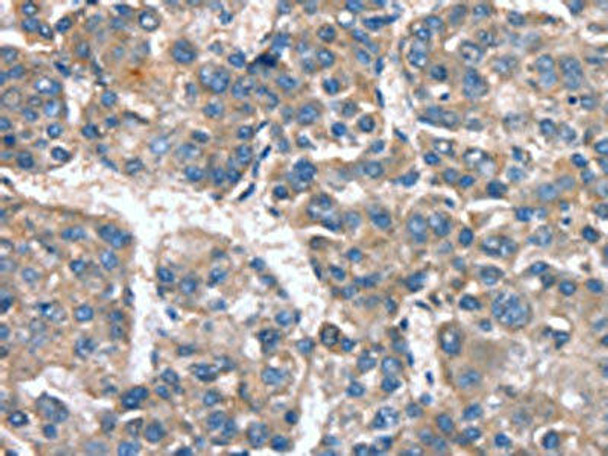
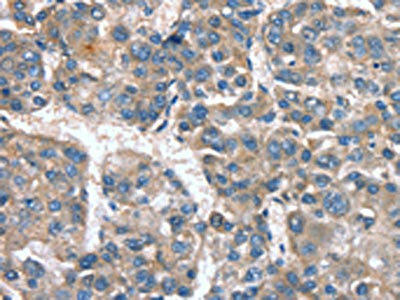 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using PACO19378(CACNA1G Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
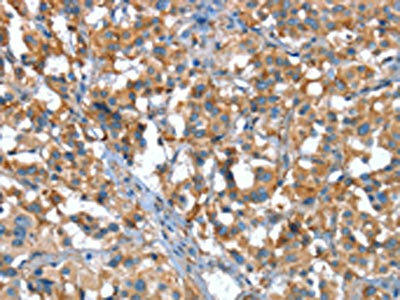 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using PACO19378(CACNA1G Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | Voltage-dependent calcium channels mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells, and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, and gene expression. Calcium channels are multisubunit complexes composed of alpha-1, beta, alpha-2/delta, and γ subunits. The channel activity is directed by the pore-forming alpha-1 subunit, whereas, the others act as auxiliary subunits regulating this activity. The distinctive properties of the calcium channel types are related primarily to the expression of a variety of alpha-1 isoforms, alpha-1A, B, C, D, E, and S. This gene encodes the alpha-1A subunit, which is predominantly expressed in neuronal tissue. Mutations in this gene are associated with 2 neurologic disorders, familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia 2. |
| Synonyms: | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, α 1G subunit |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1G gives rise to T-type calcium currents. T-type calcium channels belong to the "low-voltage activated (LVA)" group and are strongly blocked by mibefradil. A particularity of this type of channels is an opening at quite negative potentials and a voltage-dependent inactivation. T-type channels serve pacemaking functions in both central neurons and cardiac nodal cells and support calcium signaling in secretory cells and vascular smooth muscle. They may also be involved in the modulation of firing patterns of neurons which is important for information processing as well as in cell growth processes.Subcellular location: Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Tissue specificity: Highly expressed in brain, in particular in the amygdala, subthalamic nuclei, cerebellum and thalamus. Moderate expression in heart; low expression in placenta, kidney and lung. Also expressed in colon and bone marrow and in tumoral cells to a lesser extent. Highly expressed in fetal brain, but also in peripheral fetal tissues as heart, kidney and lung, suggesting a developmentally regulated expression.Domain: Each of the four internal repeats contains five hydrophobic transmembrane segments (S1, S2, S3, S5, S6) and one positively charged transmembrane segment (S4). S4 segments probably represent the voltage-sensor and are characterized by a series of positively charged amino acids at every third position.The linker region between repeat III and IV probably play a role in the inactivation of the channel. The C-terminal part may be implicated in the anchoring of the protein to the membrane, this by interfering/restricting its lateral diffusion.Post-translational modification: In response to raising of intracellular calcium, the T-type channels are activated by CaM-kinase II.Sequence similarities: Belongs to the calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family. CACNA1G subfamily. [View classification] |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | |
| UniProt Code: | O43497 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 34783701 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 12291 |
| NCBI Accession: | AAH57399 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O43497 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O43497 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cacna1g protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Cacna1g |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | a1G; [a]1G; Cav3.1d; alpha-1G; mKIAA1123 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1G |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1G |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cav3.1c; NBR13; Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav3.1 |
| Protein Family: | |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CACNA1G |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CAC1G_HUMAN |