Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-TTN Antibody (CAB16730)
- SKU:
- CAB16730
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-TTN Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16730 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
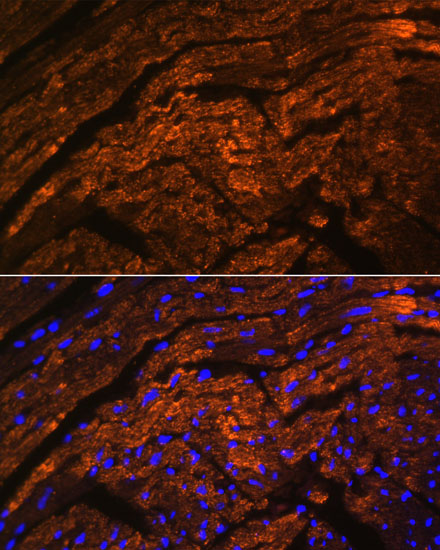
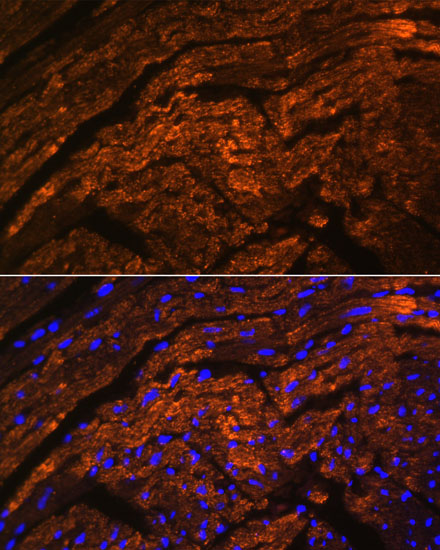
| Application: | IF |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Protein of human TTN. |
| Application: | IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Protein of human TTN. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 7273 |
| Uniprot: | Q8WZ42 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 3816KDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
| Synonyms: | TTN, CMD1G, CMH9, CMPD4, EOMFC, HMERF, LGMD2J, MYLK5, TMD, SALMY, titin |
| Background: | This gene encodes a large abundant protein of striated muscle. The product of this gene is divided into two regions, a N-terminal I-band and a C-terminal A-band. The I-band, which is the elastic part of the molecule, contains two regions of tandem immunoglobulin domains on either side of a PEVK region that is rich in proline, glutamate, valine and lysine. The A-band, which is thought to act as a protein-ruler, contains a mixture of immunoglobulin and fibronectin repeats, and possesses kinase activity. An N-terminal Z-disc region and a C-terminal M-line region bind to the Z-line and M-line of the sarcomere, respectively, so that a single titin molecule spans half the length of a sarcomere. Titin also contains binding sites for muscle associated proteins so it serves as an adhesion template for the assembly of contractile machinery in muscle cells. It has also been identified as a structural protein for chromosomes. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Considerable variability exists in the I-band, the M-line and the Z-disc regions of titin. Variability in the I-band region contributes to the differences in elasticity of different titin isoforms and, therefore, to the differences in elasticity of different muscle types. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 9, and autoantibodies to titin are produced in patients with the autoimmune disease scleroderma. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Key component in the assembly and functioning of vertebrate striated muscles. By providing connections at the level of individual microfilaments, it contributes to the fine balance of forces between the two halves of the sarcomere. The size and extensibility of the cross-links are the main determinants of sarcomere extensibility properties of muscle. In non-muscle cells, seems to play a role in chromosome condensation and chromosome segregation during mitosis. Might link the lamina network to chromatin or nuclear actin, or both during interphase. Ref.28 |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Catalytic activity: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. Cofactor: Magnesium. Enzyme regulation: Full activation of the protein kinase domain requires both phosphorylation of Tyr-32341, preventing it from blocking the catalytic aspartate residue, and binding of Ca/CALM to the C-terminal regulatory tail of the molecule which results in ATP binding to the kinase. Ref.28 Subunit structure: Interacts with MYOM1, MYOM2, tropomyosin and myosin. Interacts with actin, primarily via the PEVK domains and with MYPN By similarity. Interacts with FHL2, NEB, CRYAB, LMNA/lamin-A and LMNB/lamin-B. Interacts with TCAP/telethonin and/or ANK1 isoform Mu17/ank15, via the first two N-terminal immunoglobulin domains. Interacts with TRIM63 and TRIM55, through several domains including immunoglobulin domains 141 and 142. Interacts with ANKRD1, ANKRD2 and ANKRD23, via the region between immunoglobulin domains 77 and 78 and interacts with CAPN3, via immunoglobulin domain 79. Interacts with NBR1 through the protein kinase domain. Interacts with CALM/calmodulin. Isoform 6 interacts with OBSCN isoform 3. Interacts with CMYA5. Ref.3 Ref.16 Ref.17 Ref.18 Ref.19 Ref.20 Ref.21 Ref.22 Ref.23 Ref.26 Ref.28 Ref.38 Subcellular location: Cytoplasm Probable. Nucleus Ref.23. Tissue specificity: Isoforms 3, 7 and 8 are expressed in cardiac muscle. Isoform 4 is expressed in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Isoform 6 is expressed in skeletal muscle (at protein level). Ref.3 Ref.7 Domain: ZIS1 and ZIS5 regions contain multiple SPXR consensus sites for ERK- and CDK-like protein kinases as well as multiple SP motifs. ZIS1 could adopt a closed conformation which would block the TCAP-binding site.The PEVK region may serve as an entropic spring of a chain of structural folds and may also be an interaction site to other myofilament proteins to form interfilament connectivity in the sarcomere. Post-translational modification: Autophosphorylated By similarity. Ref.14 Ref.28 Involvement in Disease: Hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure (HMERF) [MIM:603689]: Autosomal dominant, adult-onset myopathy with early respiratory muscle involvement.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.38Cardiomyopathy, familial hypertrophic 9 (CMH9) [MIM:613765]: A hereditary heart disorder characterized by ventricular hypertrophy, which is usually asymmetric and often involves the interventricular septum. The symptoms include dyspnea, syncope, collapse, palpitations, and chest pain. They can be readily provoked by exercise. The disorder has inter- and intrafamilial variability ranging from benign to malignant forms with high risk of cardiac failure and sudden cardiac death.