Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 5
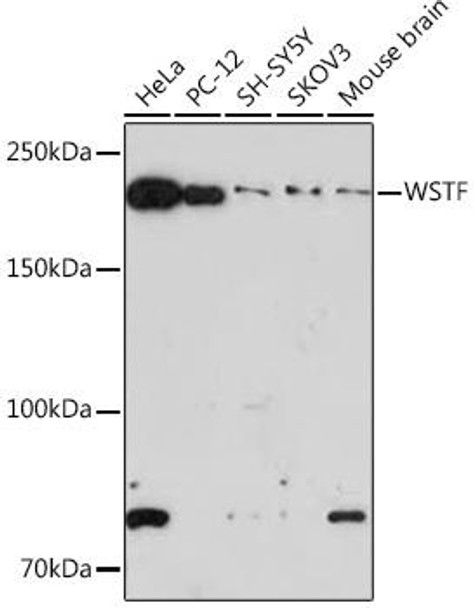
Anti-WSTF Antibody (CAB9519)
- SKU:
- CAB9519
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-WSTF Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9519 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human WSTF |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, PC-12, SH-SY5Y, SKOV3, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human WSTF |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 9031 |
| Uniprot: | Q9UIG0 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 185kDa |
| Observed MW: | 185KDa |
| Synonyms: | WBSCR10, WBSCR9, WSTF |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the bromodomain protein family. The bromodomain is a structural motif characteristic of proteins involved in chromatin-dependent regulation of transcription. This gene is deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, a developmental disorder caused by deletion of multiple genes at 7q11.23. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | WSTF: plays a central role in chromatin remodeling and acts as a transcription regulator. Apparently possesses tyrosine-protein kinase activity, but bears no sequence resemblance classical tyrosine kinase proteins. Involved in DNA damage response by phosphorylating Y142 of histone H2AX. H2AXpY142 plays a central role in DNA repair and acts as a mark that distinguishes between apoptotic and repair responses to genotoxic stress. Essential component of the WICH complex, a chromatin remodeling complex that mobilizes nucleosomes and reconfigures irregular chromatin to a regular nucleosomal array structure. The WICH complex regulates the transcription of various genes, has a role in RNA polymerase I and RNA polymerase III transcription, mediates the histone H2AX phosphorylation at Y142, and is involved in the maintenance of chromatin structures during DNA replication processes. In the complex, it mediates the recruitment of the WICH complex to replication foci during DNA replication. Also involved in vitamin D-coupled transcription regulation via its association with the WINAC complex, a chromatin-remodeling complex recruited by vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is required for the ligand-bound VDR-mediated transrepression of the CYP27B1 gene. In the WINAC complex, plays an essential role by targeting the complex to acetylated histones, an essential step for VDR-promoter association. Accumulates in pericentromeric heterochromatin during replication. Targeted to replication foci throughout S phase via its association with PCNA. Ubiquitously expressed with high levels of expression in heart, brain, placenta, skeletal muscle and ovary. Two alternatively-spliced human isoforms have been reported. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.10.2; DNA replication; ATYPICAL group; BAZ family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q11.23 Cellular Component: nuclear replication fork; nucleoplasm Molecular Function:chromatin binding; histone kinase activity; protein binding; protein-tyrosine kinase activity Biological Process: chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription; double-strand break repair; heart morphogenesis; histone phosphorylation; positive regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to DNA damage stimulus |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the bromodomain protein family. The bromodomain is a structural motif characteristic of proteins involved in chromatin-dependent regulation of transcription. This gene is deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, a developmental disorder caused by deletion of multiple genes at 7q11.23. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9UIG0 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 22653670 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 9031 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9UIG0.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9UIG0,O95039, O95247, O95277, Q6P1K4, Q86UJ6, B9EGK3 D3DXE9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9UIG0 |
| Molecular Weight: | 170,447 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Tyrosine-protein kinase BAZ1B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain 1B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | BAZ1B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | WSTF; WBSCR9; WBSCR10 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | tyrosine-protein kinase BAZ1B |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Tyrosine-protein kinase BAZ1B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain protein 1B; Williams syndrome transcription factor; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 10 protein; Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 9 protein; hWALp2 |
| Protein Family: | Tyrosine-protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | BAZ1B |
| UniProt Entry Name: | BAZ1B_HUMAN |
View AllClose