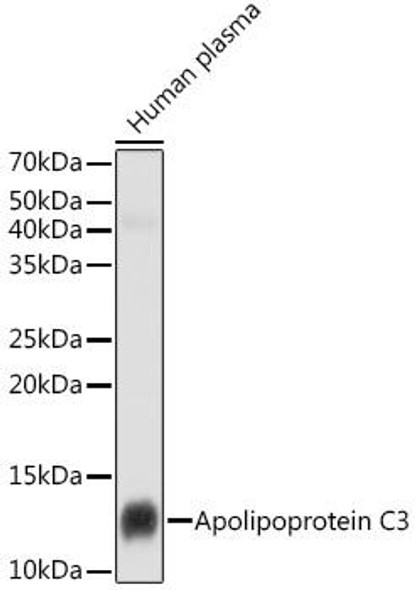
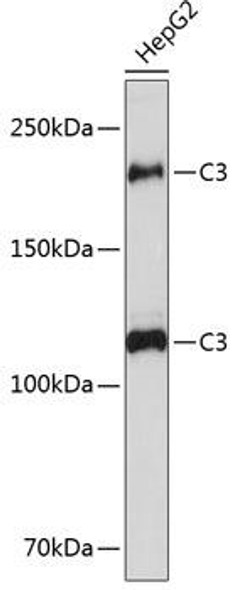
Description
| Antibody Name: | C3 Antibody (PACO52242) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO52242 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA |
| Recommended Dilutions: | |
| Species Reactivity: | Rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Rat Complement C3 protein (671-746AA) |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 |
| Purification Method: | >95%, Protein G purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Background: | C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its processing by C3 convertase is the central reaction in both classical and alternative complement pathways. After activation C3b can bind covalently, via its reactive thioester, to cell surface carbohydrates or immune aggregates. |
| Synonyms: | Complement C3 [Cleaved into: Complement C3 β chain; C3-beta-c (C3bc) (Neutrophil chemotactic factor-2) (ENCF-2); Complement C3 α chain; C3a anaphylatoxin (Neutrophil chemotactic factor-1) (ENCF-1); Acylation stimulating protein (ASP) (C3adesArg); Complement C3b alpha' chain; Complement C3c alpha' chain fragment 1; Complement C3dg fragment; Complement C3g fragment; Complement C3d fragment; Complement C3f fragment; Complement C3c alpha' chain fragment 2], C3 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | C3: C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its processing by C3 convertase is the central reaction in both classical and alternative complement pathways. After activation C3b can bind covalently, via its reactive thioester, to cell surface carbohydrates or immune aggregates. Defects in C3 are the cause of complement component 3 deficiency (C3D). A rare defect of the complement classical pathway. Patients develop recurrent, severe, pyogenic infections because of ineffective opsonization of pathogens. Some patients may also develop autoimmune disorders, such as arthralgia and vasculitic rashes, lupus-like syndrome and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Genetic variation in C3 is associated with susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration type 9 (ARMD9). ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin- containing structure known as Bruch membrane. Defects in C3 are a cause of susceptibility to hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 5 (AHUS5). An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. Susceptibility to the development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome can be conferred by mutations in various components of or regulatory factors in the complement cascade system. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype. Increased levels of C3 and its cleavage product ASP, are associated with obesity, diabetes and coronary heart disease. Short-term endurance training reduces baseline ASP levels and subsequently fat storage. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Inhibitor; Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q12 Cellular Component: extracellular space; protein complex Molecular Function:C5L2 anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor binding; cofactor binding; endopeptidase inhibitor activity; lipid binding; protein binding Biological Process: blood coagulation; chemotaxis; complement activation; complement activation, alternative pathway; complement activation, classical pathway; fatty acid metabolic process; inflammatory response; phagocytosis, engulfment; positive regulation of activation of membrane attack complex; positive regulation of angiogenesis; positive regulation of developmental growth; positive regulation of G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; positive regulation of phagocytosis; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation; positive regulation of type IIa hypersensitivity; response to estradiol; response to estrogen; response to glucocorticoid stimulus; response to magnesium ion; response to progesterone; tolerance induction |
| NCBI Summary: | putative complement component C3; likely involved in innate immune response [RGD, Feb 2006] |
| UniProt Code: | P01026 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 158138561 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 24232 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_058690.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01026,Q9ET19, Q9QV57, Q9QV58, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01026 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | complement C3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | complement C3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | C3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | complement C3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Complement C3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Complement C3 beta chainC3-beta-c; C3bc |
| Protein Family: | Complement C3 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | C3 |