Signal Transduction Antibodies 1
Anti-TTPA Antibody (CAB14473)
- SKU:
- CAB14473
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-TTPA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB14473 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-110 of human TTPA (NP_000361.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
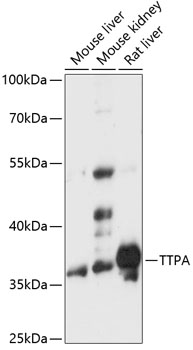
| Positive Samples: | Mouse liver, Mouse kidney, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-110 of human TTPA (NP_000361.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MAEA RSQP SAGP QLNA LPDH SPLL QPGL AALR RRAR EAGV PLAP LPLT DSFL LRFL RARD FDLD LAWR LLKN YYKW RAEC PEIS ADLH PRSI IGLL KAGY HGVL RSRD PT |
| Gene ID: | 7274 |
| Uniprot: | P49638 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 31kDa |
| Observed MW: | 38kDa |
| Synonyms: | TTPA, ATTP, AVED, TTP1, alphaTTP |
| Background: | This gene encodes a soluble protein that binds alpha-trocopherol, a form of vitamin E, with high selectivity and affinity. This protein plays an important role in regulating vitamin E levels in the body by transporting vitamin E between membrane vesicles and facilitating the secretion of vitamin E from hepatocytes to circulating lipoproteins. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary vitamin E deficiency (ataxia with vitamin E deficiency, AVED) and retinitis pigmentosa. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | TTPA: Binds alpha-tocopherol and enhances its transfer between separate membranes. Defects in TTPA are the cause of ataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency (AVED). AVED is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by spinocerebellar degeneration. It causes ataxia and peripheral neuropathy that resembles Friedreich ataxia. AVED patients have markedly reduced plasma levels of vitamin E. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q12.3 Molecular Function:phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding; protein binding; vitamin E binding Biological Process: intermembrane transport; lipid metabolic process; transport; vitamin transport Disease: Vitamin E, Familial Isolated Deficiency Of |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a soluble protein that binds alpha-trocopherol, a form of vitamin E, with high selectivity and affinity. This protein plays an important role in regulating vitamin E levels in the body by transporting vitamin E between membrane vesicles and facilitating the secretion of vitamin E from hepatocytes to circulating lipoproteins. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary vitamin E deficiency (ataxia with vitamin E deficiency, AVED) and retinitis pigmentosa. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P49638 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1351322 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7274 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49638.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49638,Q71V64, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49638 |
| Molecular Weight: | 32kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | alpha tocopherol transfer protein |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TTPA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ATTP; AVED; TTP1; alphaTTP |
| NCBI Protein Information: | alpha-tocopherol transfer protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein |
| Protein Family: | Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TTPA |
View AllClose