Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 4
Anti-TFAP2B Antibody (CAB7935)
- SKU:
- CAB7935
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-TFAP2B Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7935 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
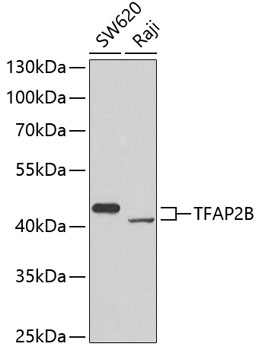
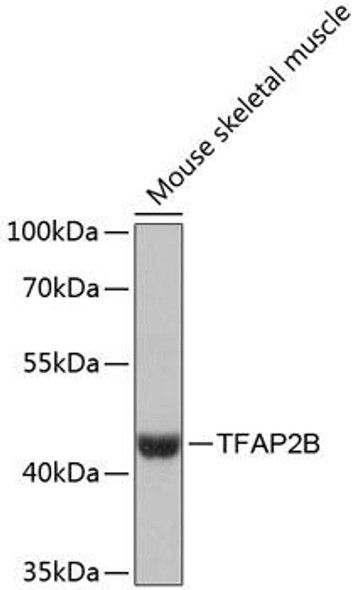
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human TFAP2B |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | SW620, Raji |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human TFAP2B |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 7021 |
| Uniprot: | Q92481 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 50kDa/51kDa |
| Observed MW: | 50kDa |
| Synonyms: | TFAP2B, AP-2B, AP2-B, PDA2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the AP-2 family of transcription factors. AP-2 proteins form homo- or hetero-dimers with other AP-2 family members and bind specific DNA sequences. They are thought to stimulate cell proliferation and suppress terminal differentiation of specific cell types during embryonic development. Specific AP-2 family members differ in their expression patterns and binding affinity for different promoters. This protein functions as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal dominant Char syndrome, suggesting that this gene functions in the differentiation of neural crest cell derivatives. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | AP-2 beta: Sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with inducible viral and cellular enhancer elements to regulate transcription of selected genes. AP-2 factors bind to the consensus sequence 5'-GCCNNNGGC-3' and activate genes involved in a large spectrum of important biological functions including proper eye, face, body wall, limb and neural tube development. They also suppress a number of genes including MCAM/MUC18, C/EBP alpha and MYC. AP-2-beta appears to be required for normal face and limb development and for proper terminal differentiation and function of renal tubular epithelia. Binds DNA as a dimer. Can form homodimers or heterodimers with other AP-2 family members. Interacts with CITED4. Interacts with UBE2I. Interacts with KCTD1; this interaction represses transcription activation. Interacts with CITED2 (via C-terminus); the interaction stimulates TFAP2B-transcriptional activity. Belongs to the AP-2 family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6p12 Cellular Component: nucleus Molecular Function:caspase inhibitor activity; DNA binding; protein binding; protein dimerization activity; protein heterodimerization activity; protein homodimerization activity; sequence-specific DNA binding; transcription coactivator activity; transcription corepressor activity; transcription factor activity Biological Process: calcium ion homeostasis; fat cell differentiation; forelimb morphogenesis; glucose homeostasis; glucose metabolic process; hindlimb morphogenesis; kidney development; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of caspase activity; negative regulation of cell proliferation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; phosphate ion homeostasis; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of neuron apoptosis; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; potassium ion homeostasis; regulation of BMP signaling pathway; regulation of cell differentiation; regulation of insulin secretion; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; renal water homeostasis; sodium ion homeostasis; sympathetic nervous system development Disease: Char Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the AP-2 family of transcription factors. AP-2 proteins form homo- or hetero-dimers with other AP-2 family members and bind specific DNA sequences. They are thought to stimulate cell proliferation and suppress terminal differentiation of specific cell types during embryonic development. Specific AP-2 family members differ in their expression patterns and binding affinity for different promoters. This protein functions as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal dominant Char syndrome, suggesting that this gene functions in the differentiation of neural crest cell derivatives. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92481 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 152031557 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7021 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q92481.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92481,Q5JYX6, Q9NQ63, Q9NU99, Q9UJI7, Q9Y214, Q9Y3K3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92481 |
| Molecular Weight: | 51,524 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transcription factor AP-2-beta |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | transcription factor AP-2 beta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TFAP2B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PDA2; AP-2B; AP2-B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transcription factor AP-2-beta |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transcription factor AP-2-beta |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Activating enhancer-binding protein 2-beta |
| Protein Family: | Transcription factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TFAP2B |
| UniProt Entry Name: | AP2B_HUMAN |