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.32Cardiomyopathy, dilated 1G (CMD1G) [MIM:604145]: A disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.34 Ref.35 Ref.37Tardive tibial muscular dystrophy (TMD) [MIM:600334]: Autosomal dominant, late-onset distal myopathy. Muscle weakness and atrophy are usually confined to the anterior compartment of the lower leg, in particular the tibialis anterior muscle. Clinical symptoms usually occur at age 35-45 years or much later.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.33 Ref.36Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2J (LGMD2J) [MIM:608807]: An autosomal recessive degenerative myopathy characterized by progressive weakness of the pelvic and shoulder girdle muscles. Severe disability is observed within 20 years of onset.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.Early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy (EOMFC) [MIM:611705]: Early-onset myopathies are inherited muscle disorders that manifest typically from birth or infancy with hypotonia, muscle weakness, and delayed motor development. EOMFC is a titinopathy that, in contrast with the previously described examples, involves both heart and skeletal muscle, has a congenital onset, and is purely recessive. This phenotype is due to homozygous out-of-frame TTN deletions, which lead to a total absence of titin's C-terminal end from striated muscles and to secondary CAPN3 depletion.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.39 Miscellaneous: In some isoforms, after the PEVK repeat region there is a long PEVK duplicated region. On account of this region, it has been very difficult to sequence the whole protein. The length of this region (ranging from 183 to 2174 residues), may be a key elastic element of titin. Sequence similarities: Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family.Contains 132 fibronectin type-III domains.Contains 152 Ig-like (immunoglobulin-like) domains.Contains 19 Kelch repeats.Contains 1 protein kinase domain.Contains 17 RCC1 repeats.Contains 14 TPR repeats.Contains 15 WD repeats. Sequence caution: The sequence AAH58824.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Contaminating sequence. Potential poly-A sequence starting in position 553.The sequence AAH70170.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Contaminating sequence. Potential poly-A sequence starting in position 627.The sequence CAA62188.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at positions 17036 and 17043. The sequence CAD12455.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at positions 17036 and 17043. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a large abundant protein of striated muscle. The product of this gene is divided into two regions, a N-terminal I-band and a C-terminal A-band. The I-band, which is the elastic part of the molecule, contains two regions of tandem immunoglobulin domains on either side of a PEVK region that is rich in proline, glutamate, valine and lysine. The A-band, which is thought to act as a protein-ruler, contains a mixture of immunoglobulin and fibronectin repeats, and possesses kinase activity. An N-terminal Z-disc region and a C-terminal M-line region bind to the Z-line and M-line of the sarcomere, respectively, so that a single titin molecule spans half the length of a sarcomere. Titin also contains binding sites for muscle associated proteins so it serves as an adhesion template for the assembly of contractile machinery in muscle cells. It has also been identified as a structural protein for chromosomes. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Considerable variability exists in the I-band, the M-line and the Z-disc regions of titin. Variability in the I-band region contributes to the differences in elasticity of different titin isoforms and, therefore, to the differences in elasticity of different muscle types. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 9, and autoantibodies to titin are produced in patients with the autoimmune disease scleroderma. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | Q8WZ42 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 384872704 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7273 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8WZ42.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8WZ42 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Titin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | titin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TTN |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | TMD; CMH9; CMD1G; CMPD4; EOMFC; HMERF; MYLK5; SALMY; LGMD2J; LGMDR10 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | titin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Titin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Connectin; Rhabdomyosarcoma antigen MU-RMS-40.14 |
| Protein Family: | Titin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TTN |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TITIN_HUMAN |


![Anti-CTTN Antibody (CAB18038)[KO Validated] Anti-CTTN Antibody (CAB18038)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/55182/59925/anti-cttn-antibody-cab18038ko-validated__28042__74350.1706529191.jpg?c=1)

