| Background: | This gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It encodes a heparin-binding protein, which exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. This growth factor induces proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, and is essential for both physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Disruption of this gene in mice resulted in abnormal embryonic blood vessel formation. This gene is upregulated in many known tumors and its expression is correlated with tumor stage and progression. Elevated levels of this protein are found in patients with POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) and atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. There is also evidence for alternative translation initiation from upstream non-AUG (CUG) codons resulting in additional isoforms. A recent study showed that a C-terminally extended isoform is produced by use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon via a stop codon readthrough mechanism, and that this isoform is antiangiogenic. Expression of some isoforms derived from the AUG start codon is regulated by a small upstream open reading frame, which is located within an internal ribosome entry site. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth. Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. NRP1/Neuropilin-1 binds isoforms VEGF-165 and VEGF-145. Isoform VEGF165B binds to KDR but does not activate downstream signaling pathways, does not activate angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family and encodes a protein that is often found as a disulfide linked homodimer. This protein is a glycosylated mitogen that specifically acts on endothelial cells and has various effects, including mediating increased vascular permeability, inducing angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth, promoting cell migration, and inhibiting apoptosis. Elevated levels of this protein is linked to POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Mutations in this gene have been associated with proliferative and nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding either freely secreted or cell-associated isoforms, have been characterized. There is also evidence for the use of non-AUG (CUG) translation initiation sites upstream of, and in-frame with the first AUG, leading to additional isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P15692 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 17380528 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7422 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15692.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P15692,O60720, O75875, Q074Z4, Q16889, B5BU86, H0Y2S8 H0Y407, H0Y414, H0Y462, H0Y8N2, H3BLW7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15692 |
| Molecular Weight: | 34,406 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | VEGFA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | VPF; VEGF; MVCD1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | vascular endothelial growth factor A; vascular permeability factor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Vascular permeability factor; VPF |
| Protein Family: | VEGF coregulated chemokine |
| UniProt Gene Name: | VEGFA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VEGFA_HUMAN |


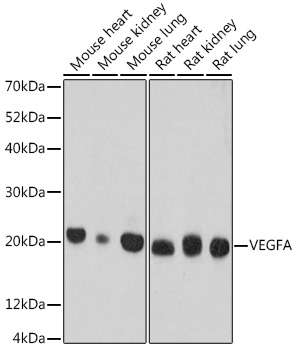
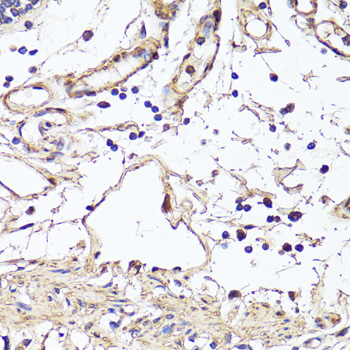
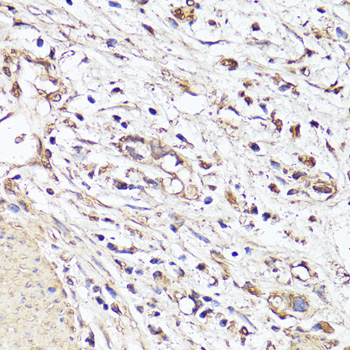
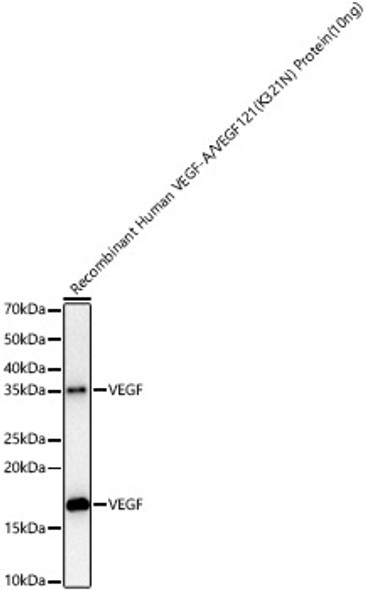

![VEGF Monoclonal Antibody [NYRhVEGF] (CPAB0032) VEGF Monoclonal Antibody [NYRhVEGF] (CPAB0032)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/58261/63443/vegf-monoclonal-antibody-nyrhvegf-cpab0032__28426__91778.1706534950.jpg?c=1)

